* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download THE AMERICAN CIVIL WAR - This area is password protected [401]
Battle of Appomattox Station wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Wilson's Creek wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Shiloh wikipedia , lookup
Texas in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Cavalry in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Island Number Ten wikipedia , lookup
Blockade runners of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
List of American Civil War generals wikipedia , lookup
Gettysburg Address wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Sumter wikipedia , lookup
East Tennessee bridge burnings wikipedia , lookup
Battle of New Bern wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Lewis's Farm wikipedia , lookup
Fort Fisher wikipedia , lookup
Fort Sumter wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Namozine Church wikipedia , lookup
Baltimore riot of 1861 wikipedia , lookup
First Battle of Bull Run wikipedia , lookup
Economy of the Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Pacific Coast Theater of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Radical Republican wikipedia , lookup
Capture of New Orleans wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Reconstruction era wikipedia , lookup
Anaconda Plan wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Pillow wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Lost Cause of the Confederacy wikipedia , lookup
Confederate privateer wikipedia , lookup
Conclusion of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
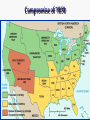
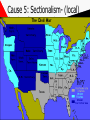
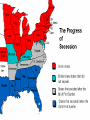
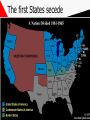
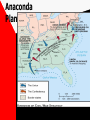
THE AMERICAN CIVIL WAR 1861-1865 This Powerpoint is hosted on www.worldofteaching.com Please visit for 100’s more free powerpoints Warm- UP 1. Complete “ A Tree with three Branches” exercise. 2. Complete “You get your Bill Passed” exercise. SWBAT: • Identify and examine the functions of the Executive, Judicial and Legislative branches of the U.S. government which are defined in the U.S. Constitution. • Complete a Civil War assessment in an effort to determine what was learned. • Identify key peoples and events while determining some key factors that caused the American Civil War. The Civil War: Union vs Confederacy Warm-up (Second Lesson) Complete SkillBuilder: Interpreting Graphs “Northern and Southern Resources”, questions 1 and 2, page 339. Warm-up review Q: Which side, north of south, had the advantage in terms of industrial production? A: North, graphs (Blue = North) advantage in every category (Military/Population) Q: What do the overall data suggest about the eventual outcome? A: North may win an easy victory. (Not true) SWBAT: • Identify nationalism as a key cause of war • Analyze the weakness of the articles of confederation. • Examine slavery and societal differences as a cause of war. Cause #1 (Representation) n.p.o. South (Anti- Federalists) • A. Less people/less representation (10 million) • B. Difficult to pass legislation on tariffs & taxes because of limited representation in government • C. Supported Articles of Confederation North (Federalists) • A. Held a population advantage (22 million) • B. Held an advantage in proposing and passing laws. • C. More representation in the House of Representatives. • D. Supported U.S. Constitution Cause #2 (Nationalism) N.P.O Southern Nationalism • Extreme devotion to the interest and culture of one’s nation • South- Articles of confederation • Agricultural Society • Pro-slavery Northern Nationalism • Extreme devotion to the interest and culture of one’s nation. • North- U.S. Constitution • Industrialized Society • Antislavery Articles Quiz • List 5 weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation. • Draw logic from your studies of articles 1,2,& 3 of the U.S. Constitution to compare/contrast strengths and weaknesses. Use this logic to answer the question above. Weakness of the Articles Congress • Congress could not enact and collect taxes • Congress could not regulate interstate or foreign trade • Regardless of population, each state had one vote in congress • 9 of 13 states needed to agree to pass any law Balance of power? • Articles could be amended only if all states approved • No executive branch • No national court system for legal disputes • 13 national states that lacked national unity. Background Causes for War Quiz to War causes part one 1. List the dividing points between the north & south. (You may bullet) 2. Who invented the Cotton Gin 3. Of all the causes discussed: representation, nationalism, economic exploitation and slavery; which do you find was the greatest cause? Why? SWBAT: Warm –Up A 1. Identify and examine the US Electoral college. 