* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Roman Civilizations
Food and dining in the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Roman economy wikipedia , lookup
Legislative assemblies of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Senatus consultum ultimum wikipedia , lookup
Conflict of the Orders wikipedia , lookup
Roman historiography wikipedia , lookup
Roman agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Promagistrate wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Augustus wikipedia , lookup
Roman consul wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Executive magistrates of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Education in ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Roman army of the late Republic wikipedia , lookup
Roman Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Elections in the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Sulla wikipedia , lookup
Travel in Classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Culture of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Roman technology wikipedia , lookup
Early Roman army wikipedia , lookup
Constitution of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
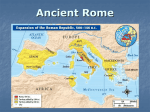
Roman Civilizations Geography Italy is centrally located in the Mediterranean Sea Rome is in the center of Italy More open land Mountains are less rugged Broad, fertile plains Early settlers Latins migrated to Italy around 800 B.C. Twin Brother Romulus and Remus founded the city Son of a Latin woman and the war god Mars Gave Rome a divine origin Shared their land with Greeks and the Etruscans Romans soon drove out the Etruscan leader and formed their own republic around 509 B.C. New form of Government, res publica, or republic Government that belongs to the people Prevent one person from gaining too much power New political structure Senate 300 members All patricians, or landholding upper class Served for life Strongly influenced the republic’s laws Consuls Each year two consuls were nominated by the senate Ran the business of the government and commanded the army Could only serve one term Had to have approval of the other consul Dictator Only needed in a time of war Could only rule for 6 months, then had to give up power Plebeians Farmers, merchants, artisans, and traders Made up bulk of population Fought for their right to influence government Gained the right to elect their own officials Tribunes Could veto any law that they felt harmed the plebeians Eventually they were able to be consuls and senators Roman Society Family Male was head of household Enforced strict discipline and demanded respect for his authority Wives were not allowed to administer their own affairs Supposed to be loving, dutiful, dignified, and strong Women Roles changed over time Could own property and run businesses Some even had strong political influence Children All children were educated Some hired tutors Religion Believed in many Gods and Goddesses Adapted from the Greek religion Zeus=Jupiter Calendar was full of feasts that honored gods and goddesses to ensure divine favor for the city Army As the political and social systems grew, the armies grew as well Rome conquered many Greek and Etruscan city states and soon controlled most of Italy Loyal, well-trained army Legions had 5,000 citizen-soldiers Volunteers who provided their own weapons Soldiers were rewarded with the spoils of victory Enemies Once Rome conquered new land, they treated their enemies fairly Gave them rights and let them keep their own culture Roads Built all-weather roads to link territories Roads connected trade and Roman ideals all throughout Italy United Italy under Roman rule