* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download el-Guebaly - University of Calgary
Mental disorder wikipedia , lookup
Social anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Spectrum disorder wikipedia , lookup
Public-order crime wikipedia , lookup
Antisocial personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Generalized anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Bipolar II disorder wikipedia , lookup
Major depressive disorder wikipedia , lookup
Behavioral theories of depression wikipedia , lookup
Dissociative identity disorder wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary approaches to depression wikipedia , lookup
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders wikipedia , lookup
History of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
Child psychopathology wikipedia , lookup
Impulsivity wikipedia , lookup
Addictive personality wikipedia , lookup
Causes of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
Treatment of bipolar disorder wikipedia , lookup
Externalizing disorders wikipedia , lookup
Depression in childhood and adolescence wikipedia , lookup
Substance abuse wikipedia , lookup
Substance use disorder wikipedia , lookup
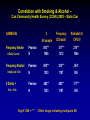
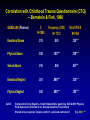
Centre PROGRAM Network Addressing Comorbidities* in the Treatment of Gambling Problems Nady el-Guebaly, MD Professor & Head, Division of Substance Abuse, University of Calgary Medical Director, Addictions Program, Calgary Health Region * “Two or more concurrent, independent disorders in single individual interacting in the clinical picture” Community Prevalence: Problem vs Non-Gambler OR ECA (2) 1 problem = 161 incl 29 PG DSM III Comorbidities with (1): Substance Use Disorders: Alc Nicotine Illicit Mood Disorders: Bipolar Suicidality Anxiety Disorders, spec Phobias (not OCD) Somatoform Disorders Schizophrenia (severe & persistent MI) ADHD? Antisocial Personality (1ery & 2 ary) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. OR 3.3 2.1 1.3 3.3 3.4 1.6 2.3 3.0 3.5 --6.1 NESARC (3) N=42898 PG .42; N=195 Lifetime 73% 60% 38% 50% 41% OR 6.0 6.7 4.4 4.4 ----3.9 ----- CCHS (4) N=36984 Gamblers 14934; Problem = 1513 OR 2.9 1.8 (Mood & Anx) 2.3 (5) Both 5.2 20% trt 61% PD 6.0 (obsC, par) >F Crockford, el-Guebaly. Can Psych 1998;43:43-50. Cunningham-Williams, et al. Am J Public Health 1998;88:1093-1096; St. Louis DSM III DIS Petry et al. J Clin Psychiatry 2005; 66:564-573; Nat Epid S Alc & Related Conditions; DSM IV AUDADIS; lifetime el-Guebaly N et al J Gambling Stud 2006; 22: 275-287; CPGI, 12 m prev McIntyre et al. J Affective Dis 2007 [In Press] Correlation with Smoking & Alcohol – Can Community Health Survey (CCHS) 2003 – Stats Can GAMBLING $ All sample Frequency Smoke 0-Daily Current Frequency Alcohol 0-daily, last 12 m 5 Drinks + 0 to > 1/wk Frequency CIDI-adult Risk/adult G CPGI 9 Pearson N .093*** 1806 .157*** 1372 .219*** 1064 Pearson N .090*** 1353 .180*** 1187 .064* 965 Pearson N .082** 1353 .083** 1187 .171*** 965 Signif .000 = *** - Other drugs including marijuana NS RISK OF GAMBLING CPGI 8-16 Thinking about the past 12 months (scale 1-4): Have you bet more than you could really afford to lose? Have you needed to gamble larger amounts to get same excitement? Have you gone back another day to try & win back the money you lost? Have you borrowed money or sold anything to get money to gamble? Have you felt that you might have a problem with gambling? Have people criticized your betting or told you that you had a problem? Have you felt guilty about the way you gamble? Has your gambling caused you any health problems (stress & anxiety)? Has your gambling caused any financial problems? Correlation with Personality Assessment Inventory (PAI) – Morey, 1991 GAMBLING (Pearson) $ N = 1370 Frequency CIDI N=1371 Risk CPGI 9 N=1063 Depression .065* .030 .265*** Mania .018 -.086** .176*** Suicidal Ideation .033 -.005 .236*** .074** -.070* .238*** Anxiety related Dis (OCD, Phobia) .038 -.068* .227*** Aggression .059* .058* .136*** Somatic Complaints .064* .035 .219*** Schizophrenia .038 -.023 .244*** Paranoia .069* -.013 .231*** Antisocial Features .118*** .028 .231*** Anxiety Signif .000 = *** - Composite Intern Diagn Interview (CICD-SF/DSM IV) = NS