* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Endocrine System
Sexually dimorphic nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Menstrual cycle wikipedia , lookup
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
Xenoestrogen wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Breast development wikipedia , lookup
Mammary gland wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Endocrine disruptor wikipedia , lookup
Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
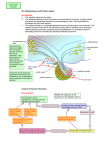
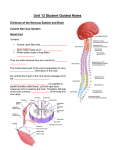
Endocrine System A chemical communication system of the body tissue Types of communication • Gap Junctions: similar to pores that are connected, allow signal molecules to pass from cell to cell • Neurotransmitters • Paracrines (Local hormones): a cell of tissue that stimulates other cells around them with secretion • Hormones: chemical messenger that travels through blood and stimulates target cells Hypothalamus & Pituitary Gland Most important glands in system they have the largest effect on bodily functions They are closely related the pituitary sits on a structure of the hypothalamus. The hypothalamus often acts through the neurohypophysis(posterior pituitary) Hypothalamus Is connected to the third ventricle of the brain It regulates primitive body functions from hydration to sex drive It produces 9 hormones five that stimulate the pituitary, two that inhibits and two that are secreted through the posterior pituitary(oxytocin (OT), antidiuretic hormone (ADH)) Pituitary Gland Made of two parts the adenohypophysis and neurohypophysis Adenohypophysis: also known as the anterior lobe. It has no nervous connection it only responds to hormone interaction Neurohypophysis: posterior lobe. It is only ¼ the size of the anterior lobe. It has nervous connection and is not a true gland it is a collection of different tissue. Contains the hypothalamic stalk. Pituitary Hormones Most of the pituitary hormones are trophic hormones Trophic hormones: stimulates other endocrine organs to secrete their own hormones Axis: the interaction between the hypothalamus, pituitary and a remote endocrine gland. (There are 3 different axis) Posterior Pituitary Lobe It doesn’t produce any hormones it just stores two OT and ADH OT: causes contraction of the uterus darning Birth, contraction of lactation, contraction during sexual response ADH: Controls hydration and vasoconstriction Anterior Lobe Follicle Stimulating Hormone(FSH): targets gonads causes the development of eggs and sperm Luteinizing Hormone(LH): targets gonads in females causes ovulation, in males cause production of testosterone Thyrotropin(TSH): targets thyroid effects metabolism Anterior Lobe Corticotropin(ACTH): targets adrenal cortex effects sugar, fat and protein metabolism (“cortisol”) Prolactin(PRL): targets mammary glands increase in number and production Growth Hormone(GH): targets all tissue is produced 1000 times more than any other hormone promotes mitosis thus tissue growth