* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download b-cells - APBiology2015-2016
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
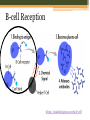
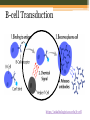
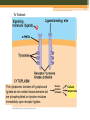
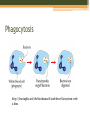
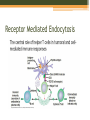
B-CELLS Rachel Gluski, Vickie Le, Lena Wachs https://courses.candelalearning.com/anatomyphysiology2/chapter/21 -4-the-adaptive-immune-response-b-lymphocytes-and-antibodies/ What are B-cells? • B-Cells belong to the variety of white blood cells and play a role in the immune system by making y-shaped proteins called antibodies. • They are found in the bone marrow where stem cells develop them. • They are also known as B lymphocytes. http://www.clker.com/clipart-naive-b-cell.html http://www.bdbiosciences.com/sg/research/bcell/ B-Cell Receptor • The B-cell receptor’s(BCR) role is to specifically bind intact antigens on the surface of invasive bacteria or viruses. • It can be found exposed at the cell surface in thousands and as soluble molecules in the extracellular fluid. Signaling (reception) • B-cells bind intact antigens through receptor-mediated endocytosis, causing the antigen to be digested into fragments. • The ligand is the antigen (Signal) • The receptor is the BCR (reception) B-cell Reception https://askabiologist.asu.edu/b-cell To Textbook EXTRACELLULAR FLUID Receptor Signaling molecule CYTOPLASM Plasma membrane Transduction • The fragments will later appear on the cell surface inside a molecule because it is now a plasma cell. • T-cells help b-cells function properly by releasing chemicals that signal the b-cells to divide in multiples and attack invaders inside the cell that may interfere with the signal pathway. B-cell Transduction https://askabiologist.asu.edu/b-cell To Textbook EXTRA-CELLULAR FLUID Signaling molecule (first messenger) The cytoplasmic domains of Ig-alpha and Ig-beta do not contain kinase domains but are phosphorylated on tyrosine residues immediately upon receptor ligation. Various proteins activated Cellular responses Phagocytosis http://leavingbio.net/the%20human%20defence%20system-web2.htm Receptor Mediated Endocytosis Cellular Response • The response of B-cells is the function of realeasing antibodies • Antibodies made by the B-cells bind to antigens on the surface of germs and clump up. This process is called “agglutination.” • The accumulation of antibodies alerts your body to the presence of intruders. • The body then sends phagocytes to engulf and destroy antibody-covered intruders. B-cell Response https://askabiologist.asu.edu/b-cell Amplification • One B-cell can result in many plasma cells, in turn resulting in even more antibodies being released Reception, Transduction, & Response https://askabiologist.asu.edu/b-cell Citations • Campbell, Neil A., and Jane B. Reece. Biology. New York, NY: Custom, 2008. Print. • "B Cells and T Cells." B Cells and T Cells. N.p., 17 Aug. 2015. Web. 08 Nov. 2015. • National Center for Biotechnology Information. U.S. National Library of Medicine, n.d. Web. 08 Nov. 2015. • "OpenStax CNX." OpenStax CNX. N.p., n.d. Web. 08 Nov. 2015. • "School of Life Sciences | Ask A Biologist." B-Cells. N.p., n.d. Web. 08 Nov. 2015.