* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Classification of Animals 2014 use for notes
History of zoology since 1859 wikipedia , lookup
Emotion in animals wikipedia , lookup
Thermoregulation wikipedia , lookup
Aquatic locomotion wikipedia , lookup
Deception in animals wikipedia , lookup
Zoopharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Animal communication wikipedia , lookup
History of zoology (through 1859) wikipedia , lookup
Pain in invertebrates wikipedia , lookup
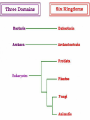
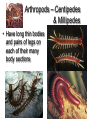
Classification Grouping & Identifying Living Things This Powerpoint is hosted on www.worldofteaching.com Please visit for 100’s more free powerpoints Taxonomy • The study of how living things are classified • Classification is the sorting of organisms based on similar characteristics • Carolus Linnaeus is known as the Father of Taxonomy Levels of Classification • • • • • • • • Domain Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species • • • • • • • • Dear King Phillip Came Over For Good Spaghetti • Most General • Most Specific Genus and Species • The last two levels make up an organisms scientific name – This is called Binomial Nomenclature • Bi—two • Nomial—Name Felis Concolor Penicillium chrysogenum Acer grandidentatum Classifying Living Things • We put livings things into three Domains Eukaryota Bacteria Archaea • Which are divided into 6 Kingdoms Plant Animal Fungi Protist Eubacteria Archaebacteria • We are in the Domain Eukaryota and the Kingdom Animalia Prokaryotes no nucleus Do have a nucleus Animal Kingdom • All animals are multi-cellular! • All animal cells are eukaryotic! – What does this mean? • Their cells have a nucleus and membrane bound organelles. • Animal cells are only surrounded by cell membranes…no cell wall! • Animals are heterotrophs • Most animals can move Animal Kingdom • All animals have specialized parts that do specific jobs. – Animals have different types of cells (ex. Heart cell vs. brain cell) – Animals have different kinds of tissues for their various organs. – The different organs in an animal perform different jobs for the whole body. Animal Kingdom • So…what makes an animal an animal? – Multicellular – Heterotrophs – Eukaryotes Symmetry • Bilateral—Can be divided into two mirrorimages halves • Radial—many lines of symmetry through a central location Animals • Animals are spilt into two major groups: – Vertebrates • Phylum Chordata – Invertebrates • Most animals are invertebrates • 29 different Phyla Vertebrates • These are animals with a backbone. • There are five groups of vertebrates: – Amphibians – Birds – Fish – Mammals – Reptiles Endo or Ecto? • Endothermic means their body temperature does not change much, even when the temperature of the environment changes. (Warm Blooded) – Mammals and Birds • Ectothermic means their body temperature changes with the environment. (cold blooded) – Fish, Amphibians, and Reptiles • • • • Fish Have wet scales Lays eggs in water Lives in water Uses gills for breathing • Ectothermic Amphibians • Have moist skin • Obtains oxygen through lungs and skin • Lay jelly coated eggs in water • Lives on land and water • Ectothermic Reptiles • Have dry scales • Lay waterproof eggs on land • Skin is adapted to keep water in the body • Breaths through lungs • Ectothermic Birds • Have feathers, scales on feet and legs and hollow bones • Have a gizzard that holds small stones to help grind food • Have a four chambered heart • Lay hard shelled eggs • Endothermic Mammals • Have hair or fur and produce milk • Specialized teeth • Give birth to live offspring (no eggs) • Have a four chambered heart • Endothermic Summary of Vertebrates Invertebrates • These are animals without a backbone • There are eight groups of invertebrates – – – – – – – – Mollusks Flatworms Segmented Worms Roundworms Sponges Echinoderms Cnidarians Arthropods Sponges • Filter feed • Simplest Animals Worms • Bilateral symmetry • Have head and tail ends • Simplest organism with a brain Flatworms • Have flat worm like bodies • Tapeworms and planarians Annelids—Segmented Worms • Have bodies made up of many linked sections • Earthworms Roundworms • Digestive system is like a tube open at both ends • Have bodies with no segments Arthropods • Have – segmented bodies – Jointed appendages – External skeleton • There are four group of arthropods: – Arachnids – Centipedes & Millipedes – Crustaceans – Insects Arthropods - Arachnid • Have four pairs of legs. • Have bodies divided into two sections Arthropods – Centipedes & Millipedes • Have long thin bodies and pairs of legs on each of their many body sections Arthropods - Crustacean • Have five-seven pairs of legs • First pair often used as pincers • Bodies covered in shell Arthropods - Insects • Have three pairs of legs • Bodies divided into three sections • Often have wings Mollusks • Soft bodies, some have a hard outer shell, foot for moving • Three Groups – Gastropod-most diverse – Bivalve – Cephalopod Cnidarians • Have stinging tentacles • Radial Symmetry • Two body forms – Medusa-the form during the movement stage of life – Polyp- sessile (doesn’t move) Madusa • Shaped like a bowl Polyp • Shaped like a vase Echinoderms • Have radial symmetry • Have spiny outer covering • Have a water vascular system