* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download IgM - Akademik Ciamik 2010
Herd immunity wikipedia , lookup
Social immunity wikipedia , lookup
Sjögren syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Complement system wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Anti-nuclear antibody wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Immunocontraception wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
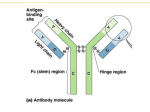
IMMUNODIAGNOSTIC Anna Tjandrawati Clinical Pathology Department Medical Faculty Padjadjaran University Dr Hasan Sadikin General Hosptital Bandung THE COMPONENT OF IMMUNITY INNATE/NATURAL/NON SPECIFIC IMMUNITY: • Normal flora ADAPTIVE/ACQUIRED/SPECIFIC IMMUNITY: Lymphocytes • Anatomic barriers • Inflammation (complement) • Phagocytic cells HUMORAL: CELLULLAR: B lymphocytes T lymphocytescells Plasma cells Lymphokines Antibody ANTIBODIES/IMMUNOGLOBULINS Proteins produced by plasma cells and secreted into body fluids in response to antigen exposure CLASSES OF IMMUNOGLOBULINS IgG:Long lasting immunity, crosses the placenta IgM:First response antibody IgA:Present in secretions IgD:Functions unknown IgE: Allergic reactions IMMUNE RESPONSE Primary Antibody response: • First exposure to ag • IgM appears 3-5 days, increased and then drops over a few weeks-months • IgG detectable 1-2 weeks , increased and decreases over a period of time Secondary Antibody response/ Anamnestic response: • After reexposure to ag • Antibody production increases rapidly • IgG increase in 2 – 3 days and increases higher levels than primary response and remains detectable for months or years PRIMARY AND SECONDARY Ab IMMUNE RESPONSE A Healthy immune system is fundamental to overall good health Diseases involving the immune system Immunocompetent Immunocompromised Overactive/misdirected Acquired: Inherited: Hypersensitivities immunosupression Chromosomal, gene Autoimmune disease drugs, microorganism TYPES OF IMMUNOLOGICAL TESTS Tests of immune function: Tests based on Ag-ab reaction: • CD4, CD8 The presence of an ab to a defined ag depends on the immune response of the patients • Quantitation of Ig subgroup • Tests of leucocyte function • Allergy tests Ab detection (qualitative/quantitative) is used to evaluate N or AbN immune responses IMMUNODIAGNOSTIC Clinical Laboratory Methods for Detection of Antigens(Ag) and Antibodies(Ab) Antigen-antibody interactions underlie many immunological technique, in which the high specificity of the ab is used to identify,isolate or quantify a particular ag The technique can identify ag or ab The classical illustration of ag-ab reaction in-vitro is THE PRECIPITIN REACTION Antibody excess zone: The amount of Ag is insufficient to react with and precipitate all the ab present, thus free ab can be detected in the supernatant (PROZONE EFFECT) Equivalence zone: The added ag is sufficient to combine with and precipitate all the ab present and neither free ag nor ab can be detected in the supernatant Antigen excess zone: The amount of ag exceeds that required to bind all the ab and this leads to a reduction in the amount of ab precipitated. This falls is due to the formation of soluble ag-ab complex by the excess ag Testing methods that depend on formation of immune complex Immunodiffusion Immunodiffusion (ID) is the simple technique by which ag and abs are placed in separate wells within a semisolid medium (agar) then allowed to mix through the medium by diffusion When a zone of equivalence is reached, a line of precipitation occurs Eg. Total Ig G, total IgM and total IgA Precipitin reaction in gels: immuno-double diffusion-Antibody binding Single radial immunodiffusion Agglutination Agglutination assay that test for the presence of an ab depend on the availability of a particle that is coated with the appropriate ag. The particle can be an RBC (hemaglutination), synthetic particle (latex agglutination) and can be seen in the tube, microtitres well or simple glass slide. AGGLUTINATION test The antibody is mixed with the particulate antigen and a positive test is indicated by the agglutination of the particulate antigen. + Agglutination Latex agglutination RBC/Haemagglutination E.g : E.g: • RA factor * ABO Blood typing • Pregnancy test * TPHA • CRP • ASLO Latex Agglutination for Rheumatoid factor RA/ are autoantibodies, usually of the IgM class, directed agaist human IgG Principle the test: Latex particle are coated with specially treated human IgG. When serum containing RF is mixed with the IgG coated latex particle, the RF bind to the IgG and cause agglutination of the particle ELISA(Enzyme-linked immunoassay) The ab or ag is fixed to a surface, such as a well or microtiter plate or plastic bead. The test sample is applied and bound material is detected by secondary, enzymatically labeled antibody enzym + substrates a colored product Spectrophotometer E.g: Anti CMV IgM, Anti Rubella IgG,Anti HAV, Anti HCV Tumor marker, Hormon Ab/Ag + secondary enzymatically labeled antibody (conjugate) + substrate product (chromogen) . IMMUNOCHROMATOGRAPHY •RAPID •EASY TO PERFORM • LIMITED SENSITIVITY & SPECIFICITY Assay Principle Membrane with Immobilised Antibodies Add 10µL bloodline or serum • IgM of capture • IgG capture line • Control Line Add 2 drops of running buffer Blood Separation Device Wicking Material 15 min Cassette Enclosure Absorbent Pad Colloidal Gold Pad • Flavivirus specific MAb conjugated to gold colloid • Dengue 1-4 Recombinant Antigens Release of Serum Components Release of Assay Reagents Backing Sheet IgG Capture Line Antibody Complexing Control Line IgM Capture Line PROCEDURE Immunohistochemical methods INDIRECT Immunofluorescence Assay (IFA) The specific ag conjugated to the cells or tissues and the patient serum incubated with the cells. Unbound ab removed by washing, and the specifically bound ab are visualized with fluorescently labeled anti-Ig antisera. When observed in the fluorescence microscope againts a dark background, fluorescent labeled anti-Ig antisera bound specifically to agab complex can be visualized by their bright color E.g: ANA, anti DS-DNA RESULT OF ANA TEST NEG. ANA POS. CONTROL Homogenous NEG. CONTROL RESULT OF ANA TEST POS. ANA Homogenous POS. CONTROL Homogenous NEG. CONTROL RESULT OF ANA TEST POS. ANA Nucleolar POS. CONTROL Nucleolar NEG. CONTROL