* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Gluten immunochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Sjögren syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
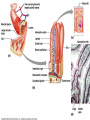
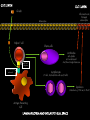
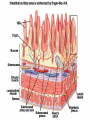
Immunology of CELIAC DISEASE Ibrahim, Ibrahim; Kandoth, Littin; Naqvi, Shabab; Sims, Tyreen; Julien, Tabitha Mentor: Dr. Sanil Manavalan Columbia University, College of Physicians & Surgeons Celiac disease •a digestive disease that damages the small intestine and interferes with absorption of nutrients from food . •When people with celiac disease eat foods containing gluten, their immune system responds by damaging the small intestine. •Because the body's own immune system causes the damage, celiac disease is considered an autoimmune disorder. AUTOIMMUNE DISEASE: condition in which the immune system mistakenly attacks the body's own organs and tissues • Type 1 Diabetes – affects the pancreas • Systemic Lupus erythmatotosus (Lupus)– affects the skin • Crohn’s Disease- affects the gut • Multiple Sclerosis- affects the brain Key Terms • Cytokine – proteins secreted by macrophages and leukocytes that stimulate or inhibit the proliferation or function of immune cells. – Interleukin – cytokines that only affect leukocytes. • Lymphocyte – A type of leukocyte (white blood cell) of the immune system. – T-Regulatory Cell – slows down and stops immune response – T-Helper Cell – has antigen-receptors, releases cytokines – Natural Killer Cell – kills macrophage and bad stuff – Cytotoxic T-Cell – kills with cytotoxins – B-Cell – creates antibodies. • Antigen – invading microbe • Antibody – protein that fights bacteria and viruses. Cytokines The Gut Lumen • Villi- (singular: villus) are tiny, finger-like structures that protrude from the wall of the intestine -Microvilli- hairlike structure on the surface of absorptive and secretory epithelial cells • Epithelial Tissue- layer of cells which line the GI tract • Enterocytes – layer between gut lumen and absorptive cells diagram GUT LUMEN GUT LUMEN Gliadin Inflammation & Damaged enteroctytes Enterocytes Helper T cell Plasma cells Antibodies anti-gliadin anti-endomysial And tissue trasgliutaminase ab T cell receptor HLA-DQ2/DQ8 molecule Lymphocytes (T cells , Natural Killer cells and B cells) Cytokines (Interferon-g, TNF-a, IL-15 etc) Antigen Presenting Cell LAMINA PROPRIA AND INTRA EPITHILIAL SPACE Mucosal Immune System Objective • To find the cytokine levels in the serum of patients in the following groups – Healthy Patients (Control) – Active Celiac Disease Patients – Celiac Disease patients on Gluten-free diets – Refractory Disease Patients • The following cytokines were checked in the serum of these patients; – IL-1β – IL-6 – IL-8 – IL-12 p70 – IFN-γ – TNF-α Flow Cytometry DEFINITION: technique for counting, examining and sorting microscopic particles suspended in a stream of fluid ROLE IN OUR EXPERIMENT: Results Conclusions References THANK YOU To: Dr. Sanil Manavalan Dr. Jamal Naiyer Sindhu Kunduvaram Dr. Sat Bhattacharya Harlem Children Society Cytokines Cytokine IL-1β IL-6 IL-8 IL-12 p70 IFN-γ TNF-α Principal cell Targets and biological effects Endothelial cells: activation B cells: proliferation of antibody producing cells Activator of neutrophils NK cells and T cells: IFN-gamma synthesis, increased cytolytic activity Macrophages: Activation Endothelial cells: Activation