* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The CIVIL WAR
Cavalry in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Island Number Ten wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Roanoke Island wikipedia , lookup
Red River Campaign wikipedia , lookup
East Tennessee bridge burnings wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Appomattox Station wikipedia , lookup
Ulysses S. Grant and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Baltimore riot of 1861 wikipedia , lookup
Second Battle of Corinth wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Wilson's Creek wikipedia , lookup
Reconstruction era wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Gaines's Mill wikipedia , lookup
Fort Fisher wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
Anaconda Plan wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Seven Pines wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Shiloh wikipedia , lookup
Battle of New Bern wikipedia , lookup
Lost Cause of the Confederacy wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Western Theater of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Capture of New Orleans wikipedia , lookup
Confederate privateer wikipedia , lookup
Economy of the Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
First Battle of Bull Run wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Lewis's Farm wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Cedar Creek wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Namozine Church wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Pillow wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Conclusion of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
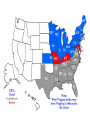
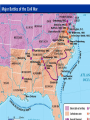
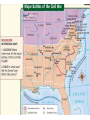
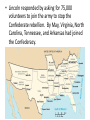
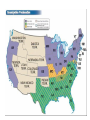
The CIVIL WAR Differences between the North and the South North • Nicknames: Union, North Blue, Yankees • Lots of factories • Lots of railroads and track • Large cities • Larger population • Telegraph wires • Lots of immigrants • UNION South • Nicknames: South, gray, Confederates, rebels, secess • Large farming areas (plantations) • Not many factories • Smaller cities • Not many railroad tracks • Over a million slaves • CONFEDERACY NORTH UNION • BLUE • YANKEES SOUTH CONFEDERACY • GRAY REBELS, SECESS The Civil War boils down to: the tension between the northern and southern states on two basic issues: • #1. Slavery - is the Federal government going to pass laws that eventual end slavery? If so, let’s get out of here • #2. States rights – can the Federal government continue to pass laws that states in the South do not want to follow • If so, the Southern states think it best to quit the United States • IN SUM – We in the South are NOT going to live in a country where the Northern States make rules that we don’t like • On February 4, 1861 representatives from the Southern states met and formed their own country, the Confederate States of America. Their Constitution protected the institution of slavery and the sovereignty of the states. • President Lincoln tried to convince the states in the South who had not joined the Confederacy to remain loyal to the Union. The South also tried to convince these states to join the Confederacy. • The Confederacy also began demanding that the US abandon military bases in the South including Fort Sumter in Charleston harbor South Carolina. • President Lincoln refused to abandon the fort and on April 12, 1861 the Confederates opened fire on the fort. After 34 hours the Union commander surrendered the fort. Label • 1. What advantages did each side have • Lincoln responded by asking for 75,000 volunteers to join the army to stop the Confederate rebellion. By May, Virginia, North Carolina, Tennessee, and Arkansas had joined the Confederacy. Southern Victories • Even though the North enjoyed many advantages the South did have some of their own advantages including better generals, and soldiers who were fighting to defend their homes. • The Union developed a strategy that included blockading Southern ports to keep the South from selling cotton. The Union’s 3 part strategy • 1. Blockade the South’s coast • 2. take the Mississippi top to bottom • 3. Take Richmond, Virginia –the Confederate capital • Another part of their plan was to capture the Confederate capital city of Richmond located less than 100 miles south of Washington D.C. • In the first year of the war the Confederates easily defeat two separate attempts by the Union to capture Richmond. The Union suffered humiliating defeats and people began questioning the war. • In the Western area of fighting the Union was able to defeat a Confederate army at the battle of Shiloh. Another group was also able to capture the city of New Orleans. The Emancipation Proclamation • Lincoln personally viewed slavery as a sin but did not believe that he had any power to abolish it where it existed. • As commander of the armed forces Lincoln believed that he had the power to confiscate any property Southerners owned that could be used against the Union, including slaves. • After the Union victory at the battle of Antietam President Lincoln issued the Emancipation Proclamation. This document freed all of the slaves in areas of the US still in rebellion and also allowed African Americans to join the military. • The Proclamation took effect on January 1, 1863. Many Northerners believed that the Proclamation gave the North a moral advantage. The South viewed this as further proof that the North wanted to destroy their way of life. • By the end of the war over 180,000 African Americans had joined the army and made a significant contribution to the Union victory. The War Turns • In 1863 the war turned in the North’s favor. From July 1st-3rd a Union and Confederate army clashed around the city of Gettysburg, Pennsylvania. • The three day battle was a huge Union victory and it would be the last major offensive fought by the Confederates. • On July 4th a Union army under the command of General Ulysses S. Grant captured the city of Vicksburg on the Mississippi River; this gave the Union complete control of the river cutting the Confederacy in half. • In November 1863, President Lincoln visited Gettysburg to help dedicate a National Cemetery. The speech he gave there known as the Gettysburg Address is one of his most famous speeches. • In March 1864 President Lincoln chose General Grant to command all of the Union armies. Grant pledges to destroy the Confederate armies and never retreat until the job is done. Appomattox • In Virginia, General Grant continued to push General Lee and the Confederates further south and with each battle Lee’s army shrank. • Another Union army under the command of General Sherman cut a wide path of destruction through the South first by capturing Atlanta, Georgia and then continuing on to the city of Savannah. Sherman’s March to the Sea • Burned and destroyed cities, towns, houses, crops, railroads, livestock • On April 9th, 1865 General Lee and his army was forced to surrender to General Grant at Appomattox Court House, Virginia. • On April 14th President Lincoln was assassinated while attending a play with his wife. He was one of the more than 620,000 Americans to die. • About 970,000 Americans were wounded during the war, many wounds required amputation. RECONSTRUCTION 1865-1877 • The period after the Civil War when Congress was making laws about how to put the country back together and • how to allow the southern states back into the union • Congress added the 13th Amendment to the Constitution. This law officially outlawed slavery in the United States. • Next Congress passed the 14th Amendment that said “all persons born or naturalized in the United States” were citizens and therefore entitled to equal protection of the law. • Finally in 1870 the 15th Amendment was added giving people the right to vote regardless of “race, color, or previous condition of servitude”. • Many Southern states passed “black codes” or “Jim Crow laws” to deny African Americans the rights the federal government had given them. It will be 100 years before African Americans will have equal rights in the South. Reconstruction • After the fighting stopped the country went through a period known as Reconstruction, this lasted from 1865 to 1877 and included military occupation of the South. • Congress tried to pass many laws and create organizations to help the newly freed exslaves including the Freedmen’s Bureau and the Civil Rights Act of 1866. • Some people tried to take advantage of the situation. Northerners, known as carpetbaggers, moved to the South to buy cheap land and start businesses. This angered many Southerners. • Many Southerners tried to oppose Northern Reconstruction and limit the rights of African Americans. Others formed vigilante groups including the Ku Klux Klan to restore white supremacy. • Reconstruction ended in 1877 with the South being physically reconstructed but not socially.