* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Leukaemia Section t(1;21)(p32;q22) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Copy-number variation wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Short interspersed nuclear elements (SINEs) wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Molecular Inversion Probe wikipedia , lookup
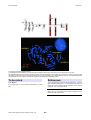
Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology OPEN ACCESS JOURNAL AT INIST-CNRS Leukaemia Section Mini Review t(1;21)(p32;q22) Charles D Bangs Cytogenetics Laboratory, Rm. H1517, Stanford Hospital and Clinics, 300 Pasteur Dr. Stanford, CA 94305, USA (CDB) Published in Atlas Database: June 2003 Online updated version: http://AtlasGeneticsOncology.org/Anomalies/t0121p32q22ID1259.html DOI: 10.4267/2042/37990 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 2.0 France Licence. © 2003 Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology Clinics and pathology Cytogenetics Disease Cytogenetics morphological Acute myelomonoblastic leukemia (M4 by FAB subtype). Single case der(1)t(1;21). Phenotype/cell stem origin Cytogenetics molecular CD34+, DR+, CD117+, CD15+, CD13+, CD33+, MPO+, CD64+ blast population consistent with ANLLM4 by FAB subtype. AML1 fusion suggested by partial translocation of 500 kb probe signal to der(1)t(1;21). presented with second copy of Probes Etiology Commercially available 500 kb AML1 probe. Unknown, reported agricultural chemical exposure in single case. Genes involved and proteins Epidemiology Note The putative 1p32 gene partner is unknown. Cryptic t(12;21) TEL(ETV6)/AML1 rearrangement is unlikely due to normal TEL metaphase FISH signal using commercial TEL/AML1 probe. Single case involving 25 year old male. Clinics Patient presented w/o palpable adenopathy, gingival hyperplasia, systolic murmur, hepatosplenomegaly and petechia. WBC was normal with anemia and thrombocytopenia. AML1 Location 21q22 DNA/RNA AML1 is oriented 3' toward the centromere. Protein Contains a runt domain and at C-term a tranactivation domain; forms heterodimers, widely expressed; nuclear localization; transcription factor (activator) for various hematopoietic-specific genes. Cytology Predominately large blasts with moderate cytoplasm, smooth nuclear chromatin, and pro-minent nucleoli, folded nuclear contours present in blast subset. Treatment Patient lost to treatment. Evolution Unknown. Prognosis Unknown. Atlas Genet Cytogenet Oncol Haematol. 2003; 7(3) 183 t(1;21)(p32;q22) Bangs CD Chromosome and FISH images showing : 1) partial karyotype and ideogram of t(1;21)(p32;q22) including a second copy of the der(1)t(1;21) present in the clone; and 2) metaphase FISH showing red AML1 signal on the two copies of the der(t)t(1;21), the der(21)t(1;21) and the normal 21 homolog. Green TEL signal is present of both 12 homologs indicating that no cryptic TEL/AML1 gene rearrangement is present. The adjacent interphase nucleus shows four AML1 signals and two TEL signals consistent with the metaphase pattern. To be noted References Case Report t(1;21)(p32;q22) as a non-random abnormality in AML M4 Cherry AM, Bangs CD, Jones P, Hall S, Natkunam Y. A unique AML1 (CBF2A) rearrangement, t(1;21)(p32;q22), observed in a patient with acute myelomonocytic leukemia. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2001 Sep;129(2):155-60 This article should be referenced as such: Bangs CD. t(1;21)(p32;q22). Atlas Genet Cytogenet Oncol Haematol. 2003; 7(3):183-184. Atlas Genet Cytogenet Oncol Haematol. 2003; 7(3) 184