2. Analyze how this process lead to secession 3. Debate causes of civil war 4. Discuss election of Lincoln Read “How the President is elected” packet. Do not answer the questions until after the video. 1860 Election Results Warm- Up (9/21/12) • Complete Geography Skill Builder “The Underground Railroad”, questions 1-3, page 313. • Take Alma Mater test SWBAT: Determine the most important cause for the start of the civil war by participating in a in-class debate. Electoral College WRK Sheet q1. attempt to balance power between large & small states q2. electors caste votes for the president based on the popular vote; nj state officials choose members of the electoral college q3. based from the popular vote of the people, decide the American president. Yes, but has only happened twice q4. 538, based from state districts, nj 14, population based plus senators q5. 270 needed for victory, it will be decided by the house. Yes Thomas Jefferson (1801) , John Quincy Adams, (1825) q6. Twice, Compromise of 1876 (Hayes/Tilden) & Gore/Bush 2000 q7. balance of power, equal representation, responsible elections q8. smaller states have less voting power, larger populated states have more political authority. Electoral College • electoral college • Causes Part 2 • Answer the pbs worksheet after the video. Work in groups of four when completing the packet. Classwork grade. CAUSE #3? • Election of Lincoln • Southern States felt they were bullied by the North when he was elected • (expansionism)-A nation's practice or policy of territorial or economic expansion. Abolitionism Abolitionists • Frederick Douglas was the editor of an abolitionist newspaper. Harriet Tubman • Helped slaves escape via the Underground Railroad. John Brown • He and his sons brutally murdered 5 slave masters in Kansas. (1858) • Tried to incite a slave revolt Cause 4: slavery Compromise of 1850 Harriet Beecher Stowe 1811 - 1896 So this is the lady who started the Civil War. -- Abraham Lincoln Uncle Tom’s Cabin 1852 Sold 300,000 copies in the first year. 2 million in a decade! Cause 5: Sectionalism- (local) Sectionalismexcessive ddexcessive kdkdExcessive devotion to local interests and customs. oExcessive devotion to local interests and customs. Sectionalism • Excessive regard for sectional or local interests, regional or local spirit; prejudice • Southerners banned together • Northerners banned together • Moved into sections based upon beliefs 6th Cause Economy • • • • Sothern economy $122 million after production Northern economy $155 Billion after production Civil War (1861-1865) Causes • Representation • Nationalism • Election of Lincoln • Slavery • Sectionalism • Economic explotation Debate • Review rubric • In your group, create and opening, supporting and closing paragraph. • Concept: Debate why your cause was the most significant cause of the American Civil War. (Use your notes as a resource) In- Class Debate Warm-Up • Meet in your groups for 10 minutes to organize your opening statements • Review debate rubric • Be sure to review Debating: Tips, Tricks and Advice • Review define topic & Show team split (especially) Avoid • Reading from paper, remember “reference don’t read” • Slow Down- emphasize your point • Elaborate, use data and stats to support your position • debate tips • Rebuttal Presidential Election Warm –up / SWBAT: • Read the Examiner.com article about the first of three presidential debates. Divide policies on a piece of loose leaf • Choose a political side based from data learned from the article & video. • Debate as a supporter of President Obama or Mitt Romney (last 30 of class) Data • Rasmussen Report • • • • • • • Debate Education Taxes Military China Federal vs. state Health Care/Obama Care Civil War Begins Warm-Up • Read and answer questions from Abraham