* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ImmunLec22
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Duffy antigen system wikipedia , lookup
Major histocompatibility complex wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Anaphylaxis wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
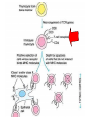
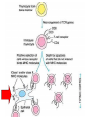
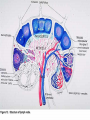
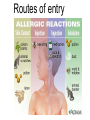
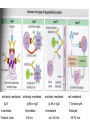
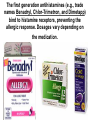
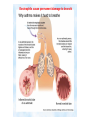
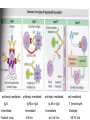
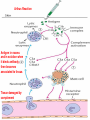
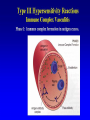
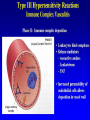
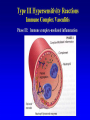
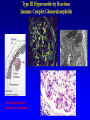
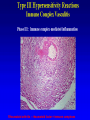
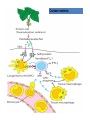
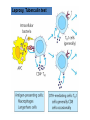
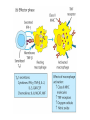
Lecture 22 December 7th 2010 Hypersensitivity Reactions Domains of the thymus In cortex, thymic epithelial cells presents 2X the amount of MHC2 molecules as MHC1 molecules. This determines the ratio of Th to Tc as 2:1. They present all the alleles in the persons genome: 6 MHC class 1 molecules and 12 different MHC class 2 molecules. This determines that only T cells with a TCR receptor that recognizes the persons own MHC survives the cortex. Delta Three outcomes with regard to what the TCR chosen sees: TCR does not recognize any of your own MHCI or MHCII molecules TCR recognizes but reacts to one of your own MHCI or MHCII molecules by proliferating even when unoccupied by antigen TCR recognizes as self one of your own MHCI or MHCII molecules but does not proliferate to the unoccupied MHC molecule. Now those T cells that survive the cortex move to the medulla, they upregulate the number and affinity of their TCRs and become committed as either CD4 or CD8 positive. In medulla they express either CD4 or CD8 not both. Three outcomes with regard to what the TCR chosen sees: TCR does not recognize any of your own MHCI or MHCII molecules (cortex, positive selection) TCR recognizes but reacts to one of your own MHCI or MHCII molecules by proliferating even when unoccupied by antigen (medulla, negative selection) TCR recognizes as self one of your own MHCI or MHCII molecules but does not proliferate to the unoccupied MHC molecule (only these cells get . Routes of entry antibody mediated Ig E antibody mediated antibody mediated Ig M or IgG Ig M or IgG Immediate Immediate Fastest (sec) 4-6 hrs Immediate w/i 4-6 hrs cell mediated T lymphocyte Delayed 48-72 hrs. Type 1 hypersensitivity • All hypersensitivity reactions require a first asymptomatic exposure to antigen • Second exposure manifests a exaggerated and extensive reaction • In type one reactions, these are very fast within secs and usually but not always can resolve not causing permanent damage. They can during the reactive phase however cause death. Type 1 hypersensitivity • A. Systemic anaphylaxis • B. Local Anaphylaxis-atopic allergies – 1. – 2. – 3. – 4. Allergic rhinitis 20% of the population Asthma Food allergies Atopic dermatitis First exposure All type 1 Rxs. Second exposure HS1 A. Systemic anaphylaxis • Portier and Richet Nobel 1913 • Dogs with jelly fish toxins • Guinea pigs with penicillin Systemic Analyphaxis-Shock • Within secs of second exposure to drugs, venoms or specific foods (peanuts). • Mast cells degranulate. • GI tract –increased fluid (edema), increased peristalsis = severe diarrhea and vomiting. • Lungs- this is life threatening . Every time the person exhales, SMC constrict causing further decreased diameter of bronchi, increased mucous secretion and swelling of connective tissue closes airways completely. Within minutes they cant take a breathe in = asphyxiation. Upper and lower respiratory At multiple sites Tract, GI tract, skin reaction. simultaneouslyGI tract, upper and lower respiratory tract, skin Severe constriction Severe permeability Severe secretion Severe Histamine release 1. Processing of antigen 2. T help that produces a Ig E response 3. 2- 10 X more mast cells 4. Mast cells with 10 x higher affinity receptors What is different about an allergic individual and a non-allergic individual. 5. Mast cells with 10-100 x more histamine per cell 6. More and higher histamine receptors on SMC 7. Mast cells with 10 x higher affinity receptors If you suspect that you or someone you are with is having an anaphylactic reaction, inject epinephrine immediately. The shot is given into the outer thigh and can be administered through light fabric. Rub the site to improve absorption of the drug. An Epi Pen kit is shown. Epinephrine antagonist of histamine and causes EC tight junction to reformation and SMC relaxation. Type 1 hypersensitivity Systemic anaphylaxis-severe. • Local Anaphylaxis-mild-severe – Allergic rhinitis 20% of the population. hay fever, animal dander. – Asthma (Extrinsic not Intrinsic)-pollen, dust mites, fumes, insect products. – Food allergies-hives, anaphylaxis. – Atopic dermatitis-fabric softeners, wool. B. Local anaphylaxis 1. Allergic rhinitis Milder forms of HS1. Upper airways only. Ragweed 16 tons of pollen per sq. mile Antigens are complex. Enzymes break them down. 5 fractions 2 are allergens E and K – 95% of HS1 RA3, RA4 and RA 5 5-20% of HS1 rhinitis Allergic individuals process