* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download HUMAN TRANSPORT SYSTEM ( lesson 3 )
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
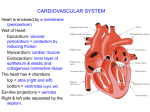
HUMAN TRANSPORT SYSTEM Composed of two systems : The closed circulatory system ( The blood vascular system ) : consists of : Heart and Blood Vessels through which the blood flows . 2) The lymphatic system : consists of : Lymph nodes and lymph vessels through which the lymph flows . CIRCULATORY SYSTEM HEART : - hollow muscular organ , lies nearly in the middle of the chest cavity - encloses in Pericardium which protects the heart + facilitates its pumping action - the heart divided into 4 chambers : Upper 2 Atria ( Auricles ) , thin walls , receive blood from veins and pumped to ventricles Lower 2 Ventricles , thick walls , receive blood from Atria and pumped it through arteries - the heart divided longitudinally by muscular walls into right and left sides . - each atrium connected to its ventricle by opening guarded by valve : - Right valve is the Tricuspid ( 3 flaps ) - Left valve is the Bicuspid or the Mitral valve ( 2 flaps ) each valve consists of thin flaps whose free edges attached by tendons to the ventricle wall so it prevent the flaps from turning inside ,permitting flow of blood in one direction , from atrium to ventricle , not the reverse direction - there are Semilunar valves : Aortic valve at the connection between heart and Aorta Pulmonary valve at the connection between heart and Pulmonary artery G.R ... Walls of Atria are less thick than walls of Ventricles because Ventricles pump blood to a longer distance than Atria . G.R ... Walls of left ventricle is thicker than walls of right ventricle because left ventricle pump the blood to a longer distance than right ventricle Blood Vessels : A) Arteries : wide vessels , carry blood from heart to body organs , usually buried between muscles ,pulsating , consist of 3 layers : - outer layer ( connective tissue coat ) - middle layer ( thick involuntary muscles contract and relax by nerve fibers ) - inner layer ( endothelium ) , one row of epithelial cells , with elastic fibers to give elasticity during ventricular contractions . All Arteries carry Oxygenated blood except Pulmonary artery which carries Deoxygenated blood from right ventricle to the lungs . B) Veins : narrow vessels , carry blood from body organs to the heart , usually under the skin , thinner than arteries , not pulsating , there walls formed of 3 layers but less elastic fibers and the middle layer is less thick . some veins contain internal valves , to prevent back flow of blood + direct the blood towards the heart . All Veins carry Deoxygenated blood except the 4 Pulmonary veins which carry Oxygenatedblood from lungs to left atrium . C) Capillaries : tiny microscopic blood vessels , connecting arterioles to venules , diameter 7 - 10 micron ,thin wall , one row of epithelial cells with tiny pores , its wall 0.001 micron to facilitate the quick exchange of substances between blood and tissue cells . HEART BEATS Rhythmic heart beats are spontaneous as they originated from Cardiac tissue itself It has proved that the heart continues beating regularly even after it has been disconnected from the body and Cardiac nerves ( sympathetic + vagus nerves ) . Source of Regular Rhythm of heart beats : A) Sino-atrial node : S-A node : Pace-maker of the heart : specialized cardiac muscular bundle buried in right atrial wall near connection between right auricle and large veins , it sends impulses continuously stimulating atrial contraction . B) Atrio-Ventricular node : A-V node : at the junction between Atria and Ventricles: when electrical impulse reach A-V node , impulses spread through interventricular septum causing ventricular contraction . S-A node beats regularly throughout life , 70 beats / minutes in normal age = 5 liters of blood / minutes which is equal all the blood of the body . Heart beats change according to the physical and psychological state of the body . - it is lowered during sleep and gradually increases after waking up - it is lowered during grief and increases in state of joy - it increases with sever physical effort S-A node connected to 2 nerves " Cardiac Nerves " ..... Vagus nerve lowers heart rate Sympathetic nerve increases heart rate Heart Sound : First Heart Sound (Lubb) which is Low pitched and due to closure of 2 valves between Atria and Ventricles during ventricular contraction WHILE Second Heart Sound (DUPP) is High pitched and due to closure of Pulmonary and Aortic valves during ventricular relaxation