* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nonspecific Immunity
Herd immunity wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Anti-nuclear antibody wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Immunocontraception wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
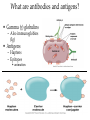
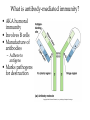
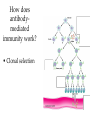
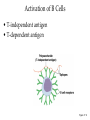
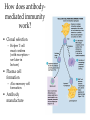
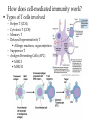
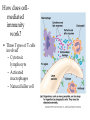
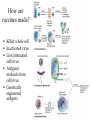
Specific Immunity What is specific immunity? • Third line of defense • Pathogen specific • Involves antigens and antibodies What are B- and T-cells? • Both start in marrow • T cells – Matures in _____ – Kill infected/cancerous cells – Helper, cytotoxic • B cells – Matures in ______ – Become plasma cells – Produce antibodies What are antibodies and antigens? • Gamma () globulins – Also immunoglobins (Ig) • Antigens – Haptens – Epitopes • animation The Two Types of Specific Immunity What is antibody-mediated immunity? • AKA humoral immunity • Involves B cells • Manufacture of antibodies – Adhere to antigens • Marks pathogens for destruction What types of antibodies are there? • IgA • IgG • Ig M • IgE • IgD How does antibodymediated immunity work? • Clonal selection Activation of B Cells • T-independent antigen • T-dependent antigen Figure 17.6 How does antibodymediated immunity work? • Clonal selection – Helper T cell must confirm (with exception— see later in lecture) • Plasma cell formation – Also memory cell formation • Antibody manufacture How do antibodies work to protect me? • Bind with antigen • Possible outcomes – Opsonization – Agglutination – Complement activation – Neutralizatio n How does cell-mediated immunity work? • Types of T cells involved – – – – Helper T (CD4) Cytotoxic T (CD8) Memory T Delayed hypersensitivity T • Allergic reactions, organ rejection – Suppressor T – Antigen Presenting Cells (APC) • MHC-I • MHC-II Antigen-Presenting Cells • Digest antigen • Ag fragments on APC surface with MHC – B cells – Dendritic Cells Activated macrophages: Macrophages stimulated by ingesting Ag or by cytokines Figure 17.12 How does cellmediated immunity work? • Three Types of T cells involved – Cytotoxic lymphocyte – Activated macrophages – Natural killer cell How does cell-mediated immunity work? • All players How does I become immune to a pathogen? • Acquired immunity – Natural • Active • Passive – Artificial • Active • passive Do antibodies stay around forever? • Nearly so! • Primary vs. secondary immune response What are monoclonal antibodies? • Use cancerous plasma cells – Myeloma – Hybridoma : cancerous + normal B cells together – animation How are vaccines made? • Killed whole cell • Inactivated virus • Live/attenuated cell/virus • Antigenic molecule from cell/virus • Genetically engineered antigens Figure 17.18