the antigen in a different way. Animal dander is a protein deposited on hair. Upper respiratory only Upper airways only Local not systemic Type 1 Hypersensitivity reactions The first generation antihistamines (e.g., trade names Benadryl, Chlor-Trimetron, and Dimetapp) bind to histamine receptors, preventing the allergic response. Dosages vary depending on the medication. Type 1 hypersensitivity Systemic anaphylaxis-severe. Local Anaphylaxis-mild-severe Allergic rhinitis 20% of the population: hay fever, animal dander. – Asthma (Extrinsic not Intrinsic)-pollen, dust mites, fumes, insect products. – Food allergies-hives. – Atopic dermatitis-fabric softeners, wool. Asthma • Mild to severe –lower airways . • Can cause permanent damage because of eosinophil involvement in lower bronchi. Eosinophils also possessing high affinity receptors for Ig E. • Eosinophils produce leukotrines which recruit and activate neutrophils to make proteases that carve up and damage tissue. Lower bronchi only Eosinophils cause permanent damage to bronchi BRONCHODILATORS dilate the small airways to increase airflow. Long-acting bronchodilaors are given prophylactically to prevent asthma attacks, and may last up to 12-hours. Rapid-acting bronchodilators have effects that last 3-4 hours and are used to relieve a sudden attack. Rapid-acting bronchodilators may also be used as a preventative in some cases, as before exercising to prevent exercise induced asthma. ANTI-INFLAMMATORY medications are used to prevent and/or relieve airway inflammation, thus reducing the patient's susceptibility to a sudden attack. Most of these medications are steroids, although there are some widely used non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications. The prevalence of asthma has been increasing since the early 1980s for all age, sex and racial groups. • higher among children than adults • higher among girls than boys • higher among blacks than whites LEUKOTRIENE MODIFIERS are oral medications that interrupt the body's allergic response, thus preventing attacks in some patients. They are more effective in patients with allergies than in those with chemical sensitivity. NEBULIZERS and NEBULIZED MEDICATIONS are used not only by EMS and medical facilities, but are not uncommon in home use. Basically the same medications as are supplied in inhalers, nebulization usually results in a more rapid response to the medications antibody mediated Ig E antibody mediated antibody mediated Ig M or IgG Ig M or IgG Immediate Immediate Fastest (sec) 4-6 hrs Immediate w/i 4-6 hrs cell mediated T lymphocyte Delayed 48-72 hrs. Immediate 6-8 hrs. 6-8 hrs. 48-72 hrs. Allergic rhinitis Anaphylaxis Asthma (extrinsic) Blood transfusions rH disease of newborn Pernicious anemia Post Strep infection Arthus reaction Pigeon Fanciers Syn. Poison Ivy Tuberulin Test Allograft Rejection Type 1 diabetes Multiple sclerosis Blood transfusions rH disease of newborn Pernicious anemia A, B O blood group antigens are T cell independent antigens. If transfused with different blood, immediate response because you have been exposed to A, B due to symbiotic microorganisms in gut possessing isohemaglutinins on surface. Effects of Mis-matched blood transfusion • Ig M binds to RBC and complement or innate cells lyse the RBCs in mass. • Free hemoglobin goes to kidney and is converted to bilirubin. • Bilirubin is toxic and is deposited in skin and liver and brain capillaries. • Jaundice, severe anemia, liver failure and coma can result. rH disease of the newborn occurs Most often with mothers married to husbands with same ABO blood type as them. Severity only seen In rH disease, a Ig G is produced. How ? After mother has had a first Preqnancy whether it goes to Term or not. Dr. Vincent Freda • Took Sing Sing prisoners (male) and injected them with different blood types. • Identified a D antigen, a minor antigen that is T cell dependent and evokes a Ig G response, but only if Ig M to major blood group antigens hasn’t occurred. • Developed Rhogam , recombinant Ig G to D antigen. Injected after each pregnancy. Pernicious Anemia: Vitamin B12 cannot be absorbed through the small intestine unless complexed to Intrinsic Factor (IF) which transports it across the intestinal mucosa. Pernicious anemia (PA) is associated with circulating antibodies to intrinsic factor (IF). IF antibodies bind to IF on the surface of gut epithelial cells and blocks binding of vitamin B12 to IF in the stomach. This brings about a deficiency in vitamin B12 that prevents RBC production and thus causes anemia. If penicillin becomes bound to RBC membrane. Arthus reaction Post Streptococcal Glomerulonephritis Pigeon Fanciers Syndrome- excess of dried pigeon fecal protein. Farmers Lung- excess of thermophilic actinomycetes from moldy hay. Arthus Reaction Antigen in excess and in solution when it binds antibody; then becomes associated to tissue. Tissue damaged by complement Poststreptococcal glomerular nephritis Rheumatoid arthritis – rheumatoid factor = immune complexes Poison Ivy Tuberculin Test Leprosy Contact reactions Leprosy, Tuberculin test Leprosy Cannot be grown in the laboratory. In vivo, it is one of the slowest growing of all organisms and incubations periods in humans with a minimum of 3-5 years. The organism is an obligate, intracellular parasite of peripheral nerves, skin cells, and nasal mucosa. US Marine contracting Leprosy in Australian after getting a tattoo there.