A Simple Legal Lacrosse Check
... with rest. The pain was rated at 5/10 in severity. Ibuprofen and Tylenol provided little relief. She was previously seen by a Podiatrist and had custom foot orthotics made, but her heel pain persisted. As such, she sought further evaluation and management from an orthopedic foot & ankle surgeon and ...
... with rest. The pain was rated at 5/10 in severity. Ibuprofen and Tylenol provided little relief. She was previously seen by a Podiatrist and had custom foot orthotics made, but her heel pain persisted. As such, she sought further evaluation and management from an orthopedic foot & ankle surgeon and ...
Sponges, Cnidarians, and Worms
... Phylum Porifera: Sponges Over 5000 species of all shapes and colors. All live in water—mostly salt water. ...
... Phylum Porifera: Sponges Over 5000 species of all shapes and colors. All live in water—mostly salt water. ...
Transforaminal Lumbar Epidural Steroid Injections
... under the pedicle with a downward course of 40 to 50 degrees from horizontal and occupy the superior portion of each foramen (89). It is considered that the upper portion of the foramina just beneath the adjacent pedicle is as a safe zone to place the injectate close to the lumbar nerve root (Fig 1) ...
... under the pedicle with a downward course of 40 to 50 degrees from horizontal and occupy the superior portion of each foramen (89). It is considered that the upper portion of the foramina just beneath the adjacent pedicle is as a safe zone to place the injectate close to the lumbar nerve root (Fig 1) ...
Anatomic Landmarks and Morphometric Measurements for Accurate
... in both the sagittal and coronal planes. In the infrazygomatic approach, the SPG was between 4.5 and 6.3 cm from the skin and an angle of about 7° posterior and inferior. Conclusion: These morphometric measurements will be of help to the clinician for accurate electrode or needle placement for SPG b ...
... in both the sagittal and coronal planes. In the infrazygomatic approach, the SPG was between 4.5 and 6.3 cm from the skin and an angle of about 7° posterior and inferior. Conclusion: These morphometric measurements will be of help to the clinician for accurate electrode or needle placement for SPG b ...
Slide 1 - Athletic Medicine
... after exercise. Delayed-onset muscle soreness (DOMS) – becomes most intense after 24 to 48 hours and then gradually subsides so that the muscle becomes symptom-free after 3 or 4 days. (This second type of pain is described as a syndrome of delayed muscle pain leading to increased muscle tension, swe ...
... after exercise. Delayed-onset muscle soreness (DOMS) – becomes most intense after 24 to 48 hours and then gradually subsides so that the muscle becomes symptom-free after 3 or 4 days. (This second type of pain is described as a syndrome of delayed muscle pain leading to increased muscle tension, swe ...
THE EFFECT OF THE ACTIVATOR ADJUSTING INSTRUMENT IN
... consultation three and at the follow consultation. This procedure occurred with four interventions over a two week period. ...
... consultation three and at the follow consultation. This procedure occurred with four interventions over a two week period. ...
PowerPoint - The Neurologic Exam
... • Signs of unilateral vestibular ataxia: – Head tilt (ipsilateral or contralateral) – Abnormal nystagmus ...
... • Signs of unilateral vestibular ataxia: – Head tilt (ipsilateral or contralateral) – Abnormal nystagmus ...
TMD Exam last updated 3/15 - University of Western States
... night guard or splint. A chronic or chronic recurrent presentation may have underlying structural or dental issues that may need to be explored. Stress or anxiety may lead to episodes of jaw clenching. An appropriate psychosocial history may uncover key precipitating or sustaining psychological fact ...
... night guard or splint. A chronic or chronic recurrent presentation may have underlying structural or dental issues that may need to be explored. Stress or anxiety may lead to episodes of jaw clenching. An appropriate psychosocial history may uncover key precipitating or sustaining psychological fact ...