Lincoln’s famous Gettysburg Address • 15 minutes SWBAT: • Analyze the Gettysburg address and determine its relation to the theme of war. • Examine the first shots fired in the Civil war; what would become Lincoln’s dilemma? • View Glory in an effort to visualize the Civil War The Gettysburg Address • November 19th, 1863 • Q1: 1776, Declaration of Independence, “All men are created Equal” • Q2: A nation can long endure a bloddy Civil War • Q3: Men Shall not die in vain rather a birth of a new nation; for the people by the people • Q4: World will little note; nor remember The war begins - the firing on Fort Sumter Fort Sumter: April 12, 1861 Fort Sumter April 12th, 1861 • Prior to the fall of Fort Sumter; confederate soldiers were taking over courthouses, post offices and forts. • Confederates demanded Fort Sumter; a union fort in Charleston, South Carolina. • Lincoln decides not to use navy to put down rebellion; put the ball in Jefferson Davis’ court! Fort Sumter Fort Sumter th April 12 , 1861 • 4am, April 12th, Jefferson Davis orders the attack on the Union Fort. • Jefferson Davis looks like the aggressor of war; Lincoln avoids aggression toward the south and keeps peace with Northern Republicans • Confederates fire 4,000 rounds before Union Major Robert Anderson surrendered. The first States secede Advantages of the Union (north)? • Union had double the population • Double the railroads • 5 times as many factories Confederate (Rebel) advantages (South) • Confederates had the best generals • Defending is always easier than attacking • Farmers fight better than factory workers First Major Battle- (Bull Run) • July 21st, 1861; 3 months after Fort Sumter fell to the Confederacy. • Location, Virginia; 25 miles from confederate capital of Richmond. • Union General, Irvin McDowell • Confederate General, Thomas J. Jackson (Stonewall Jackson) • Seesaw affair that lead to a Confederate Victory (C= 2K) (U= 3K) Quiz #1 / Battle of Antietam Warm –up • Warm –up: Look over section 1, chapter 11 or review notes. • Take Quiz SWBAT: • Complete quiz recalling important information while analyzing key battles • Analyze key issues, events, and personalities of the Civil War period • Discuss how common and shared America Civic culture is based on commitment to central ideas in founding-era documents Glory & the Battle of Antietam • Glory • Battle of AntietamSharpsburg, Maryland, September 17th, 1862 • Antietam- bloodiest day in Civil War History • 26,000 casualties • Victory for the Union; Confederacy retreated back to Virginia • Impact- tide begins to swing Union & Confederate Strategies • Warm –up • Students should complete Geography Skillbuilder, questions 1 & 2, page 340 of the text SWBAT: • Analyze the strategies of both the Union & confederate army. • Analyze key issues, events, and personalities of the Civil War period Anaconda Plan Union & Confederate Strategies • Union- (Anaconda Plan) • Blockade Southern ports • Riverboats and armies would move down the Mississippi thus cutting the rebels in half • Capture Richmond, • Confederate • Play a defensive strategy however when given an opportunity, the Rebels shall strike in the North • Anaconda Plan (Union) Group Work Assignment • Throughout the text or using your device; survey the battles of the Civil War. • Determine if the battle fell under the Confederate plan or Union plan • • • • Example Bull Run July 21st, 1861 Goal: Union army to seize the confederate capital, Richmond, VA • Victor, Confederate • Anaconda Plan Second Class Debate • Warm-up • Report the who, what, when, where, why and in three sentences write the potential impact of the outcome of the election. • SWBAT: • Create opening statements and present them extemporaneously • Engage in a debate supporting either Governor Romney or President Obama Second Class Debate Procedure • Review your hmk for the debate; look over fact sheet warm-up. • Report the who, what, when, where and why of the yahoo article • Choose a side; Romney, Obama, or Independent. • Use materials from your binder, warmup or device when assisting you in preparing for the debate. • Move to debate procedures. • Foreign Policy Trump/ Turning Point of the War • Warm up • View trump video and write your opinion on the subject on a loose leaf piece of paper • Trump • Obama • Lincolns Army of the Potomac vs the Army of Northern