Correlation for SF-8 Health Survey (Ware et al, 2001) GAMBLING (Pearson) $ N=1370 Frequency CIDI N=1371 Risk CPGI 9 N=1063 .082** .060* .174*** .043 .097*** .128*** .088** .072** .167*** .026 .083** .095** Vitality .089** .050* .182*** Physical/Emotional Problems limit social function .113*** -.030 .227*** Presence of Emotional Problems .107*** -.052* .201*** Impact of Mental Health in Daily Life .093** -.070** .220*** General Health V poor- Excellent Physical Health Impact of Physical Health in Daily Life Bodily Pain 0 – V severe Signif .000 = *** Correlation with Childhood Trauma Questionnaire (CTQ) – Bernstein & Fink, 1998 GAMBLING (Pearson) $ N=1806 Frequency (CIDI) N= 1372 Risk CPGI 9 N=1064 Emotional Abuse .013 .043 .125*** Physical Abuse .038 .105*** .129*** Sexual Abuse .016 .044 .097** Emotional Neglect .021 .098*** .124*** Physical Neglect .034 .096*** .155*** ALSO: Vietnam Vets Twins Registry – Health Related QOL: gambling, SUD & MH> Physical PG & Depression (Potenza et al): Overlap Genetics> Environment Shared stress response, impulse control? µ alleles & naltrexone? Sig .000 = *** Case “A” (1) 42 y/o, married female; postal clerk 8 y; 2 daughters: 20 y & 14 y “Job was stressful”; ending a 4 yr educational leave; Quite involved in her union PRESENTING COMPLAINT: GAMBLING (last 3 yrs): - progressive increase in VLT use - currently gambles ~ once/week, 8-10 hours/session, spending 3-600$ each time - last month, stole husband’s bank card: worried! - reported being given the “run-around” when seeking help & no follow-up “A” (2) SUBSTANCES - age 18-24, 26 oz liquor every W/E, many blackouts; currently drinking once/week, 4 drinks/sitting - one joint of cannabis/day, “most difficult to give up” - 1/2 pack cigs/day - experimented with solvents, LSD & cocaine - FH +ve: mother & 5 out of 7 siblings from 4 fathers have alcohol problems “A” (3) DEPRESSION/DYSTHYMIA - emotional abuse from parents & siblings, no sexual abuse - episodes of depression throughout her life, particularly severe 1 yr ago - occasional suicide ideation & one serious attempt - Paroxetine 20 mgm/day “A” (4) CHRONIC PAIN - chronic cervical disc degeneration from “repetitive movement at work” - history of TM Jaw pain & fainting spells for 6 years - Medications: Tylenol #3, 3 times/day Elavil, 150 mgm hs, for sleep & pain Physical comorbidities? Stress related disorders, Medication side-effects CHR 1000/3 hospital-wide consults: 12 Prob G, all MH Survey of 51 New Zealand urban & rural practices (N=2536): no relation with physical inactivity or weight concerns “A” (5) PERSONALITY - 5 y ago, 6 m psychological FU for Union “bullying” - Charge of mischievous conduct; running key down co-workers’ cars with whom she had difficulty - Postal service may release her; on probation for abusing educational leave. She plans legal action. COURSE: motivated to seek help for GAMBLING! - Residential program entered but on relapse wished to deal with “one addiction at a time” - Repeated complaints up “the managerial chain” about “personality conflicts” with therapist! The Role of Gambling? PRESENTING COMPLAINT: GAMBLING (last 3 years) BUT Substances Depression/Dysthymia Chronic Pain Personality Treatment Course WHERE TO START? Rules of engagement “common ground” Find out sources of strength & your true friends “co-therapists”: sig other; daughters? Address the behaviors! No RCTs! the closest : - Hollander et al ’02: lithium & bipolar spectrum gamblers - Grant & Potenza ’06: Escitalopram “open label” anxiety & gamblers (N=13 - 12 w) (1) PATHOLOGICAL GAMBLING Persistent & recurrent maladaptive gambling 5+ (if not mania) (2) SUBSTANCE DEPENDENCE Maladaptive pattern of substance use 3+ within 12 months: 1. 2. 3. 4. Increasing amounts of money for excitement Restless or irritable when cutting down/ stop Unsuccessful efforts to control, stop… Preoccupied with gambling 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Escaping from problems or dysphoria 5. 