A Cadaveric Study Evaluating the Feasibility of an Ultrasound
... RFA techniques, difficulty in identifying the posterior sacral foramina3,4 may result in needle placement within or directly adjacent to the foramina, risking ablation of the sacral spinal nerves.9 This could result in increased pain, incontinence, and lower limb muscle weakness.9 The current study ...
... RFA techniques, difficulty in identifying the posterior sacral foramina3,4 may result in needle placement within or directly adjacent to the foramina, risking ablation of the sacral spinal nerves.9 This could result in increased pain, incontinence, and lower limb muscle weakness.9 The current study ...
Needle Position Analysis in Cases of Paralysis From Transforaminal
... to be embolization, direct injury, muscle spasm, compression, intimal flaps, and transection of either the artery of Adamkiewicz or the radicular artery. Consequently, multiple anatomic studies, as well as various approaches considered as safer have been described ...
... to be embolization, direct injury, muscle spasm, compression, intimal flaps, and transection of either the artery of Adamkiewicz or the radicular artery. Consequently, multiple anatomic studies, as well as various approaches considered as safer have been described ...
Inferior Hypogastric Plexus Blockade: A Transsacral Approach
... pain relief and no evidence of complications. Consequently, the results are similar to the results of superior hypogastric plexus blockade utilizing either a classic approach or transdiscal approach. This study shows that the short-term results of a transsacral inferior hypogastric plexus blockade a ...
... pain relief and no evidence of complications. Consequently, the results are similar to the results of superior hypogastric plexus blockade utilizing either a classic approach or transdiscal approach. This study shows that the short-term results of a transsacral inferior hypogastric plexus blockade a ...
Safety and efficacy of undenatured type II collagen in the
... U n d e r s t a n d i nogl R Ap a t h o g e n e shi sa sc h a n g e d ciencvof the svstcm18) Autoimmunedisordersare with advancoverthe years.RA is characterized by attacko{ kjller less prevalentin the young,increasing T-cellson type ll jointcollagen,whjchresultsin dam- i n n a n e : n r - 1 d e r : ...
... U n d e r s t a n d i nogl R Ap a t h o g e n e shi sa sc h a n g e d ciencvof the svstcm18) Autoimmunedisordersare with advancoverthe years.RA is characterized by attacko{ kjller less prevalentin the young,increasing T-cellson type ll jointcollagen,whjchresultsin dam- i n n a n e : n r - 1 d e r : ...
Invertebrate Chordate Features
... Invertebrate chordates are deuterostomes with additional features that echinoderms lack. ...
... Invertebrate chordates are deuterostomes with additional features that echinoderms lack. ...
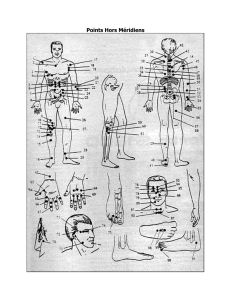
Points Hors Méridiens
... Sanhsiao : Middle of nasiolabial sulcus below LI 20 (nasal stiffness, rhinitis, facial nerve involvement) Keliao : Directly below ST 34, same level as CV 24 (facial nerve involvement, gingivitis, toothache) Waiyuyeh : 3 Fen lateral and one above laryngeal prominence (salivation, apoplexy, deaf mutis ...
... Sanhsiao : Middle of nasiolabial sulcus below LI 20 (nasal stiffness, rhinitis, facial nerve involvement) Keliao : Directly below ST 34, same level as CV 24 (facial nerve involvement, gingivitis, toothache) Waiyuyeh : 3 Fen lateral and one above laryngeal prominence (salivation, apoplexy, deaf mutis ...
Dry pitfall trapping for vertebrates and invertebrates
... Harvesting Study and Operation Foxglove. It is used for monitoring changes in population densities and movements of small to medium sized vertebrates. Forest Check also uses a similar integrated trapping grid incorporating pitfall traps. Details of the project and the trapping design may be found in ...
... Harvesting Study and Operation Foxglove. It is used for monitoring changes in population densities and movements of small to medium sized vertebrates. Forest Check also uses a similar integrated trapping grid incorporating pitfall traps. Details of the project and the trapping design may be found in ...
