* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download learning and memory
Cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Educational psychology wikipedia , lookup
Behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Psychophysics wikipedia , lookup
Learning theory (education) wikipedia , lookup
Psychological behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
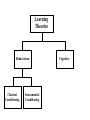
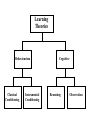
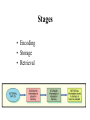
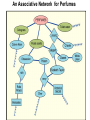
Learning and Memory What is Learning? A change in Behaviour caused by experience. What is Consumer learning? From a marketer’s perspective learning becomes teaching Learning Theories Behaviorism Classical Conditioning Instrumental Conditioning Cognitive Classical Conditioning learning occurs when a stimulus (unconditioned stimulus) elicits a response (unconditioned response) that is paired with another stimulus (conditioned stimulus) that initially does not elicit a response on its own, but will cause a similar response (conditioned response) over time because of its association with the first stimulus. Ivan Pavlov’s Classic Experiment Before Conditioning UCS (food in mouth) UCR (salivation) During Conditioning Neutral stimulus (tone) No salivation After Conditioning UCS (food in mouth) Neutral stimulus (tone) Slide 10 UCR (salivation) CS (tone) CR (salivation) The bears (UCS) generate positive feelings (UCR) towards them Coke (CS) is associated with the positive feelings that. Later you have a positive feeling towards coke (CR) (Coke, before conditioning does not elicit a warm feeling response) The goal of advertisers is to get the exposed person at the grocery store to associate the positive feeling they had for the ad with the product What feelings are associated with the Disney logo? Brand Equity Instrumental or Operant Conditioning B.F. Skinner Positive Reinforcement Negative Reinforcement Punishment Negative reinforcement Reinforcements Schedules Interval Fixed-Interval Reinforcement Variable-Interval Reinforcement Ratio Fixed-Ratio Reinforcement Variable-Ratio Reinforcement Learning Theories Behaviourism Classical Conditioning Instrumental Conditioning Cognitive Reasoning Observation COGNITIVE LEARNING THEORY • Observational Learning • Reasoning Applications of Cognitive Learning Principles • Modelling The Role of Memory in Learning Stages • Encoding • Storage • Retrieval An Associative Network for Perfumes Draw an associative network for Pepsi Things to consider might include: • specific brands • a celebrity identified with Pepsi • related activities • related products • where purchased • packaging • attributes • concepts • feelings “Every time I learn something new, it pushes some old stuff out of my brain” Forgetting Recognition Versus Recall • Recognition i.e. remembering when shown •Recall: try and remember without stimulus 1. Zoom Zoom Zoom 2. Just for the fun of it Mazda Diet Coke 3. Grab Life By The Horns Dodge 4. Driven Nissan 5. Taking care of business Office Depot 6. The best a man can get." Gillette 7. The ultimate driving machine BMW 8. Engineered to be great cars 10. No More Tears Chrysler Visa J & J Baby Shampoo 11. You've Got Questions, We've Got Answers Radio shack Maxwell House 9. It's everywhere you want to be 12. Good to the last drop Advertising Recall as function of timing and number of exposures (Zielske 1959) 70 1 exposure/ week for 13 weeks 60 50 13 exposures at 4-week intervals 40 % 30 20 10 0 25 week of the year 50 How Can Marketers improve Memory retention? Repetition • Repetition of a central theme with some variation • KISS • how many times a consumer should be exposed to an ad before the advertising message is effective. Meaningful or more vivid material Material presented first (primacy) or last (recency) is better retained than material presented in the middle