* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Attitudes
Introspection illusion wikipedia , lookup
Implicit self-esteem wikipedia , lookup
Albert Bandura wikipedia , lookup
Group dynamics wikipedia , lookup
In-group favoritism wikipedia , lookup
Vested interest (communication theory) wikipedia , lookup
Mnemic neglect wikipedia , lookup
Impression formation wikipedia , lookup
Social tuning wikipedia , lookup
Social perception wikipedia , lookup
Self-perception theory wikipedia , lookup
Attitude (psychology) wikipedia , lookup
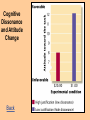
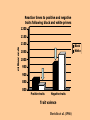
Social Psychology What Is Social Psychology? • how our thoughts, feelings, and behavior are affected by others. The four “A”s • • • • Attitudes Attributions Attraction Authority and Aggression Attitudes • tendency to think, feel, or act positively or negatively toward object • can drive behavior in absence of reward • “neat room, neat kids” • Components: • cognitive • emotional • behavioral When Is Behavior Consistent with Attitude? • • • • thoughts and feelings agree behavioral agrees with subjective norms can do something attitude acquired by direct experience with object Attitudes Formation • • • • • argumentation reinforcement pairing mere exposure observation Change • cognitive dissonance • baby steps • latitudes of acceptance/rejection • sequential • foot in door • door in face • low reactance, no behavioral restrictions Next Elaboration Likelihood Model of Attitude Change Back Cognitive Dissonance and Attitude Change Back What Influences Attitude Change? • Source • trusted • likable • authority • Target • low ego-involvement • no threat to esteem • little experience in defending positions • Message • • • • • • • fear attack unsignalled two-sided rhetorical questions (“Don’t you think that”) well organized examples not statistics redundancy What Are Stereotypes? • perceptions, beliefs, and expectations a person has about members in some group • effects of stereotypes on behavior can be automatic and unconscious Kinds of Stereotypes • auto-stereotype (what the “out group” thinks about themselves) • 50% of blacks in USA have negative stereotypes about themselves • stereotype threat • meta-stereotype (what “in-group” believes the “out-group” is thinking about the “ingroup”) What Is Prejudice? • attitude toward an individual based solely on the person’s group membership • behavioral component is discrimination • often not based on direct experience Why? • prejudice might serve to increases one’s sense of security • prejudice linked with authoritarianism Explicit Prejudice • Blatant Prejudice Items • ‘Would you personally mind or not mind if a suitably qualified aboriginal person was appointed as your boss?’ • “Subtle” Prejudice Items • ‘If aboriginals living would only try harder, they could be as well off as other Canadians’. Explicit and Implicit • Explicit prejudice operates in a conscious mode • self-report • bogus pipeline • Implicit stereotypes are automatic activation of negative traits in memory • priming • IAT Studies of Implicit Stereotyping • • • • • Is it a word or nonword? Categories = black and white Traits = positive and negative White participants Reaction times measured after prime (word ‘black’ vs ‘white’) Reaction times to positive and negative traits following black and white primes 1200 1150 milliseconds 1100 Black White 1050 1000 950 900 850 800 Positive traits Negative traits Trait valence Dovidio et al. (1986) IAT • https://implicit.harvard.edu/implicit/ Nelson Mandela, Long Walk to Freedom • “No one is born hating another person because of the colour of his skin, or his background, or his religion. People must learn to hate, and if they can learn to hate, they can be taught to love . . .”