* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Matter Change
Chemical reaction wikipedia , lookup
Photopolymer wikipedia , lookup
Electrolysis of water wikipedia , lookup
Abundance of the chemical elements wikipedia , lookup
Water splitting wikipedia , lookup
Chemical element wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular theory wikipedia , lookup
California Green Chemistry Initiative wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Chemical plant wikipedia , lookup
Chemical industry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical weapon proliferation wikipedia , lookup
Al-Shifa pharmaceutical factory wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical weapon wikipedia , lookup
Vapor–liquid equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Chemistry: A Volatile History wikipedia , lookup
Chemical Corps wikipedia , lookup
Chemical potential wikipedia , lookup
Condensed matter physics wikipedia , lookup
Stoichiometry wikipedia , lookup
Gas chromatography wikipedia , lookup
Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Safety data sheet wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
VX (nerve agent) wikipedia , lookup
Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals wikipedia , lookup
Chemical thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
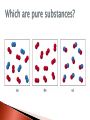
Anything that has mass & take up space Mass = measurement of the amount of matter an object contains Chemistry = the study of matter & the changes that it undergoes Quantitative – numerical information how much how little how big how small Qualitative – descriptive information condition, color, size, shape, odor, texture Let’s Play Physical Properties – a characteristic that can be observed or measured w/out changing the identity of a substance ex. color, odor, taste, hardness, density, melting/boiling points, state of matter States of Matter – the physical forms in which all matter exists on Earth Solid def. shape & volume shape independent of container particles are packed together Liquid def. volume shape depends on container particles can move freely Gas indefinite volume & shape particles move quickly & spread apart Physical Changes – a change that occurs in the physical appearance of a substance, but does not change its identity Ex. melting, boiling, freezing, evaporating, dissolving, condensing breaking, splitting, grinding, cutting, crushing COLOR STATE OF MATTER AT GIVEN TEMPERATURE MELTING POINT BOILING POINT DENSITY SOLUBILITY ELECTRICAL CONDUCTIVITY MALLEABILITY DUCTILITY How easily can it be drawn into a wire? VISCOSITY How susceptible is a liquid to flow? SOLID , LIGUID, GAS (mass per unit volume) Does it conduct or is it an insulator? How easily can it be deformed? 4. Chemical Properties – relates to a substances ability to undergo changes that transform it into a different substance easiest to see when a chemical is reacting Chemical changes – a change that produces matter with a different composition than the original matter ex. burning, rotting, rusting, reacting, cooking, digestion, respiration BURN ROT RUST DECOMPOSE FERMENT EXPLODE CORRODE EVOLUTION OF A GAS FORMATION OF PRECIPITATE (two clear solutions when combined form solid) RELEASE OF ABSORPTION OF ENERGY COLOR CHANGE Let’s Play A combination of 2 or more types of matter Each component keeps its own identity & properties Components are only physically mixed & can be separated using physical means Heterogeneous mixture a mixture in which the substances are not evenly distributed Homogeneous mixture – a mixture or ‘solution’ in which the substances are evenly distributed Phase – used to describe any part of a sample with uniform composition & properties Homogeneous mixture Heterogeneous mixture 1 phase 2 phases ‘Plays’ on differences in physical properties 1. Filtration – a technique that uses a porous barrier to separate a solid from a liquid Can you think of any common applications? 2. Distillation – a technique that can be used to physically separate most homogeneous mixtures based on differences in the boiling points of the substances involved 3. Chromatography – a technique that is used to physically separate the components of a mixture based on the tendency of each component to travel or be drawn across the surface of another material Every sample has same: ◦ characteristic properties ◦ composition Are made of: ◦ one type of atom: element Ex: iron, gold, oxygen ◦ 2 or more types of atoms: compound Ex: salt, sugar, water Simplest form of matter that has its own unique set of properties Can not be separated into simpler substances by physical or chemical means Each element is made up of a single type of atom ex. hydrogen, nitrogen, lead A substance that contains 2 or more elements chemically combined in a fixed proportion Properties are different than the individual elements ex. Glucose (sugar) Glucose – sweet, white solid Carbon – black, tasteless solid Oxygen – colorless, tasteless gas Hydrogen – colorless, tasteless gas Physical methods do not work Recall… Chemical changes – a change that produces matter with a different composition than the original matter Chemical Symbol each element is represented by a oneor two-letter symbol H K Au H2O C6H12O6 Hydrogen Potassium Gold Water Glucose Trends: 1st letter = always capitalized 2nd letter = always lowercase Subscripts = indicate the relative proportions of the elements in a compound The process by which the atoms of one or more substances are rearranged to form different substances Occurrence can be indicated by changes in temperature, color, odor, & physical state Also known as a chemical change Chemical properties can only be observed when a substance undergoes a chemical change The process of photosynthesis is a chemical reaction in which light energy, carbon dioxide and water, are transformed to create glucose and oxygen. The photosynthetic chemical reaction can be shown by writing out the element symbols for each compound. Reactants Products substances to the left of the arrow ‘ingredients’ CO2 and H2O substances to the right of the arrow ‘what is made’ or produced C6H12O6 and O2 How can you tell whether a chemical change has taken place? 1. Transfer of energy Energy may be given off in the form of heat or light 2. Change in color Substances may ‘brown’ Indicators 3. Precipitate A solid that settles out of a liquid mixture 4. Gas production Indicated by the formation of ‘gas bubbles’ During any chemical reaction, the mass of the products is always equal to the mass of the reactants + O2 + CO2 + H2O vapor Conservation of mass also applies to physical changes… 10g of ice 10g of liquid H2O Law of Conservation of Mass In any physical or chemical change, mass is conserved i.e. Mass is neither created or destroyed