* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 3 part 2 PPT
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
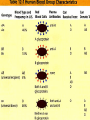
UNIT 3 PART 2: IMMUNE SYSTEM • The blood is a liquid tissue that has three major functions: – Transportation of nutrients, hormones, wastes, etc. – Regulation of body temperature, pH, and water balance – Protection from disease and from excess loss of blood by forming clots 1 2 PATHOGENS • Something foreign that enters the body and causes disease such as: – Viruses (AIDS, chicken pox, common cold) – Bacteria (strep throat, E. coli) – Fungi (athlete’s foot, ringworm) – Parasites (tapeworm, leech, malaria) – Toxins (lead poisoning, carbon monoxide) 4 5 6 7 The Immune System • The function of the immune system is to protect the body from disease • Recognizes, attacks, destroys, and remembers each kind of pathogen • Components: bone marrow, WBCs, lymph nodes, tonsils, thymus, and spleen 8 9 10 IMMUNITY • The ability to fight infection through the production of antibodies or the production of phagocytic cells that kill foreign cells. • It works because the body can distinguish between itself and foreign substances or “nonself” by recognizing cell markers. • Lymphocytes (B cells and T cells) recognize foreign antigens and either produce antibodies or kill foreign cells. Each B or T cell recognizes a different antigen. 11 12 13 14 15 16 • Antigen – A molecule on the surface of a cell that identifies that particular cell. All cells have many kinds of antigens. • Antibody – Binds to the antigen and helps destroy it – Made by T and B cells – Each one recognizes a different antigen Antigen 18 19 20 Bellringer 1/4 • How does a vaccine work? 21 ACTIVE IMMUNITY • You make your own antibodies when exposed to an antigen, like when you get sick, or when you get a vaccination. The antigens used are dead or weakened viruses or bacteria. They trigger the immune response without making you sick. • This type of immunity is permanent. 22 23 PASSIVE IMMUNITY • Antibodies are given to a person – From the blood of another person or animal – From your mother during her last month of pregnancy, or in mother’s milk • This type of immunity is temporary. 24 25 BLOOD GROUPS • All human cells have antigens; that is how self and nonself are recognized. • There are 4 major blood groups that depend on the presence or absence of 2 antigens on a person’s RBCs. • You are born with antibodies against the antigen that is NOT present on your RBCs. 26 Lab: Human Blood Groups 27 28 29 What happens if you are given the wrong blood type? • If you are given a type that you have antibodies for, then the blood will clump, clog vessels, and cause kidney failure. • Transplanted organs are also rejected because they have nonself antigens and your body makes antibodies against them. • This effect can be lessened if the recipient and donor are closely related and if the recipient takes immunosuppressant drugs to slow or stop the body’s immune response. 30 31 ALLERGIES • An allergic response is caused by your immune system reacting to something it thinks is harmful but really isn’t, such as pollen, pet dander, nuts, shellfish, or bee stings. • This causes special cells to release a substance called histamine which causes sneezing and itchy, watery eyes. • Severe allergic reactions can cause swelling that closes off airways and can cause death if not treated immediately. 33