BIG Dissection Packet
... The frog heart is the only organ contained within the coelom which has its own protective covering. This is the pericardium. There are two upper chambers of the heart, the right atrium and the left atrium. The frog heart, however, has only one lower chamber, a single ventricle. In man, the lower hea ...
... The frog heart is the only organ contained within the coelom which has its own protective covering. This is the pericardium. There are two upper chambers of the heart, the right atrium and the left atrium. The frog heart, however, has only one lower chamber, a single ventricle. In man, the lower hea ...
Nervous System II- The Brain, Cranial Nerves & Autonomic
... – In the middle of the hemispheres is the corpus callosum which enables the 2 hemispheres to communicate and share sensory and motor information • Below the corpus callosum in each hemisphere are the lateral ventricles which secrete CSF ...
... – In the middle of the hemispheres is the corpus callosum which enables the 2 hemispheres to communicate and share sensory and motor information • Below the corpus callosum in each hemisphere are the lateral ventricles which secrete CSF ...
Frog Body Parts and Functions
... Functions of the Frog Heart • Right Atrium - Chamber of the frogs heart which receives blood from the sinus venosus. • Left Atrium - The chamber of the heart that receives blood from the lungs. • Pulmonary Veins - The blood vessels that carry blood form the lungs to the left atrium. • Ventricle - C ...
... Functions of the Frog Heart • Right Atrium - Chamber of the frogs heart which receives blood from the sinus venosus. • Left Atrium - The chamber of the heart that receives blood from the lungs. • Pulmonary Veins - The blood vessels that carry blood form the lungs to the left atrium. • Ventricle - C ...
Frog Body Parts and Functions - chatham
... Functions of the Frog Heart • Right Atrium - Chamber of the frogs heart which receives blood from the sinus venosus. • Left Atrium - The chamber of the heart that receives blood from the lungs. • Pulmonary Veins - The blood vessels that carry blood form the lungs to the left atrium. • Ventricle - C ...
... Functions of the Frog Heart • Right Atrium - Chamber of the frogs heart which receives blood from the sinus venosus. • Left Atrium - The chamber of the heart that receives blood from the lungs. • Pulmonary Veins - The blood vessels that carry blood form the lungs to the left atrium. • Ventricle - C ...
Grade 5: The Brain and Nervous System
... books or other information in school or at home). b. The steps to be done to acquire that information. (Note: It may work better if students want to conduct simple experiments for them to do that as part of the Lesson Two, Extend activity.) 3. Divide the tasks among themselves to complete their Lear ...
... books or other information in school or at home). b. The steps to be done to acquire that information. (Note: It may work better if students want to conduct simple experiments for them to do that as part of the Lesson Two, Extend activity.) 3. Divide the tasks among themselves to complete their Lear ...
Boulder Brain Coral
... domed hemispherical structure (IUCN, 2017). Based on conditions including location on reef, as well as geographical location, Colpophyllia natans are slow growing corals, growing, at a rate of roughly 1cm a year. Remarkably, they can live for over 250 years. REPRODUCTION. Colpophyllia can either rep ...
... domed hemispherical structure (IUCN, 2017). Based on conditions including location on reef, as well as geographical location, Colpophyllia natans are slow growing corals, growing, at a rate of roughly 1cm a year. Remarkably, they can live for over 250 years. REPRODUCTION. Colpophyllia can either rep ...
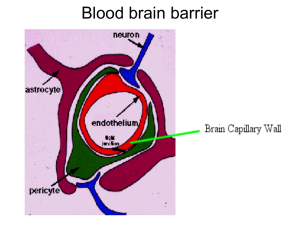
Blood brain barrier - Selam Higher Clinic
... transport systems, including carrier-mediated transporters such as glucose and amino acid carriers; receptor-mediated transcytosis for insulin or transferrin; and blocking of active efflux transporters such as p-glycoprotein. • Strategies for drug delivery behind the BBB include intracerebral implan ...
... transport systems, including carrier-mediated transporters such as glucose and amino acid carriers; receptor-mediated transcytosis for insulin or transferrin; and blocking of active efflux transporters such as p-glycoprotein. • Strategies for drug delivery behind the BBB include intracerebral implan ...
