* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Sjögren syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Inflammation wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
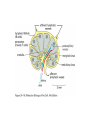
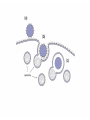
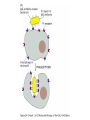
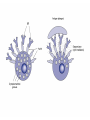
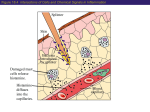
1. INTRODUCTION, PRINCIPLES, CELLS…, molecular and cellular principles IMMUNE SYSTEM MUST RECOGNIZE: __________________________________________________ SELF VS. FOREIGN resp. „CORRECT VS. INCORRECT“ resp. HARMLESS VS. DANGEROUS IT SHOULD NOT DAMAGE THE ORGANISM (BUT TOO OFTEN DAMAGES – „DOUBLE EDGED SWORD“ PROBLEM: WHAT IS „SELF“ WHAT IS „FOREIGN“ IMMUNE SYSTEM RECOGNIZES: “SOME SELF COMPONENTS FROM SOME FOREIGN“ IMMUNE MECHANISMS - “NONSPECIFIC” (PHAGOCYTOSIS, COMPLEMENT LECTINS, INTERFERONS...) - ANTIGEN-SPECIFIC ANTIGEN SPECIFIC MECHANISMS - HUMORAL (ANTIBODY) - CELL-MEDIATED BASIC TERMS ANTIGEN INFLAMMATION IMMUZIZATION (PASSIVE, ACTIVE) IMMUNODEFICIENCY TOLERANCE ALERGIES MEMORY AUTOIMMUNITY ANTIBODIES MHC PROTEINS CYTOKINES Cell type Relative representation (%) Neutrophil granulocytes 60 - 70 Eosinophil granulocytes 1-3 Basophil granulocytes <2 Monocytes 5 - 10 Lymphocytes 20 - 40 LYMPHOID TISSUES AND ORGANS BONE MARROW – DEVELOPMENT FROM STEM CELLS THYMUS – DEVELOPMENT OF T-LYMPHOCYTES DIFFUSE LYMPHOID TISSUE – UNDER EPITELIAL SURFACE LYMPHOID FOLLICLES ORGANIZED AGGREGATES OF FOLLICLES: - TONSILS - PEYER PLAQUES - APPENDIX LYMPH NODES SPLEEN 2. ANTIGEN NONSPECIFIC MECHANISMS; PHAGOCYTES, GRANULOCYTES PHAGOCYTOSIS NEUTROPHIL GRANULOCYTES REMOVAL OF BACTERIA; PUS MACROPHAGES – MAINLY REMOVAL OF DAMAGED AND DYING CELLS MECHANISMS: RECEPTORS OF “FOREIGN“ STRUCTURES (TLR, LECTINS) OPSONIZATION (Ig, COMPLEMENT) – BINDING TO Fc-RECEPTORS, COMPLEMENT RECEPTORS ENGULFMENT “KILLING” - FUSION WITH LYSOSOMES (LOW pH, ENZYMES, DEFENSINS) - OXIDATIVE BURST PHAGOCYTOSIS TOLL-LIKE RECEPTORS OXIDATIVE (RESPIRATORY) BURST Prodution of reactive oxygen compounds by the enzyme NADPH-oxidase Localized in the phagosome membrane and catalyses the reactions: (surface) O2 → O2- (superoxide anion-radical) _________________________________________ (cytoplasm) NADPH → NADP+ + H+ Superoxide reacts further to produce toxic compounds (“singlet oxygen“, H2O2, ClO-) 3. COMPLEMENT COMPLEMENT A SYSTEM OF ~ 30 SERUM AND MEMBRANE PROTEINS A PART OF „NONSPECIFIC“ MECHANISMS: ALTERNATIVE PATHWAY OF ACTIVATION A PART OF ANTIGEN-SPECIFIC (ANTIBODY-BASED) EFFECTOR MECHANISMS: „CLASSICAL“ PATHWAY OF ACTIVATION BASIC SERUM COMPONENTS C1 (q, r, s) C5 C2 C6 C3 C7 C4 C8 Factor B C9 Factor D C1 – C4, B, D - specific proteases cleaving further components of the complement cascade PROTECTION OF SELF CELLS FROM COMPLEMENT Membrane proteins interfering with the complement cascade on different levels: - BREAKDOWN OF C3-CONVERTASE - CLEAVAGE OF C3b - BLOCKING OF C9 POLYMERIZATION (CD59) ABSENCE OF CD59 – SPONTANEOUS ERYTHROCYTE LYSIS, HEMOGLOBINURIA (PNH) 4. INFLAMMATION INFLAMMATION A set of physiological reactions to damage of tissue integrity, leading to protection against infection, localization and restriction of the damaged site and finally to healing. MANIFESTATIONS OF LOCAL INFLAMMATION reddening (rubor) swelling (tumor), pain (dolor) increased local temperature (calor) acute, chronic (pathologic) Characteristics of local inflammation Signals - degranulated tissue mast cells and phagocytes, molecules liberated from damaged cells increased blood vessel permeability increased endothelial adhesivity, trapping of phagocytes, lymphocytes, penetration into tissues activation of coagulation, fibrinolytic and complement systems effects on nerve endings (pain) temperature regulation changes (mediators - pyrogens) SYSTEMIC RESPONSE TO INFLAMMATION fever (stimulation of hypothalamic thermoregulation center by inflammatory cytokines - TNF, IL-1 a IFN-) septic shock anaphylactic shock expression of heat shock proteins production of serum acute phase proteins (CRP, SAP, C3 a C4 opsonins). leukocytosis REPARATION OF THE DAMAGED TISSUE Elimination of damaged cells by phagocytes (macrophages) activation of fibroplastic mechanisms activation of angiogenesis regeneration and remodeling of tissues