* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
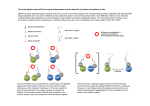
Download Figure 6 The RAD51 ATP-binding site
Implicit solvation wikipedia , lookup
Rosetta@home wikipedia , lookup
Degradomics wikipedia , lookup
Structural alignment wikipedia , lookup
Immunoprecipitation wikipedia , lookup
Protein design wikipedia , lookup
Protein domain wikipedia , lookup
Homology modeling wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein folding wikipedia , lookup
Protein mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Bimolecular fluorescence complementation wikipedia , lookup
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Protein purification wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
V07047A_supplementary_information Methods Protein expression and purification. The BRC4 - RAD51 fusion construct was subcloned into pGAT3, a member of the pGAT series of expression vectors that allow production of the target gene fused to a double amino-terminal tag consisting of a six histidine sequence followed by the glutathioneS-transferase protein 35. The BRC4 - RAD51 fusion protein was overexpressed in E. coli strain BL21(DE3) for three hours at 37°C by addition of 0.2 mM IPTG. The soluble protein was recovered from the crude bacterial lysate by Ni-NTA agarose chromatography (QIAGEN). The tag was cleaved by incubation with the TEV NIa protease and selectively removed by glutathione agarose chromatography (Amersham Biosciences). The protein was purified to homogeneity by two further steps of anion exchange chromatography on a RESOURCE Q 6ml column (Amersham Biosciences) and gel filtration on a Superdex 200 HR 10.30 column (Amersham Biosciences). The purified protein was concentrated to 12 mg/ml (0.38 mM) in 20 mM Hepes pH=7.2, 100 mM NaCl, 1 mM DTT, flash frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored in aliquots at –80° C. Figure 6 The RAD51 ATP-binding site. a Examination of the nucleotide-binding pocket of BRCA2-bound RAD51 shows that residues critical for ATP binding and hydrolysis, such as Thr133, Lys134 in Walker motif A and Asp222, in Walker motif B, are sequestered in a solvent-inaccessible hydrogen-bonding network that extends to Tyr159, Asp161 and Thr165 via a buried water molecule. Side chains of residues important for ATP catalysis, together with adjacent, interacting amino acids, are shown as sticks. A green sphere indicated the position of a buried water molecule. Dashed yellow lines represent hydrogen bonds. b A 3-D superposition shows that in BRCA2-bound RAD51 the ATP-binding loop (cyan) adopts a more closed conformation relative to the ADP-bound form of RecA (green), which is likely to preclude its occupation by the ATP phosphates. The atoms of the ADP molecule are drawn as spheres of Van der Waals radii. Table 1 Crystallographic data on the RAD51-BRC4 complex. Diffraction data (space group: P212121: a=57.30Å, b=59.14Å, c=77.20Å) Dataset Resolution Native Wavelength 1.8Å 1.5418Å Reflections1 Completeness Rsym2 (unique) (outer shell) (outer shell) 169388 99.9 (99.1) 0.051 (0.308) (24702) KAu(CN)2 2.0Å 1.5418Å I/(I) Beamline 40.9 In-house (6.7) 179758 100.0 (100.0) 0.059 (0.194) (18077) 36.6 In-house (11.9 ) 1.7Å SeMet, 0.9792Å 204230 peak 99.9 (99.9) 0.077 (0.321) (29143) 1.7Å SeMet, 0.90831Å 207259 remote 99.9 (99.6) 0.070 (0.481) (29329) 23.5 ESRF, ID- (6.5) 29 24.7 ESRF, ID- (4.2) 29 Phasing KAu(CN)2 SeMet, peak SeMet, remote Rcullis (iso/ano)3 0.93 / 0.95 - , 0.70 0.84 / 0.84 Phasing power (iso/ano)4 0.72 / 0.74 - , 2.1 0.48 / 1.65 Figure of merit5 0.21 0.51 Refinement6 Resolution Reflections (Å) 24.8-1.7 Number of R7 Rfree <B> Rmsd bonds Rmsd angles non-H atoms (%) (%) (A2) (Å) (°) 2179 19.1 20.6 21.1 0.006 1.229 55746 1 For MAD data, the Bijvoet pairs were not merged. 2 Rsym = I (hkl) I hkl I hkl i hkl i i i hkl i 3 Rcullis as defined in SHARP. 4 Phasing power as defined in SHARP. 5 Figure of merit as defined in SHARP. 6 Statistics for all data. 7 R-factor = F obs hkl Fcalc F obs hkl