Lecture #14
... – supportive rod that extends most of the animal’s length – extends into the tail – dorsal to the body cavity – flexible to allow for bending but resists compression – composed of large, fluid-filled cells encased in a fairly stiff fibrous tissue – will become the vertebral column in many chordates ...
... – supportive rod that extends most of the animal’s length – extends into the tail – dorsal to the body cavity – flexible to allow for bending but resists compression – composed of large, fluid-filled cells encased in a fairly stiff fibrous tissue – will become the vertebral column in many chordates ...
Handout #12
... •Exhibit a clear trend toward larger brain size. •H. habilis brains are about 30% larger than those of A. africanus. •Males were much larger than females, as shown by the two skulls at far right. The male is pictured on the left. Sexual dimorphism in early Hominid species expressed itself in signifi ...
... •Exhibit a clear trend toward larger brain size. •H. habilis brains are about 30% larger than those of A. africanus. •Males were much larger than females, as shown by the two skulls at far right. The male is pictured on the left. Sexual dimorphism in early Hominid species expressed itself in signifi ...
Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System
... postsynaptic receptors in the brain that normally bind to Ach • The brain responds by ▫ making fewer receptors to which nicotine can bind ▫ altering the pattern of activation of the nicotine receptors (i.e., their sensitivity to neurotransmitters) ...
... postsynaptic receptors in the brain that normally bind to Ach • The brain responds by ▫ making fewer receptors to which nicotine can bind ▫ altering the pattern of activation of the nicotine receptors (i.e., their sensitivity to neurotransmitters) ...
Chapter 8
... The first australopithecine “the missing link” between apes and humans was discovered at a quarry at Taung (Taung Child). As the number of discoveries accumulated, it became clear that the australopithecines were not simply aberrant apes. The acceptance of the australopithecines as hominids requ ...
... The first australopithecine “the missing link” between apes and humans was discovered at a quarry at Taung (Taung Child). As the number of discoveries accumulated, it became clear that the australopithecines were not simply aberrant apes. The acceptance of the australopithecines as hominids requ ...
Early Brain Development: Implications for Early Childhood
... and experience is an intricate, complex and continually interactive process that probably continues throughout life. ...
... and experience is an intricate, complex and continually interactive process that probably continues throughout life. ...
6.3 Central Nervous System
... Functional Anatomy of the Central Nervous System A. The Brain (4 parts) - 2 to 3 pounds, 100 billion neurons, 100 billion+ glial cells 1. Cerebrum (left and right cerebral hemispheres) a. outside of the cerebrum is the Cerebral Cortex, composed of gray matter b. inside is white matter with intersper ...
... Functional Anatomy of the Central Nervous System A. The Brain (4 parts) - 2 to 3 pounds, 100 billion neurons, 100 billion+ glial cells 1. Cerebrum (left and right cerebral hemispheres) a. outside of the cerebrum is the Cerebral Cortex, composed of gray matter b. inside is white matter with intersper ...
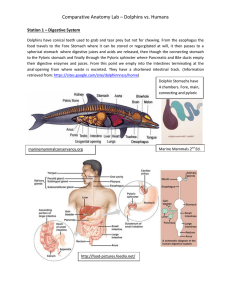
Comparative Anatomy Lab – Dolphins vs. Humans
... Dolphins, like other mammals, need air to survive. Oxygen is one of the main sources of energy. Unlike fish, dolphins have to rise to the surface frequently to breathe. The lungs of dolphins are not significantly larger than other mammal. However, the dolphin lungs contain a lot more air cells than ...
... Dolphins, like other mammals, need air to survive. Oxygen is one of the main sources of energy. Unlike fish, dolphins have to rise to the surface frequently to breathe. The lungs of dolphins are not significantly larger than other mammal. However, the dolphin lungs contain a lot more air cells than ...
Chapter 14 - The Brain and Cranial Nerves (pgs. 461
... Ranges from 750 cc to 2100 cc Contains almost 97% of the body’s neural tissue Average weight about 1.4 kg (3 lb) Six Regions of the Brain Cerebrum ...
... Ranges from 750 cc to 2100 cc Contains almost 97% of the body’s neural tissue Average weight about 1.4 kg (3 lb) Six Regions of the Brain Cerebrum ...
History Of Anatomy - King George`s Medical University
... containing blood For 1500 years his writings were unquestionable . He studied the functions of kidneys & spinal cord. ...