Cryoanalgesia in an Interventional Pain Management
... oneuroablation, with a release of sequestered proteins that may trigger an autoimmune response to the targeted to the lesioned tissues, which might explain the prolonged effect (22-24). The extent of the freezing (and subsequent nerve damage) is a function of 1) the proximity of the probe to the ner ...
... oneuroablation, with a release of sequestered proteins that may trigger an autoimmune response to the targeted to the lesioned tissues, which might explain the prolonged effect (22-24). The extent of the freezing (and subsequent nerve damage) is a function of 1) the proximity of the probe to the ner ...
Cortical tongue area studied by chronically
... hemisphere. The patient was a 19-year-old left-handed man with complex partial seizures. The Wada test showed that the language areas were represented bilaterally. The MRI scan was negative for the organic brain lesion. B l-C 1, tongue and jaw pulls to right~ and right hand finger nloven1ent stops~ ...
... hemisphere. The patient was a 19-year-old left-handed man with complex partial seizures. The Wada test showed that the language areas were represented bilaterally. The MRI scan was negative for the organic brain lesion. B l-C 1, tongue and jaw pulls to right~ and right hand finger nloven1ent stops~ ...
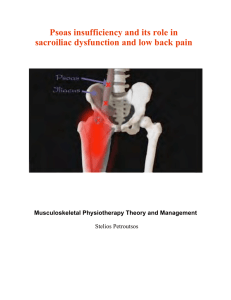
Psoas insufficiency and its role in sacroiliac dysfunction and low
... (Schwarzer et al 1995). Such studies suggest that pain in the buttock and leg which does not spread superior to L5 level has more a SIJ contribution (Harrison et al 1997, Maigne et al 1996). However, extraarticular structures can also cause pain patterns (Fortin et al 1997). Therefore, joint blocks ...
... (Schwarzer et al 1995). Such studies suggest that pain in the buttock and leg which does not spread superior to L5 level has more a SIJ contribution (Harrison et al 1997, Maigne et al 1996). However, extraarticular structures can also cause pain patterns (Fortin et al 1997). Therefore, joint blocks ...
Harr Chap Back And Neck Pain - University of California (San
... Understanding the types of pain reported by patients is essential. Attention is also focused on identification of risk factors for serious underlying diseases; the majority of these are due to radiculopathy, fracture, tumor, or infection (Table 17-1). Local pain is caused by injury to pain-sensitive ...
... Understanding the types of pain reported by patients is essential. Attention is also focused on identification of risk factors for serious underlying diseases; the majority of these are due to radiculopathy, fracture, tumor, or infection (Table 17-1). Local pain is caused by injury to pain-sensitive ...
Anatomy and Physiology of Headache by Bogduk
... tion of cervical afferents to a second-order neurone that also receives a trigeminal input may result in the source of stimulation being interpreted as arising in the cervical receptive field, the trigeminal receptive field or both. By the same token, if a neurone receives afferents from two, differ ...
... tion of cervical afferents to a second-order neurone that also receives a trigeminal input may result in the source of stimulation being interpreted as arising in the cervical receptive field, the trigeminal receptive field or both. By the same token, if a neurone receives afferents from two, differ ...
Evaluation of Patients Presenting with Knee Pain
... The patient with pes anserine bursitis reports pain at the medial aspect of the knee. This pain may be worsened by repetitive flexion and extension. On physical examination, tenderness is present at the medial aspect of the knee, just posterior and distal to the medial joint line. No knee joint effu ...
... The patient with pes anserine bursitis reports pain at the medial aspect of the knee. This pain may be worsened by repetitive flexion and extension. On physical examination, tenderness is present at the medial aspect of the knee, just posterior and distal to the medial joint line. No knee joint effu ...
