* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BIOL241connective6aJUL2012
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
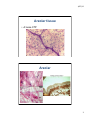
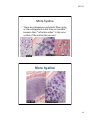
1/07/12 Connective Tissue Nervous Muscle Lab Exercise 6a-2 Classification of connective tissues 1 1/07/12 Connective Tissue • Connective tissue proper • Fluid connective tissue • Supportive connecting tissue Connective tissues Connective tissue proper • Loose connective tissue – Areolar – Adipose – Reticular • Dense connective tissue – Dense regular – Dense irregular – Elastic tissue Fluid CT – Blood Supporting CTs • Cartilage – Hyaline cartilage – Elastic cartilage – Fibrocartilage • Bone 2 1/07/12 Areolar tissue • A loose CTP Areolar 3 1/07/12 Areolar: for what to look • • • • Fibroblasts Collagen fibers Elastic fibers Mast cells and macrophages • Found? Throughout body, under dermis, divides skin from underlying tissues Fibroblasts • Resting fibroblasts typically have so little cytoplasm that the cells appear, by light microscopy, as "naked" nuclei 4 1/07/12 Fibroblast Adipose tissue • Another lose CTP (note nucleus) 5 1/07/12 Adipose: for what to look • Lots of cytoplasm • Slim nuclei pushed off the side • Found? You know where Reticular tissue • The third type of loose CTP 6 1/07/12 Reticular tissue Reticular: for what to look • Reticular fibers (network) • Found? Internal framework in many sort organs (liver, spleen) supporting the parenchyma 7 1/07/12 Dense CTP • Dense regular – strength in one direction • Dense irregular – strength in all directions • Elastic tissue - pliable Dense regular 8 1/07/12 Dense regular: what to look for • Thick parallel bundles of collagen • Small fibroblasts in between bundles • Found? Tendons, ligaments, deep fascia. Dense irregular 9 1/07/12 More dense irregular Dense irregular: for what to look • Mesh of collagen fibers (irregular looking) • Interspersed fibroblasts • Found? Dermis of skin, periosteum, perichondrium 10 1/07/12 Elastic tissue Elastic tissue: what to look for • Elastic fibers (instead of collagen fibers) in large bundles • Fibroblasts • Found? Between vertebrae, in blood vessel walls (underneath endothelium) 11 1/07/12 Fluid CT • Blood Blood: for what to look • RBCs (aka?) • White blood cells (darker): monocytes, lymphocytes, granulocytes • Platelets 12 1/07/12 Supportive CT • Cartilage – gelatinous, padding – Hyaline cartilage – Elastic cartilage – Fibrocartilage Hyaline cartilage • Glasslike because fibers not visible 13 1/07/12 More hyaline • There are collagenous and elas=c fibers lying in the car=lage matrix but they are invisible because their “refrac=ve index” is the same as that of the matrix (like cornea) More hyaline 14 1/07/12 Hyaline cartilage Hyaline • Hyaline cartilage (lavender matrix), with perichondrium (pink) outside it. The latter is a dense regular collagenous CT. Cartilage cells = chondrocytes, and they are lying in the lacunae. 15 1/07/12 Hyaline cart.: for what to look • Chondrocytes and lacunae • No visible fibers • Where? Most joints, nasal septum Elastic cartilage 16 1/07/12 Elastic Cartilage Elastic cart: what to look for • Many elastic fibers in matrix • Chondrocytes in lacunae • May be stacked up 17 1/07/12 Fibrocartilage Fibrocartilage: for what to look • Irregular, wispy collagen fibers • Chondrocytes • Found? Intervertabral discs of spine, pads in knee joint 18 1/07/12 Supportive CT: Bone • Detail of lacuna, showing radiating canaliculi. Tissue fluid from the capillaries and connective tissue of the Haversian canal can seep through these spaces and channels, bringing nutrients to the stellate osteocytes residing there. 19 1/07/12 Bone: for what to look • • • • • • Osteon (whole circular structure) Concentric lamellae (of matrix) Central canal (at center of lamellae) Osteoblasts Osteocytes in lacunae Canaliculi Found? Bones! Nervous tissue • Neuron smear • Large, pyramidal cell bodies • Long processes extending out 20 1/07/12 Nervous Tissue Figure 4.10 3 Types of Muscle Tissue • Skeletal muscle: – large body muscles responsible for movement • Cardiac muscle: – found only in the heart • Smooth muscle: – found in walls of hollow, contracting organs (blood vessels; urinary bladder; respiratory, digestive and reproductive tracts) 21 1/07/12 Muscle Tissue: Skeletal • Long, cylindrical, multinucleate cells with obvious striations • Found in skeletal muscles that attach to bones or skin Muscle Tissue: Skeletal Figure 4.11a 22 1/07/12 Muscle Tissue: Cardiac • Branching, striated, uninucleate cells interlocking at intercalated discs Muscle Tissue: Cardiac Figure 4.11b 23 1/07/12 Muscle Tissue: Smooth • Sheets of spindle-shaped cells with central nuclei that have no striations • Found in the walls of hollow organs Muscle Tissue: Smooth Figure 4.11c 24 1/07/12 Exercises • Look at all slides • Draw an example of each tissue on paper provided • 11 connective tissues: – 6 CTP (3 loose, 3 dense) – 1 Fluid CT (blood) – 4 Supportive CT (3 cartilage, 1 bone) • Neurons • 3 Muscle tissues – Skeletal – Striated – Smooth Turn in on Tues. 10 July • 7 drawings from 6a-1 Epithelia • 15 Drawings from 6a-2 Connective+ • Review sheet for lab 6a 25