* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture 15 - Adaptive Immunity Day 1 2 slides per page
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
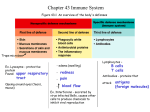
5/30/2011 Adaptive Immune Response Chapter 16 General Characteristics • Involves specialized WBC’s WBC s known as lymphocytes • Response is highly specific • Response generates memory • Can discriminate between self and non-self 1 5/30/2011 Overview of the Adaptive Immune Response Anatomy of the Lymphoid System • Lymphatic Vessels • Secondary lymphoid Organs • Primary Lymphoid Organs 2 5/30/2011 Lymphocytes are responsible for the specific immune response What promotes an immune response? • Antigens – Usually proteins or polysaccharides – Foreign substance with MW of greater than 10,000 daltons – Examples of antigens: bacterial capsules, cellll walls, ll fl flagella, ll toxins i off b bacteria i 3 5/30/2011 Antibodies bind antigens Which cell type is programmed to make antibodies? 4 5/30/2011 How is the term epitope different from antigen? The Nature of Antibodies Structure and properties of antibodies Basic structure: Y-shaped molecule •Fab regions - antigen-binding regions •Fc region - “red flag” region 5 5/30/2011 The Nature of Antibodies Structure and properties of antibodies Basic structure: Y-shaped molecule 200 a.a. a.a 450 amino acids •Fab regions - antigen-binding regions •Fc region - “red flag” region •four polypeptide chains - two heavy chains (H); two light chains (L) •variable region •constant region Protective outcomes of antigenantibody binding 6 5/30/2011 Protective outcomes of antigenantibody binding Protective outcomes of antigenantibody binding 7 5/30/2011 The Nature of Antibodies Structure and properties of antibodies Basic structure: Y-shaped molecule 200 a.a. a.a 450 amino acids •Fab regions - antigen-binding regions •Fc region - “red flag” region •four protein chains - two heavy chains (H); two light chains (L) •variable region •constant region Immunoglobulin Classes (isotypes) 6e correction Immunoglobulins = antibodies 8 5/30/2011 Basic principles are true for both B and T cells 9 5/30/2011 Clonal Selection and Expansion of Lymphocytes Basic principles are true for both B and T cells Clonal Selection and Expansion of Lymphocytes Naïve lymphocytes have a receptor, but have not “seen” antigen BCRs are membranebound antibodies ~1/2 billion naïve B cells, recognizing ~ 100 million different epitopes! Those that recognize “self” are eliminated during lymphocyte development Basic principles are true for both B and T cells 10 5/30/2011 Clonal Selection and Expansion of Lymphocytes Activated lymphocytes - able to proliferate; have received confirmatory signals Basic principles are true for both B and T cells Clonal Selection and Expansion of Lymphocytes Activated lymphocytes - able to proliferate; have received confirmatory signals Basic principles are true for both B and T cells 11 5/30/2011 Clonal Selection and Expansion of Lymphocytes Activated lymphocytes - able to proliferate; have received confirmatory signals Basic principles are true for both B and T cells Clonal Selection and Expansion of Lymphocytes Basic principles are true for both B and T cells 12 5/30/2011 Clonal Selection and Expansion of Lymphocytes Effector lymphocytes endowed with specific protective attributes (plasma cells = effector B cells) Basic principles are true for both B and T cells Clonal Selection and Expansion of Lymphocytes Memory lymphocytes long-lived; ready to become effector cells Basic principles are true for both B and T cells 13 5/30/2011 Clonal Selection and Expansion of Lymphocytes •Naïve •Activated •Effector •Memory Memory Requires confirmatory signals from another cell type Basic principles are true for both B and T cells 14 5/30/2011 B Lymphocytes and the Antibody Response (T-dependent antigens) •Most common type of response; primarily protein antigens •Requires assistance of T-helper cells (TH cells) B Cell Activation •B cell processes/presents antigen to TH cell for “inspection” in order to gain second opinion 15 5/30/2011 B Cell Activation •B cell processes/presents antigen to TH cell for “inspection” in order to gain second opinion B Cell Activation •B cell processes/presents antigen to TH cell for “inspection” in order to gain second opinion •If a TH cell recognizes a fragment being presented, it delivers cytokines that activate the B cell 16 5/30/2011 B Cell Activation •B cell processes/presents antigen to TH cell for “inspection” in order to gain second opinion •If a TH cell recognizes a fragment being presented, it delivers cytokines that activate the B cell B Cell Activation •B cell processes/presents antigen to TH cell for “inspection” in order to gain second opinion •If a TH cell recognizes a fragment being presented, it delivers cytokines that activate the B cell •If no TH cell recognizes antigen, the B cell becomes unresponsive 17 5/30/2011 B Cell Activation •B cell processes/presents antigen to TH cell for “inspection” in order to gain second opinion Characteristics of the Primary Response Affinity maturation •Naïve •Activated •Effector •Memory 18 5/30/2011 Characteristics of the Primary Response Affinity maturation - mutation fine tunes the fit Characteristics of the Primary Response Affinity maturation - mutation fine tunes the fit Class switching - IgM → IgG (or IgA or IgE) M G A… 19 5/30/2011 Characteristics of the Primary Response Affinity maturation - mutation fine tunes the fit Class switching - IgM → IgG (or IgA or IgE) Formation of memory cells - cells have undergone affinity maturation and class switching Characteristics of the Primary Response Affinity maturation Class switching Formation of memory cells 20 5/30/2011 Characteristics of the Secondary Response Vaccines Pre-natal care Swifter response, primarily IgG in blood/tissues (due to memory cells) (mucosal response is IgA) More effective response (due to affinity maturation) Continued fine-tuning 21