* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Bio 12 Brain
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
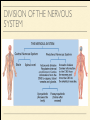
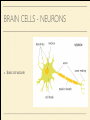
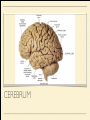
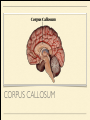
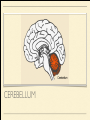
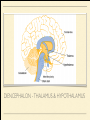
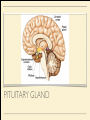
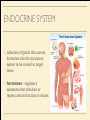
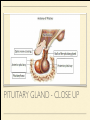
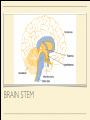
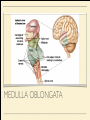
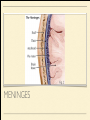
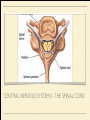
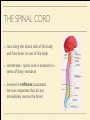
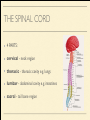
MS. YANG Mar. 12th 2014 SCIENCE & ENGLISH ABOUT ME: CONTACT Site: https://blogs.ubc.ca/biology12 Email: [email protected] BIOLOGICAL TALENT SHOW say your name 3 times and something biologically interesting you can do INTRO TO NERVOUS SYSTEM central nervous system (CNS) brain & spinal cord peripheral nervous system (PNS) nerves (bundles of neurons) that carry info to and from the CNS DIVISION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM VIDEO! http://youtu.be/wlvU5wKqDr8 BRAIN COMPARISON Our brain is the result of millions of years of evolution many similarities within the animal kingdom BRAIN CELLS - NEURONS basic structure: CONNECTION B/W NEURONS SYNAPSE connection between one neuron's axon ending and another's dendrite CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM I - THE BRAIN BRAIN JIGSAW look up the assigned brain part and answer the following: 1. Anatomy - what does it look like 2. Location - where is it in the brain 3. Functions - must be written in a way that you can understand 4. Any related structures - state how they are related/interdependable CEREBRUM CEREBRUM 2 cerebral hemispheres - 85% of total brain volume "highest" level of processing, responsible for: motor activity, sensory perception, consciousness cerebral cortex - outer layer of cerebrum composed of grey matter (neuronal cell bodies, dendrites, synapses) white matter composed of myelinated axons arranged in bundles/tracts - lies below the cortex CORPUS CALLOSUM CORPUS CALLOSUM corpus callosum - dense tissue that holds the two hemispheres of the cerebrum together conducts nerve impulses from one side of the brain to the other, coordinating the two sides CEREBELLUM CEREBELLUM cerebellum - second largest part of brain coordinates movement and balance small, smooth movements (fine motor control) maintains muscle tone (tension) & posture DIENCEPHALON - THALAMUS & HYPOTHALAMUS DIENCEPHALON Thalamus - important relay station for processing/filtering sensory information going to the "higher brain" - cerebrum receiving end of all sensory input and directs information to the correct region of the cerebrum DIENCEPHALON Hypothalamus - fundamental role in regulation of "automatic" bodily functions such as body temperature, hunger, fatigue, sex (regulates homeostasis) produces hormones for the pituitary gland - link to endocrine system (hormones) samples the blood that travels through it and responds through initiation of nervous impulses or causing pituitary gland to release hormones PITUITARY GLAND PITUITARY GLAND small gland with 2 parts: anterior and posterior lobes produces hormones, many of which control the release of hormones from other gland in the body the pituitary gland, along with the hypothalamus, form the neuroendocrine control centre (communication between the nervous and endocrine systems) ENDOCRINE SYSTEM collection of glands that secrete hormones into the circulatory system to be carried to target tissue hormones - regulatory substances that stimulate or repress certain functions in tissues PITUITARY GLAND - CLOSE UP ANTERIOR PITUITARY GLAND anterior pituitary - makes & releases its own hormones releases hormones upon stimulation from hypothalamus hormones - growth hormones, FSH/LH (reproduction), ACTH (stimulates) adrenalin release POSTERIOR PITUITARY posterior pituitary - stores & releases the hormones made in the hypothalamus hormones - oxytocin (stimulates certain smooth muscle contraction), ADH (stimulates kidney to conserve water) CRASH COURSE - HORMONES & THE PITUITARY GLAND https://www.youtube.com/watch? v=WVrlHH14q3o&list=PL3EED4C1D684D3ADF BRAIN STEM BRAIN STEM smallest, oldest and most primitive part of the brain continuous with spinal cord composed of medulla oblongata and pons MEDULLA OBLONGATA BRAIN STEM - MEDULLA OBLONGATA medulla oblongata - closest to the spinal cord, regulation of heartbeat, breathing, blood pressure reflex centres - coughing, sneezing, swallowing contain receptors that are receptive to the conditions of blood (increase in CO2 => inhalation) controls internal organs - unconscious part of brain MENINGES MENINGES meninges - the membranes that surround and protect the CNS 3 layers - dura mater, arachnoid mater, pia mater (outer => inner) CRASH COURSE - THE BRAIN https://www.youtube.com/watch? v=vHrmiy4W9C0&list=UUX6b17PVsYBQ0ip5gyeme-Q CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM II - THE SPINAL CORD THE SPINAL CORD runs along the dorsal side of the body and links brain to rest of the body vertebrates - spinal cord is encased in a series of bony vertebrae involved in reflexes (automatic nervous responses that do not immediately involve the brain) THE SPINAL CORD 4 PARTS: cervical - neck region thoracic - thoracic cavity e.g. lungs lumbar - abdominal cavity e.g. intestines sacral - tail bone region OVER THE BREAK - REVIEW & MAKE SOME ART draw & colour the human brain, labelling the following parts: medulla oblongata hypothalamus corpus callosum cerebrum cerebellum meninges CNS QUIZ - Tuesday, April 1st thalamus pituitary gland