* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What could have caused this?
Complement system wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
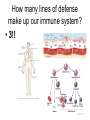
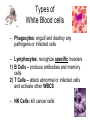
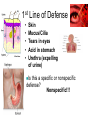
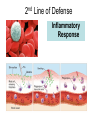
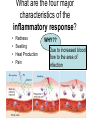
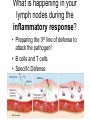
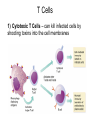
Aim: How does our body defend us from pathogens? Pathogens Any disease-producing agent especially a virus, bacterium, fungus, or parasite. Immune System Made of proteins, cells, and tissues that identify and defend the body against foreign chemicals and organisms How many lines of defense make up our immune system? • 3!! What is the difference between a nonspecific and specific immune response? • Nonspecific: Targets any pathogen or infected cell • Specific: Targets only one pathogen or cells infected by the same pathogen Types of White Blood cells – Phagocytes: engulf and destroy any pathogens or infected cells – Lymphocytes: recognize specific invaders 1) B Cells – produce antibodies and memory cells 2) T Cells – attack abnormal or infected cells and activate other WBCS – NK Cells: kill cancer cells How does our immune system identify foreign cells? Antigen Recognition proteins on our cells (self) are not targeted by our immune system. • Protein markers “ID tags” on the cells of pathogens • Antigens identify the invader as foreign (nonself). 1st Line of Defense • • • • • Skin Mucus/Cilia Tears in eyes Acid in stomach Urethra (expelling of urine) Is this a specific or nonspecific defense? Nonspecific!!! 2nd Line of Defense Inflammatory Response What are the four major characteristics of the inflammatory response? • • • • Redness Swelling Heat Production Pain WHY?? Due to increased blood flow to the area of infection Which types of white blood cells are active during the inflammatory response? Phagocytes: White blood Cells that Eat a pathogen Is this specific or Nonspecific defense? What is happening in your lymph nodes during the inflammatory response? • Preparing the 3rd line of defense to attack the pathogen! • B cells and T cells • Specific Defense Lymphocytes (B Cells) • They can make antibodies!!! What are Antibodies? Pathogen Antibodies Antigens • They are “Y” shaped proteins that help to fight against pathogens How many antibodies exist for one antigen? Antibodies are made specifically to match the shape of the antigen. 1 antigen = 1 antibody What does this remind you of? B Cells B cells have specific receptors that bind with specific antigens on pathogens. Once bound, B cells are activated and become antibody producing factories Produce Antibodies How do antibodies destroy pathogens? • Antibodies bind to all of the antigens on the pathogen… • This can kill the pathogen itself OR • Acts as a marker for a phagocyte to engulf T Cells 1) Cytotoxic T Cells – can kill infected cells by shooting toxins into the cell membranes T Cells & Cell Mediated Immunity 2) Helper T Cells – help to activate more B and T cells Our Immune System has a good memory! ** After the first response, the immune system “remembers” specific pathogens by leaving behind memory cells that protect the body for years