* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Major histocompatibility complex wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Duffy antigen system wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
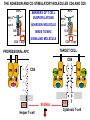
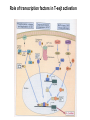
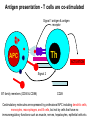
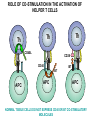
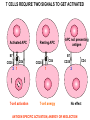
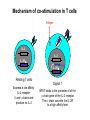
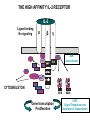
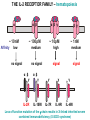
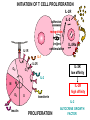
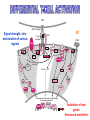
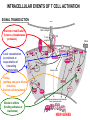
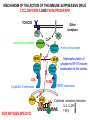
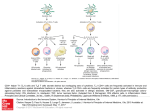
T CELL RECEPTOR MEDIATED SIGNALING Multisubunit Immune Recognition Receptors APC MIRR MHC Antigen Antigen TCR BCR αβ s V s s sV s C s s sC ss P P D/E X7 D/E X2 YXXL/I X7 YXXL/I ITAM Immunoreceptor Tyrosine-based Activation Motif ACTIVATION CD3 CD3 εδ s s s s εγ s s s s ζζ s s INTERACTION OF THE TCR WITH MHC-PEPTIDE COMPLEXES IS ESSENTIAL BUT NOT SUFFICIENT FOR T-CELL PRIMING INVOLVEMENT OF ADHESION AND COSTIMULATORY MOLECULES CONVERGING SIGNALING PATHWAYS IN T CELL ACTIVATION CD4/CD8 costimulation CD28 costimulation THE ADHESION AND CO-STIMULATORY MOLECULES CD4 AND CD8 APC MARKERS OF T CELL SUBPOPULATIONS MHCII + peptid ADHESION MOLECULE TCR CD4 APC MHCI + peptid TCR BINDS TO MHC p56lck p56lck SIGNALING MOLECULE + CD4 T-sejt CD8 CD8+ T-sejt TARGET CELL PROFESSIONAL APC CD8 1 s s 2 V4 2 s s s s α β Lck Helper T-cell SIGNAL Lck a b T-cell Cytotoxic 1 V3 2m s s 3 V2 CD4 s s 3 s s 2m V1 2 1 2 1 THE RATIO OF CD4+/CD8+ T CELLS IS STABLE IN HEALTHY INDIVIDUALS CD4+ : CD8+ = 1.6 Normal CD4+ T-cell counts = 600 – 1400/ l HIV infection AIDS = CD4+ T cell count <200/l TCR signaling Fyn Role of transcription factors in T-sejt activation Antigen presentation - T cells are co-stimulated Signal 1 antigen & antigen receptor Th APC ACTIVATION Signal 2 B7 family members (CD80 & CD86) CD28 Costimulatory molecules are expressed by professional APC including dendritic cells, monocytes, macrophages, and B cells, but not by cells that have no immunoregulatory functions such as muscle, nerves, hepatocytes, epithelial cells etc. ROLE OF CO-STIMULATION IN THE ACTIVATION OF HELPER T CELLS Th Th Th CD40L CD28 CD40 B7 B7 APC APC APC NORMAL TISSUE CELLS DO NOT EXPRESS CD40 OR B7 CO-STIMULATORY MOLECULES T CELLS REQUIRE TWO SIGNALS TO GET ACTIVATED Activated APC Resting APC B7 CD28 APC not presenting antigen B7 CD4 2 1 T-cell activation CD4 CD28 1 T-cell anergy CD4 CD28 2 No effect ANTIGEN SPECIFIC ACTIVATION, ANERGY OR NEGLECTION CO-STIMULATION IS ESSENTIAL FOR PRIMING OF NAIVE T LYMPHOCYTES The antigen-specific and the co-stimulatory signals have to be induced in concert to induce T lymphocyte activation The antigen-specific and co-stimulatory signals can be delivered simultaneously by professional antigen presenting cells, only The antigen-specific and the co-stimulatory singnals has to be delivered by the same professional antigen presenting cell Mechanism of co-stimulation in T cells Antigen 1 IL-2 IL-2 IL-2R IL-2R Resting T cells Express a low affinity IL-2 receptor and chains and produce no IL-2 Signal 1 NFAT binds to the promoter of of the chain gene of the IL-2 receptor. The chain converts the IL-2R to a high affinity form Mechanism of co-stimulation in T cells Costimulation Antigen Signal 2 1 2 Activates AP-1 and NFk-B to increase IL2 gene transcription by 3 fold Stabilises and thus increases the half-life of IL-2 mRNA by 20-30 fold IL-2 IL-2R IL-2 production increased by 100 fold overall Immunosuppressive drugs illustrate the importance of IL-2 in immune responses Cyclosporin & FK506 inhibit IL-2 by disrupting TcR signalling Rapamycin inhibits IL-2R signalling THE HIGH AFFINITY IL-2 RECEPTOR IL-2 Ligand binding No signaling α β γ JAK Janus kinase CYTOSKELETON Gene transcription Proliferation STAT Signal Transducer and Activatior of Transcription THE IL-2 RECEPTOR FAMILY – hematopoiesis α α β α β γ ~ 10nM ~ 100pM ~ 10pM medium high medium no signal signal signal Affinity low no signal α β γ IL-2R α β γ IL-15RI β γ ~ 1nM γ γ γ IL-7R IL-9R IL-4RI Loss of function mutation of the -chain results in X-linked inherited severe combined immunodeficiency (X-SCID syndrome) INITIATION OF T CELL PROLIFERATION IL-2R adhesion IL-2 recognition IL-2Rα costimulation IL-1R IL-1 IL-2R G0 IL-2R low affinity G1 IL-2 M G2 IL-2R high affinity S transferrin IL-2 insulin PROLIFERATION AUTOCRINE GROWTH FACTOR Anergy Antigen Naïve T cell 