* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Classification of Animals
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
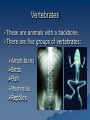
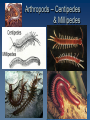
Classification Grouping & Identifying Living Things This Powerpoint is hosted on www.worldofteaching.com Please visit for 100’s more free powerpoints Why classify? Think of three examples where we group things. Why do we group these things? Classifying Living Things We put livings things into Animals Animals Animals are spilt into two major groups: Vertebrates Invertebrates Vertebrates These are animals with a backbone. There are five groups of vertebrates: Amphibians Birds Fish Mammals Reptiles Amphibians Have smooth moist skin Lay jelly coated eggs in water Lives on land and water Ectotherms Birds Have feathers and hollow bones Lay hard shelled eggs Endotherms Fish Have wet scales Lay jelly-coated eggs in water Breathes with gills Ectotherms Mammals Have hair and produce milk Give birth to live offspring (no eggs) Endotherms Reptiles Have scales Lay leathery shelled eggs Ectotherms Summary of Vertebrates Invertebrates These are animals without a backbone There are eight groups of invertebrates Molluscs Flatworms Annelids Roundworms Sponges Echinoderms Cnidarians Arthropods Molluscs Some molluscs (gastropods) crawl on a single fleshy pad. Ex. Snails, slugs, conchs. Some molluscs may burrow through or attach to a base (bi-valves) clams, oysters, mussels, brachiopod (extinct). Some molluscs swim (cephalopod). Most have a hard shell, but some do not (slugs, octopuses) Molluscs Flatworms Have flat worm like bodies Tapeworms and flukes Annelids Have round worm-like bodies Have bodies divided into segments with bristles or hairs (setae) Earthworms Have 5 hearts and no eyes Gizzard for digestion Breathe through their skin Clitellum – contains both male and female organs. Babies form in internal cocoons. Annelids Have round worm like bodies Have bodies divided into segments Roundworms Have long thin round worm like bodies. Have bodies with no segments. Are parasites. Hook worm, trichinosis, Roundworms Sponges (porifera) Simplest multi-cellular animal. Have bodies made of loosely joined cells Filter feeders Skeleton is made of needle-like fibers called spicules. Most are hermaphrodites, reproduce by releasing small planktonic larvae. Sponges Echinoderms Have radial symmetry. Appendages usually occur in fives. Have spiny outer covering Can regenerate limbs They eat by pulling apart bivalves with its suction-cup tube feet, and then it inverts its own stomach out of its mouth and surrounds its meal Echinoderms Cnidarians Have radial symmetry Have thin sack like bodies Have tentacles with stinging cells to trap their prey. Two body types: Polyp (corals and anemonies) where tentacles and mouth face up. Medussa (jellyfish) tentacles and mouth face down. Cnidarians Arthropods Have lots of legs and segmented bodies. Have exoskeletons. There are four group of arthropods: Arachnids Centipedes & Millipedes Crustaceans Insects Arthropods - Arachnid Include spiders, scorpions, ticks, and mites. Have four pair of legs and bodies divided into two sections Cephalothorax Abdomen Have chelicerae for feeding and defense. Eat by injecting poison into the prey and sucking out materials. Arthropods - Arachnid Arthropods – Myriapoda Have long thin bodies and pairs of legs on each of their many body sections. Have a “myriad” of legs. Centipedes are fast, venomous and predatory. One pair of legs per segment. Millipedes are slower, and eat leaf litter (detritus). Two pair of legs per segment. Arthropods – Centipedes & Millipedes Arthropods - Crustacean Include crabs, lobsters, shrimp, krill, barnacles and crayfish. Have more than four pairs of legs First pair often used as pincers. Most have 3 body parts – head, thorax, and abdomen. Although some have a cephalothorax. Arthropods - Crustacean Arthropods - Insects Bodies divided into three sections Head, thorax, and abdomen. Have three pairs of legs on thorax. May have wings on the thorax. Often have wings. Have compound eyes – can see almost all around themselves. Go through metamorphosis. Metamorphosis Incomplete metamorphosis. Change by molting. Egg Nymph Adult. Complete metamorposis. Egg Larva Pupa Adult. Arthropods - Insects