* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download MALFUNCTIONS of the IMMUNE SYSTEM
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Autoimmunity wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Sjögren syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
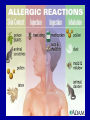
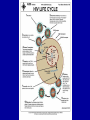
MALFUNCTIONS of the IMMUNE SYSTEM This lesson meets the following DoE Specific Curriculum Outcomes for Biology 11: 116-7 MALFUNCTIONS of the IMMUNE SYSTEM • Abnormal functioning of the immune system can cause two types of problems: – Immunodeficiency diseases – Inappropriate attacks of the immune system against nonthreatening agents (harmless cells) IMMUNODEFICIENCY • Immunodeficiency diseases may be caused by a foreign agent, such as the HIV virus, which attacks T cells. • It may also result from a hereditary condition, such as severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) that results in the inability to produce B cells and T cells. AUTOIMMUNE DISEASE • T cells or antibodies mistakenly identify your own body cells as foreign and consequently attack them. AUTOIMMUNE DISEASE • Renegade lymphocytes treat the body’s cells as aliens and make antibodies to attach to their own cell membranes. • Drugs or serious infections can weaken the suppressor T cells, leaving the body vulnerable to autoimmune diseases. ALLERGIES • A hypersensitivity to harmless agents, or a response in which the immune system begins to attack normal cells in one’s own body, can destroy tissues and organs. • Allergies occur when your immune system mistakes harmless cells for harmful invaders. • If you are allergic to peanuts, your immune system recognizes one of the proteins in the peanut as dangerous. ALLERGIC RESPONSE • For allergies to materials such as dust mites, pollen, mould and animal dander, the reaction of the antibodies releases histamines that cause sneezing, watery eyes and runny nose. • Food allergies can be more severe. AIDS • Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) retrovirus that causes AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome). • HIV virus contains one RNA molecule and two reverse transcriptase molecules. • After entering the host’s Helper T cell, the reverse transcriptase triggers the production of viral DNA (provirus) by the host nucleus. AIDS • The host’s transcribes the viral DNA into RNA for new viruses resulting in the destruction of the host cell. • The destruction of the helper T cells impedes the discover of pathogens by the immune system. • See page 480 of Bio 12 text book .