Virginia. • Battles of • Gettysburg • Battles for Atlanta • Appomattox Civil War • SWBAT: • Analyze how media and political jargon can effect voters • Determine the turning point, and conclusion of the civil War Procedure: Trump Video Gettysburg Lincoln’s Army of the Potomac vs. the Army of Northern Virginia Group research and Presentations Conclusion Of War Procedure: Test next class • Warm- up • Read and answer the concept questions based from the article on Wilmer Mclean • Teacher Presentation • Group Research and Discovery • SWBAT: • Compare/Contrast the two turning points of the Civil War • Analyze the causes for General Lee’s surrender to General Grant at Appomattox, VA Jeopardy Knowledge • Q: Where was Wilmer Mclean living at the start of the civil war and why did he move? • Q: What was his occupation during the war? • Q: What is most interesting about his life and how is it linked to the Civil War? Gettysburg – The Turning Point • July 1st through July 3rd,1863 • Victor Union • Union losses 23,000 • Confederate losses 28,000 • Concept – Last time the South would invade the north • Gettysburg Siege of Vicksburg • May 19th, 1863 • Confederate City of Vicksburg, Mississippi surrenders on July 4th, 1863 • Union Victory • Concept: Union took control of Mississippi river; cut Confederates in half • Vicksburg Campaign Road to Appomattox • Total War- Union General Grant Commander of the military division of the Mississippi, William T. Sherman; turned the fight on the civilians, not just the army and confederate government. • Grants Goalimmobilize army of Northern Virginia • Sherman's Goal- raid Georgia, move up through the Carolinas and meet Grant in Virginia Road to Appomattox • May to June of 1864Battles of Wilderness, Spotsylvania and Petersburg • Union losses 60,000 • Confederate losses 32,000 • Concept- Union could afford losses/ More men to spare • Grants total war successful • September 1864Commander Sherman burns down nearly all of Atlanta • December- Takes Savannah, GA • 1865- South Carolinaburned every house in its path until shermans army reached North Carolina • Sherman's total war Appomattox • April, 9th 1865 • Based from Grant & Sherman's total war theories; Lee & the Confederacy was forced to surrender • Appomattox Group Assignment • Complete Geography skill builders on pages 358, 361, & 363. • Why did Davis/Lee agree to attack at Gettysburg? • What did the defeat at Gettysburg symbolize? • Why was Vicksburg vital to the south? • Compare Gettysburg and Vicksburg; which was a bigger factor as the turning point of the war? • Describe total war and why it was successful for the North First metal ships in world! 1863 Emancipation Proclamation • It freed the slaves only in states that have seceded from the Union. • It did not free slaves in border states. • 1863 • Emancipation = freedom Gettysburg – turning point • Gettysburg is the largest battle in the history of the Western hemisphere. • Over 100, 000 people died in 3 days. • It was the last time the South invaded the North. Gettysburg Address • that from these honored dead we take increased devotion to that cause for which they gave the last full measure of devotion -- that we here highly resolve that these dead shall not have died in vain -- that this nation, under God, shall have a new birth of freedom -- and that government of the people, by the people, for the people, shall not perish from the earth. » Abe Lincoln Technology made Civil War . . . The Monitor More efficient and deadly Vicksburg Confederate Dead Over 618,000 military deaths during Civil War. The 54th Regiment attack on Fort Wagner, SC- July 18, 1863 Blacks in the Military William Carney • After the Emancipation Proclamation blacks began to join the Union Army • Initially they were only used for manual labor • Eventually, Blacks saw live combat • 54th regiment out of Massachusetts After four bloody years of civil war, the South was defeated. Civil War ended when Lee surrendered to Grant at APPOMATTOX COURT HOUSE Civil War Test • Open notes and study for 5 minutes. • Q & A with teacher 5 minutes • Take test • Civil War amendments • Notebook check next class • SWBAT: • Complete a test assessing Civil War knowledge • Determine how Lincoln's assassination affected the nation; post Civil war Results of the Civil War? • Reconstruction – time of rebuilding the