6. Lies to family members, therapist, or others 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Illegal acts to finance gambling Jeopardized or lost significant opportunities “Chasing” one’s losses Relies on others for money 7. Tolerance Withdrawal Unsuccessful efforts to cut/control A great deal of time spent to obtain substance Substance taken in larger amounts or over a longer period than intended Important social, occupation or recreation given up or reduced Use is continued despite physical or psychological problems COMORBID IMPACT: - Rosenthal & Lesieur DSM “plot” addiction-impulsivity-compulsivity Loss of control? Is persistence of erroneous cognition = physiological craving? - See-Saw association - Anti-craving meds: Naltr/Nalmefine - Range of Support: OP residential; Twelve Steps (3) MOOD DISORDERS Sadness MAJOR DEPRESSIVE EPISODE > 2 wks A. Depressed Mood + B. 4 for either: - change in weight, sleep … - feelings of worthlessness or guilt, - difficulty thinking or concentrating - recurrent thoughts of death/suicide + plan DYSTHYMIC DISORDER > 2 yrs More days than not, chronic, less severe depressive symptoms COMORBID IMPACT: Role of SSRI’s; ineffectual with substance CBT – gambling + depression? Suicide assessment MANIC/BIPOLAR EPISODES Mood Stabilizers: Group Support, ie, Lithium; Anticonvulsants Integrated Group Therapy (Weiss) Interpers & Social Rhythm Therapy (Frank)? ANXIETY DISORDERS Fear & Tension reduction “lost in machine” Bi-directional and complex, i.e., social phobia preceding & GAD following alcohol! SCHIZOPHRENIA Withdrawal AISH & Internet Lower “cumulative” threshold of care! Concurrent approach Review diagnoses after behavior ends! (4) CHRONIC PAIN & DISABILITY TREATMENT PHASES Assessment Education & CBT group – 10 wkly Sessions Claresholm Residential Program for Taper & Rehab 3 – 24 wks Follow-up support groups (5) AXIS II - PERSONALITY DISORDER CLUSTERS A. Paranoid* B. ANTISOCIAL: impulsivity + disregard rights C. Avoidant Schizoid Borderline: impulsivity + affect instability Dependent Schizotypa Histrionic Obsessive-Compulsive* Narcissistic* (N Petry P109) > 33% NOS COMORBID IMPACT: Idiopathic or Symptomatic? Continuum with Normalcy Stigma Therapy subject to: Crisis/Consequences Introspection potential ADDICTION CENTRE ADULT OUTPATIENT SEQUENTIAL/CONCURRENT FLEXIBILITY = RETENTION! Case management + SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES Level I (Pre-Contemplation) < 6 individual Build motivation for change Level II (Pre-Contemplation) Group (2/wk for 3 wks) Engagement & assessment; Assess group treatment suitability Level III (Contemplation) (3 days/wk) Move patient into action ( Level IV) Reduce psychiatric/Add symptoms Engage supports (e.g., AA). Level IV (Action & Maintenance) (5 days/wk) Prevent relapse Confidence; Psychiatric/SA symptoms Speciality groups Open: harm reduction & support Couple: prevent relapse, communication Chr pain: reduce med reliance, non-drug coping GAMBLING: CBT & PREVENT RELAPSE (8 sessions) Inpt for Crisis stabilization only What about Mrs. “A”? July Assessment; Family? enabling or detached Sept-Oct Second residential program During childhood was the family social worker H sold marihuana; she gambled his money! Strengths: a leader in groups; attended GA; spiritual life Oct-Dec On discharge: no shows, no GA; using alcohol & marihuana Anxious about return to work; enquired about ADHD? Requested sole focus on “gambling” which was refused Angry phone call to managers in Nov about “personality conflict” & need to switch therapist Dec Discharge back to GP with information – latter acknowledged PD PROGNOSIS “It’s a long life!” – she is a bright, resourceful lady Loss of job/income may be the crisis required Couple therapy? Or separation? Anger management Crisis management until meaningful involvement PG: TYPOLOGY OF BEHAVIORAL DRIVERS? A. GENO-PHENOTYPES? B. SEVERITY LEVELS Serotonin – impulse control Social Abuse & Dependence LI, LII, L III Endorphin – urges, cravings Non-problem Problem Pathological Dopamine – reward, re-enforcement Norepinephrine – arousal, excitement C. ONSET (Early Late), Childhood stability & Psychopathology Blaszczynski’s Pathways COMPULSIVE Body dysmorphia Anorexia Tourette Path Gambling Sexual compulsions Impulsive PD D. CORMORBIDITIES SUD incl nicotine Mood Anx/PTSD Impulse control (sex, spending) Antisocial % range 20 – 70 30 – 75 20 – 40 20 20-40 IMPULSIVE “Repetitive behavior with inhibition defect, i.e., from hyper-vigilance & rituals to risk seeking ADDICTION: Behavior with tolerance, withdrawal & loss of control causing harm “cravers”