* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Part 1
Trusted Computing wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Computer security wikipedia , lookup
Cyberattack wikipedia , lookup
Mobile security wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
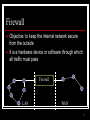
Unix security wikipedia , lookup
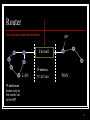
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Antivirus software wikipedia , lookup
Computer virus wikipedia , lookup
Protecting Your Computer Internet Annoyances (Already done in Chapter 3) Spam Pop-ups Identity theft phishing hoaxes Spyware 1 Computer Threats Cyber-crimes are criminal acts conducted through the use of computers by Cyber-criminals. Hacker: Anyone who unlawfully accesses a computer system 2 What Hackers Do Steal information from computers: Credit card numbers Bank account numbers Internet packet sniffing Commit identity theft 3 Denial of Service Attacks Web servers are sent millions of bogus requests Overloads the system Consequently they shut down Service is denied legitimate users 4 Denial of Service Attacks Distributed denial of service attacks use many computers Backdoor programs Trojan horse Zombies 5 How Hackers Gain Access Direct access: Hacking software Indirect access: Internet connection Logical ports 6 Computer Safeguards: Firewalls Software programs or hardware devices designed to close logical ports to invaders A firewall is built into Windows XP More robust firewalls are available from other vendors. Firewalls are critical if you have an always-on broadband connection. 7 Firewall Always on Internet service is a problem use a router or firewall software see IT website for Firewall information 8 Firewall Objective: to keep the internal network secure from the outside It is a hardware device or software through which all traffic must pass Firewall LAN WAN 9 Router Does dynamic address translation ISP Firewall IP address LAN 111.22.3.44 WAN IP addresses known only to the router, not to the ISP 10 Protecting a Wireless Network Wireless network range doesn’t stop at the property line. Default device and network ID settings allow intruders to enter the network. Internet bandwidth can be stolen Computers can be vulnerable to hacker intrusion and takeover. 11 Secure Your Wireless Router Change Your Network Name (SSID) Disable SSID Broadcast Change the Default Password on Your Router Turn on Encryption (WAP is best) Implement Media Access Control Apply Firmware Upgrades 12 Change Your Network Name Disable SSID Broadcast Turn on Encryption Change the Default Password Implement Media Access Control 13 Software Sabotage Risks Virus Worm Trojan horse Spyware DOS Attacks Protection 14 Computer Threat - Viruses A virus is a program that attaches itself to another program It hides within the code of the host program When host program executes the virus code executes also and copies itself to other programs 15 16 What Viruses Do Replicate themselves: Slow down networks Secondary objectives: Annoying messages Delete files on the hard drive Change computer settings 17 How Does a Computer Catch a Virus 18 Virus Macro virus Attach to documents Email virus Attachments 19 Antivirus Software Programs designed to detect viruses: Scan files looking for virus signatures (unique code) Provides options for deleting or fixing infected files Detect known viruses Antivirus programs need to be updated frequently 20 Use Anti-virus Software Install and update anti-virus software UofC IT anti-virus web page Free software: McAffee ISP might provide free Otherwise buy it (McAffee, Norton, …) 21 Email Virus Detection ISP mail server (UofC IT and CPSC) Scans incoming and outgoing messages, notifies user if finds virus (strips attachments), and quarantines the message User can recover message from quarantine If you suspect: don’t open the attachment Delete the message Scan in email program or save to disk and then scan with virus detection software 22 Sober Source: Calgary Herald 23 Email Virus Detection My email From: [email protected] Subject: WARNING - VIRUS (Worm.Sober.U) IN MAIL TO YOU Date: November 25, 2005 10:20:55 AM MST (CA) 24 *** VIRUS ALERT *** Dear user, This is an automatically generated message from the University of Calgary, Department of Computer Science (CPSC). The CPSC email system has detected a piece of email with a virus called: Worm.Sober.U in an email addressed to you from: <[email protected]> The Subject of this email was: Mail delivery failed Delivery of the original email has been stopped. A copy of the message has been placed under quarantine. Please visit the CPSC Maia Mailguard system located: http://imgw1.cpsc.ucalgary.ca/mail to view your quarantined messages. You will be required to log into this system using your CPSC Email address and your CPSC Login Password. For your reference, here are some selected headers from the email: -----------------------------------------------------------------Date: Fri, 25 Nov 2005 10:20:55 -0700 (MST) From: [email protected] (Empty if virus is known to forge sender address) To: Subject: Mail delivery failed Received: dpwtlcd.com (S010600112f1f983b.cg.shawcable.net [68.147.104.66]) 25 Worm Program that travels independently over computer networks, seeking uninfected sites Replicates and starts up thousands of processes Overloads a system 26 The Cost of Worms Nimba, Sept. 18, 2001 In 24 h infected 2.2 million computers Microsoft Windows Huge traffic disabled web and email servers Damaged system files 27 Trojan Horse Program that performs a useful task while also being secretly destructive A logic bomb responds to a particular event Cannot replicate E.G. Logon Trojan horse 28 Denial of Service Attacks Web servers are sent millions of bogus requests Overloads the system Consequently they shut down Service is denied legitimate users 29 Protection from Viruses and Security Risks Use anti-virus software Update frequently Use anti-spyware software Update your operating system Automatic updates and security patches Microsoft Macintosh 30 Computer Security: Reducing Risks Disaster Planning backup power monitoring, alarms backup of data redundant sites or hot sites 31 Computer Security: Reducing Risks Physical Access Restrictions something you have: key, ID card you know: password, personal information you do: signature, … About you: Biometrics 32 Passwords The most common tool for restricting access to computer systems Weakness user sustained guessing program guesses words from online dictionaries 33 Password Guidelines Don’t use real words names plurals common expressions reversal 34 Passwords Do mix letters and numbers change frequently keep secret 35 Biometrics 36