country after the Civil War Reconstruction Amendments • 13th Amendment – freed slaves Reconstruction Amendments • 14th Amendment – Everyone born in the US is a citizen, due process of law for all citizens. • 15th – Black male suffrage Remember the Reconstruction Amendments this way: Free Citizens Vote! Lincoln is assassinated • Lincoln’s assassination Assassination of Lincoln , April 14th 1865 Who: John Wilkes Booth to assassinate Lincoln George Atzerdot to assassinate V.P. Andrew Johnson Lewis Powell & David Herlod to assassinate Secretary of State William Seward Where: Fords theater, Washington D.C. • Punishment of the killers and conspirators mfk Questions? Reconstruction 1865-1877 Warm-up • Meet in groups & complete assessment questions from last class if you have not done so already. • Review your Civil War test and correct the Wrong answers only; see me with problems or questions SWBAT: • Compare and Contrast Lincoln’s plan and the Radical Republicans plan for reconstruction. • Identify and examine the Radical Republicans • Discuss the South's devious methods of limiting the newly freed slaves rights. Assess • 1. How might reconstruction be different if Lincoln was not assassinated? • 2. What part of the country needed to be rebuilt? why • 3. Punish or Forgive? What would you do to the South? Why • 4. Which amendment banned slavery? Which was a pathway for voting? Lincoln's plan for Reconstruction Lincoln • Lincoln favored a lenient reconstruction policy • Proclamation of amnesty and Reconstruction or 1/10th plan A. Must swear allegiance to the constitution B. 10% of voting population did this; Lincoln would recognize them as a state. C. Lincoln used a pocket Veto Radical Republicans • Thaddeus Stevens- leader • Wade- Davis Bill- Passed by the radicals in response to Lincolns plan A. Congress responsible for reconstruction B. A majority must swear allegiance not 10% C. Fought or held office under the confederacy; not eligible. Johnson’s Plan for Reconstruction Johnson’s Plan • Johnson Concept Questions • What did President Johnson classify his plan as, how was it similar to Lincoln’s plan? • What did Johnson issue the Confederate states? • Did Johnson set harsh or lenient rules on the South? • Who did Johnson target in his plan for reconstruction? Why Reconstruction 1865-1877 Warm-up • Complete Geography Skill builder, page 381, questions 1 and 2 • Reconstruction • What were the success of reconstruction? SWBAT: • Assess the continuing social and political issues following the civil war • Analyze social and political trends in post Reconstruction America Reconstruction Presentations Warm -up • Meet in your groups for 10 minutes; review presentations. • Place all group members names on your rubric, put AB next to absent group members names • Hand-in (after presentation) your research paper • Model of presentation: Intro, thesis idea, conclusion & determination with current event comparison. SWBAT • Assess the continuing social and political issues following the civil war • Analyze social and political trends in post Reconstruction America • Compare past policies and practices to current American Policies and practices Group Discovery Warm-up/ Group Assignment • Read & report the who, what, when, where, why & in 2-3 sentences report the impact Thaddeus Stevens had on reconstruction. • On one piece of paper record the following: Who, what, when, where, why and future American impact. Be prepared to present Each group also analyze page 400. Be prepared to take a stance for a debate next class. • • • • • • • • Group 1Presidential R.-Row 1 Congressional R.- Row 2 Johnson’s impeachment- Row 3 Civil rights set backs (398)-Row 4 Compromise of 1877- Row 5 Emergence of the KKK-Row 6 Give Presentations Create a thesis statement on how the past has impacted today Reconstruction 1865-1877 Warm-up/Procedure • View 60 minutes clip on the senate: Senate • Compare / Contrast 3 ways the senate of today is comparable to the senate during the reconstruction era • Meet in groups of 5 by rows (across/horizontally) to answer the posed question. • Debate procedures/presentations SWBAT • Assess the continuing social and political issues following the civil war • Analyze social and political trends in post Reconstruction America • Compare past policies and practices to current American Policies and practices