1 Signal 1 only IL-2 IL-2R Epithelial cell Self peptide epitopes presented by a non-classical APC e.g. an epithelial cell The T cell is unable to produce IL-2 and therefore is unable to proliferate or be clonally selected. Unlike immunosupressive drugs that inhibit ALL specificities of T cell, Signal 1 in the absence of signal 2 causes T cell unresponsiveness to a specific antigen Coreceptors deliver powerful responses Dangers of triggering strong co-stimulatory signals Mice are not humans Cytokine storm in a phase 1 trial of the anti-CD28 monoclonal antibody TGN1412. Suntharalingam G, Panoskaltsis N. N Engl J Med. 2006 Sep 7;355(10):1018-28. Six healthy young male volunteers at a contract research organization were enrolled in the first phase 1 clinical trial of TGN1412, a novel superagonist anti-CD28 monoclonal antibody that directly stimulates T cells. Within 90 minutes after receiving a single intravenous dose of the drug, all six volunteers had a systemic inflammatory response characterized by a rapid induction of proinflammatory cytokines and accompanied by headache, myalgias, (pain in multiple muscles) nausea, diarrhea, erythema, vasodilatation, and hypotension. Within 12 to 16 hours after infusion, they became critically ill, with pulmonary infiltrates and lung injury, renal failure, and disseminated intravascular coagulation. Severe and unexpected depletion of lymphocytes and monocytes occurred within 24 hours after infusion. All six patients were transferred to the care of the authors at an intensive care unit at a public hospital, where they received intensive cardiopulmonary support (including dialysis), high-dose methylprednisolone, and an anti-interleukin-2 receptor antagonist antibody. Prolonged cardiovascular shock and acute respiratory distress syndrome developed in two patients, who required intensive organ support for 8 and 16 days. Despite evidence of the multiple cytokine-release syndrome, all six patients survived. Documentation of the clinical course occurring over the 30 days after infusion offers insight into the systemic inflammatory response syndrome in the absence of contaminating pathogens, endotoxin, or underlying disease. Modulation of the CD28 co-stimulatory pathway. „Extreme response The drug, an antibody called TGN1412, is being developed by German company TeGenero with the aim of directing the immune system to fight cancer cells, or calm joints inflamed by rheumatoid arthritis. The antibody binds to a receptor molecule called CD28 on the surface of the immune system's infectionfighting T cells. (Nature March 17 2006) Scientists who work in the field say there are several possible ways that the drug could have triggered multiple organ failure. It may have stimulated T cells so much that they released an overwhelming flood of inflammatory molecules called cytokines. Or perhaps wayward T cells launched an attack on the body's own tissues, ignoring the safety mechanisms that normally keep this in check. APC MHC+antigén Signal strength, ratio and duration of various signals B7 CD4 T-sejt receptor CD28 CD45 -P DAG PKC Lck Fyn Ca2+ LAT PLC PI3K ZAP-70 Csk PtdIns4,5P2 IkB Ca2+ PtdIns3,4,5P3 Ca2+ CN PKC Vav Rho/Rac IP3 Ca2+ 2+ Ca Ca2+ 2 Ca + Ca2+ Ras LAT Sos Sos Grb2 SLP76 Cbl NF-kB Raf P MAPK P IkB CN NFAT P P NF-kB NFAT transzkripciós faktorok foszforilációja korai génexpresszió NFAT AP-1 NF-kB OCT Activation of new genes How much and which INTRACELLULAR EVENTS OF T CELL ACTIVATION SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION APC MHC+antigén Enzimatic modification (kinases, phosphatases, proteases) CD4 T-sejt receptor CD28 CD45 Local concentration (recruitment or sequestration of interacting components PKC Lck Fyn Ca2+ LAT PLC PI3K ZAP-70 Csk Ras LAT Grb2 Sos Sos SLP76 Cbl PtdIns4,5P2 IkB Ca2+ PtdIns3,4,5P3 Ca2+ CN P MAPK NF-kB NFAT transzkripciós faktorok foszforilációja korai génexpresszió NFAT AP-1 NF-kB NF-kB Raf CN NFAT P P PKC Vav Rho/Rac IP3 Ca2+ 2+ Ca Ca2+ 2 Ca + Ca2+ Timing (pathway can go to diverse directions, first one will be realized) Allosteric effects (binding activates or inactivates) -P DAG OCT NEW GENES P IkB MECHANISM OF THE ACTION OF THE IMMUNE SUPPRESSIVE DRUG CYCLOSPORIN A AND FK506/PROGRAPH TCR-CD3 Other receptors PLC Inactive phosphatase calcineurin PLC Ca2+ calcineurin PTP-ase NF-ATc P NF-AT calcineurin PTP-ase CSA FKBP2 isomerase NF-ATn TF NOT ANTIGEN SPECIFIC calcineurin PTP-ase Dephosphorylation of cytoplasmic NF-AT induces translocation to the nucleus FK506 Cycliphilin A isomerase NF-ATn Active phosphatase Cytokines, activation molecules IL-2, IL-2R TGF