... containing blood For 1500 years his writings were unquestionable . He studied the functions of kidneys & spinal cord. ...
Black Belt Medical Revision
... which cells burn fuels from food to produce energy. As the level of thyroid hormones increases in the bloodstream, so does the speed at which chemical reactions occur in the body. Thyroid hormones also play a key role in bone growth and the development of the brain and nervous system in children. Th ...
... which cells burn fuels from food to produce energy. As the level of thyroid hormones increases in the bloodstream, so does the speed at which chemical reactions occur in the body. Thyroid hormones also play a key role in bone growth and the development of the brain and nervous system in children. Th ...
Physical activity for brain health and fighting
... It is not possible to provide a physical activity formula that is optimum for brain health and function, or for lowering dementia risk. The evidence to date comes from a wide variety of studies. These measure physical activity in different ways, look at different types and intensities of activity, a ...
... It is not possible to provide a physical activity formula that is optimum for brain health and function, or for lowering dementia risk. The evidence to date comes from a wide variety of studies. These measure physical activity in different ways, look at different types and intensities of activity, a ...
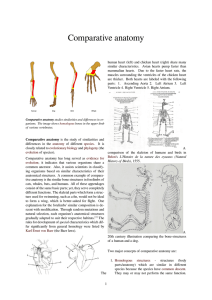
Comparative anatomy
... Comparative anatomy is the study of similarities and differences in the anatomy of different species. It is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny (the A evolution of species). comparison of the skeleton of humans and birds in Comparative anatomy has long served as evidence for Belon's ...
... Comparative anatomy is the study of similarities and differences in the anatomy of different species. It is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny (the A evolution of species). comparison of the skeleton of humans and birds in Comparative anatomy has long served as evidence for Belon's ...
nine animal phyla
... Write three sentences about what sets your subphyla apart from the others. What is special about yours? Is it more or less advanced than the others? ...
... Write three sentences about what sets your subphyla apart from the others. What is special about yours? Is it more or less advanced than the others? ...
The Nervous System
... Voluntary means that we can control what our brain tells our skeletal muscles to do. The autonomic controls involuntary actions. It sends messages back and forth between internal organs and the CNS. Involuntary means automatic - we cannot control what our brain tells our internal organs to do. The a ...
... Voluntary means that we can control what our brain tells our skeletal muscles to do. The autonomic controls involuntary actions. It sends messages back and forth between internal organs and the CNS. Involuntary means automatic - we cannot control what our brain tells our internal organs to do. The a ...
Ch. 10 Neurology
... The brain is surrounded by the meninges, three separate membrane layers. 1. Dura mater (outermost, tough, fibrous layer that protects the brain). 2. Arachnoid (subarachnoid space is filled with CSF). 3. Pia mater (innermost layer; thin, delicate membrane next to the brain that contains many small bl ...
... The brain is surrounded by the meninges, three separate membrane layers. 1. Dura mater (outermost, tough, fibrous layer that protects the brain). 2. Arachnoid (subarachnoid space is filled with CSF). 3. Pia mater (innermost layer; thin, delicate membrane next to the brain that contains many small bl ...
Peripheral Nervous System
... 3. First, carefully remove the dura mater. Be especially careful around the optic chiasma and pituitary gland. 4. Observe the external anatomy. 5. Cut along the longitudinal fissure to view internal anatomy. 6. Use the packet as your guide. Complete the handout and turn it in. ...
... 3. First, carefully remove the dura mater. Be especially careful around the optic chiasma and pituitary gland. 4. Observe the external anatomy. 5. Cut along the longitudinal fissure to view internal anatomy. 6. Use the packet as your guide. Complete the handout and turn it in. ...
Class Notes - Spirit of Health
... especially see this when the tonsils (lymph nodes) have been removed. This causes poor lymphatic drainage of the cerebral areas, leading to poor circulation and elimination within these tissues and to a host of other conditions including dizziness, equilibrium problems and blood pressure issues. F. ...
... especially see this when the tonsils (lymph nodes) have been removed. This causes poor lymphatic drainage of the cerebral areas, leading to poor circulation and elimination within these tissues and to a host of other conditions including dizziness, equilibrium problems and blood pressure issues. F. ...