* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 13 Student Guided Notes Divisions of the Nervous System and
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
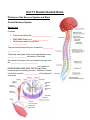
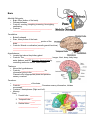
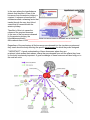
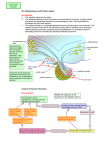
Unit 13 Student Guided Notes Divisions of the Nervous System and Brain Central Nervous System Spinal Cord Contains: Central canal filled with _____________________ ___________. Gray matter made up of ________________. White matter made of long fibers ______________. They are white because they are covered by __________ _____________. The dorsal (back) part of the cord is specialized to carry ___________________ information to the brain. the ventral (front) part of the cord sends messages from the ____________________________. ______________________________ run together in parallel bundles called tracts. Left and right tracts crossover prior to entering the brain. Therefore, left side of the brain controls _______________ of the body and vice versa. Brain Medulla Oblongata: Brain Stem (bottom of the brain). Pathway between _______________________________. Controls: vomiting, coughing, sneezing, hiccoughing, swallowing. Controls: ________________________________ ____________________________. Cerebellum: Butterfly shaped. Rear, lower protion of the brain. ____________________________ portion of the brain. Controls: Muscle co-ordination (smooth graceful motions) ________________________________ _____________________. Hypothalamus: Located just above the pituitary gland. Controls: The ____________________________, hunger, thirst, sleep, body temp, water balance, and BP. Maintains homeostasis by controlling endocrine control, Motor control. Thalamus: Above the hypothalamus Controls: ________________________ for information going to the _________________. Channels info to appropriate place and prevents sensory overload. Cerebrum: __________________ of the brain. Controls: _____________________, Perceives sensory information, Initiates movements. Contains 2 hemispheres (Right and Left). Memory. Parts: 1. Frontal Lobe - ____________ _______________ 2. Temporal Lobe - _________ _________________. 3. Parietal Lobe - ___________ ____________________. 4. Occipital Lobe - Vision. Corpus Callosum Holds the hemispheres of the Cerebrum together. Conducts impulses from one side of the brain to the other. At the center of it all is the Central Nervous System. The CNS is comprised of the Brain and the Spinal Cord. Peripheral Nervous System Is made up of nerves, which are either part of the Somatic or the Autonomic Nervous System. _____________: Contains nerves that control skeletal muscles, joints, and skin. They receive and act on external stimuli. Voluntary Control _________________: Contains nerves that control the smooth muscles of the internal organs and the glands. Automatic, usually without the need for conscious thought. Two Divisions: 1. ______________________ 2. ______________________ Both: Function automatically (involuntary). Serve all internal organs. Have two motor neurons with a ganglion between Adrenal Glands Sudden simultaneous release of ______________________ from all the sympathetic neurons (as in times of fright) has a critical effect. It causes the release of the hormone ________________ from the interior of the __________ ____________ located on top of the kidneys. The noradrenalin and the adrenalin initiate and sustain what is know as the "_______________________" response. They prepare the body to respond to danger in the following ways: 1. ________________________________ ________________________________ ________________________________ 2. ________________________________ ________________________________. ________________________________ 3. Sudden contraction of some muscles to tense the body up for action. Included in this is the contraction of the diaphragm. A scared person will gasp, inhaling suddenly. 4. ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ 5. Increased blood flow to the skeletal muscles so they are more able to act. 6. ______________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________. **Note that acetylcholine is the hormone secreted for the parasympathetic system which causes the opposite conditions (see above) in the body as compared to the sympathetic system** Neuroendocrine Control There is an association between nerve tissue and the body's hormones (endocrine = hormonal). This association is between the ______________________________________ __________________________________. It can be seen that there are _________ lobes of the pituitary gland: an anterior and a posterior lobe. Both of these extend down from the hypothalamus. As blood passes through the _________________, its composition and temperature __________________ various homeostatic responses. Those responses involve the release of hormones. The anterior pituitary releases six major hormones that range in effect from bringing about ___________________________________________________________. The posterior pituitary releases __________ hormones. The mechanism of action is slightly different for the release of the anterior pituitary hormones than it is for the posterior pituitary hormones. In the case where the hypothalamus detects that the effect of one of the hormones from the anterior pituitary is required, it releases a hormone-like substance called a releasing factor that travels through the very short blood vessel that is connected with the anterior pituitary. The effect of this is to cause the release of the required hormone. In the case of the hormones released by the posterior pituitary, the hypothalamus actually _____________ these hormones which it releases into a nerve tract that conducts them to the ____________________________________________. Regardless of the mechanism all the hormones are released into the circulatory system and they travel about the body affecting the specific target organs for which they were designed. **IMPORTANT** A good understanding of these hormones, where they are produced, what causes their release, where they are released from and the effects they have on the body is extremely important. A good knowledge of these hormones will also help you in the next two units.