A 50-Year-Old Man With Chronic Low Back Pain
... the leg. The proper term is radicular pain because stimulation of the nerve roots or the dorsal root ganglion of a spinal nerve evokes the pain. Pain is a normal physiologic process and serves as a signal of actual or impending tissue injury. Pain from tissue injury is usually well localized and ass ...
... the leg. The proper term is radicular pain because stimulation of the nerve roots or the dorsal root ganglion of a spinal nerve evokes the pain. Pain is a normal physiologic process and serves as a signal of actual or impending tissue injury. Pain from tissue injury is usually well localized and ass ...
A 50-Year-Old Man With Chronic Low Back Pain
... the leg. The proper term is radicular pain because stimulation of the nerve roots or the dorsal root ganglion of a spinal nerve evokes the pain. Pain is a normal physiologic process and serves as a signal of actual or impending tissue injury. Pain from tissue injury is usually well localized and ass ...
... the leg. The proper term is radicular pain because stimulation of the nerve roots or the dorsal root ganglion of a spinal nerve evokes the pain. Pain is a normal physiologic process and serves as a signal of actual or impending tissue injury. Pain from tissue injury is usually well localized and ass ...
ASRA News, Volume 14, Issue 4, pp 5-8,22
... Domain is assessed using the Hospital Consumer Assessment of Healthcare Providers and Systems (HCAHPS) survey. HCAHPS consists of 32 questions, publicly reports its results 4 times a year on http:// www.hospitalcompare.hhs.gov, and contains 7 questions that directly or indirectly relate to pain. O ...
... Domain is assessed using the Hospital Consumer Assessment of Healthcare Providers and Systems (HCAHPS) survey. HCAHPS consists of 32 questions, publicly reports its results 4 times a year on http:// www.hospitalcompare.hhs.gov, and contains 7 questions that directly or indirectly relate to pain. O ...
Pain in invertebrates

Pain in invertebrates is a contentious issue. Although there are numerous definitions of pain, almost all involve two key components. First, nociception is required. This is the ability to detect noxious stimuli which evokes a reflex response that moves the entire animal, or the affected part of its body, away from the source of the stimulus. The concept of nociception does not imply any adverse, subjective 'feeling' - it is a reflex action. The second component is the experience of 'pain' itself, or suffering, i.e. the internal, emotional interpretation of the nociceptive experience. Pain is therefore a private, emotional experience. Pain cannot be directly measured in other animals, including other humans; responses to putatively painful stimuli can be measured, but not the experience itself. To address this problem when assessing the capacity of other species to experience pain, argument-by-analogy is used. This is based on the principle that if a non-human animal's responses to stimuli are similar to those of humans, it is likely to have had an analogous experience. It has been argued that if a pin is stuck in a chimpanzee's finger and she rapidly withdraws her hand, then argument-by-analogy implies that like humans, she felt pain. It has been questioned why the inference does not then follow that a cockroach experiences pain when it writhes after being stuck with a pin? This argument-by-analogy approach to the concept of pain in invertebrates has been followed by others.The ability to experience nociception has been subject to natural selection and offers the advantage of reducing further harm to the organism. While it might be expected therefore that nociception is widespread and robust, nociception varies across species. For example, the chemical capsaicin is commonly used as a noxious stimulus in experiments with mammals; however, the African naked mole-rat, Heterocephalus glaber, an unusual rodent species that lacks pain-related neuropeptides (e.g., substance P) in cutaneous sensory fibres, shows a unique and remarkable lack of pain-related behaviours to acid and capsaicin. Similarly, capsaicin triggers nociceptors in some invertebrates, but this substance is not noxious to Drosophila melanogaster (the common fruit fly).Criteria that may indicate a potential for experiencing pain include: Has a suitable nervous system and receptors Physiological changes to noxious stimuli Displays protective motor reactions that might include reduced use of an affected area such as limping, rubbing, holding or autotomy Has opioid receptors and shows reduced responses to noxious stimuli when given analgesics and local anaesthetics Shows trade-offs between stimulus avoidance and other motivational requirements Shows avoidance learning Exhibits high cognitive ability and sentience↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