* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Gerard `t Hooft
Hydrogen atom wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization group wikipedia , lookup
Quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Scalar field theory wikipedia , lookup
Quantum group wikipedia , lookup
Quantum machine learning wikipedia , lookup
Bohr–Einstein debates wikipedia , lookup
Copenhagen interpretation wikipedia , lookup
Identical particles wikipedia , lookup
Particle in a box wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Orchestrated objective reduction wikipedia , lookup
Double-slit experiment wikipedia , lookup
Quantum entanglement wikipedia , lookup
Matter wave wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization wikipedia , lookup
Many-worlds interpretation wikipedia , lookup
Quantum key distribution wikipedia , lookup
Quantum teleportation wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Interpretations of quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
AdS/CFT correspondence wikipedia , lookup
Wave–particle duality wikipedia , lookup
Bell's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Quantum state wikipedia , lookup
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Symmetry in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Canonical quantization wikipedia , lookup
EPR paradox wikipedia , lookup
Hawking radiation wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
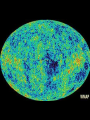
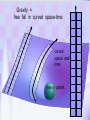
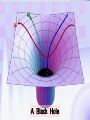
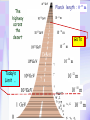
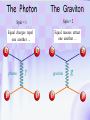
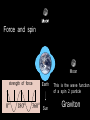
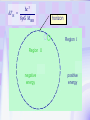
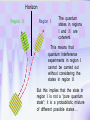
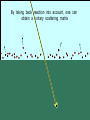
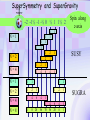
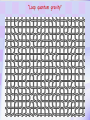
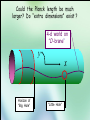
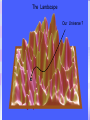
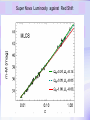
Utrecht University Gerard ’t Hooft Galileo Galilei Colloquium, Pisa, March 3, 2006 Gravity = free fall in curved space-time curved space and time heavy planet A Black Hole Black Hole Universe I “Time” stands still at the horizon Universe II So, one cannot travel from one universe to the other The part of the universe that we know contains about 80 10 particles Only a small fraction of them are of the kind that build up the world that is familiar to us The Universe of the sub-atomic particles Quantum Mechanics 4p / g2 60 Unification x Super Symmetry U (1) ? 50 40 30 SU (5) SU (2) x 20 10 Unification ? SU (3) x 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 log( m) The highway across the desert Planck length :10 35 m 10 33 m 10 30 m GUTs 10 27 m 10 24 m Today’s Limit … 10 21 m 10 18 m 10 15 m The Photon The Graviton Spin = 2 Spin = 1 Equal masses attract one another ... Equal charges repel one another ... P P photon P P graviton P P P g P M1 M 2 Force G 2 R However, mass is energy ... E h/c M 2 c Wavelength 2 Gh 1 Force 2 4 c R Gravity becomes more important at extremely tiny distance scales ! h / 2 1.0546 1034 kg m2 sec -1 G N 6.672 1011 m3 kg -1 sec-2 c 2.99792458 108 m / sec Planck Units LPlanck GN 3 c M Planck c GN TPlanck 1.616 1033 cm 21.8 g GN 5 c 5.39 1044 sec Force and spin Moon Moon strength of force 0o 180o 360o Earth Sun This is the wave function of a spin 2 particle Graviton When gravity becomes strong: super string theory? - space-time fluctuations run out of control: infinities bad understanding of UV region - the definition of time becomes ambiguous: one cannot talk of “the state of the Wheeler – universe at a given time”. DeWitt equ’n? bad understanding of probability and causality - the universe might close into itself, in which case the use of quantum mechanics Statistics of becomes ambiguous. the real universe isn’t closed ... universes ? - notions such as “distance” and “locality” become ambiguous Non-local and what about reduction ? theories ? Where does the gravitational field become as strong as it ever can get ? microscopic black holes kT H hc 3 = 8pG M BH horizon Region I Region II negative energy positive energy The black hole as an information processing machine One bit of information on every 0. 724 10 - 65 cm2 Are black holes just “elementary particles”? Imploding matter Are elementary particles just “black holes”? Hawking particles Black hole “particle” Horizon Region II Region I The quantum states in regions I and II are coherent. This means that quantum interference experiments in region I cannot be carried out without considering the states in region II But this implies that the state in region I is not a “pure quantum state”; it is a probabilistic mixture of different possible states ... Three competing theories: 1. No scattering, but indeed loss of quantum coherence (problem: energy conservation) 2. After explosion by radiation: black hole remnant (problem: infinite degeneracy of the remnants) 3. Information is in the Hawking radiation One must take interactions into account: interaction horizon By taking back reaction into account, one can obtain a unitary scattering matrix b Particles and horizons, the hybrid picture SuperSymmetry and SuperGravity -2 -1½ -1 -½ 0 ½ 1 1½ 2 N=1 1 1 1 2 1 2 1 1 4 6 N=2 N=4 N=1 1 1 N=2 1 2 1 1 4 6 N=4 N=8 1 1 1 1 1 8 28 4 56 1 1 1 2 1 1 4 1 SUSY 1 1 1 2 1 6 4 1 70 56 28 8 1 1 1 4 Spin along z-axis SUGRA “Loop quantum gravity” The SuperString Theory Could the Planck length be much larger? Do “extra dimensions” exist ? 4-d world on “D -brane” y y x Horizon of “Big Hole” “Little Hole” Super Gravity in 11 dimensions Type I Heterotic String SO(32) Open Superstring M - theory Type IIA Closed Superstring Heterotic String E8 x E8 Type IIB Closed Superstring The Landscape Our Universe ? x All degrees of freedom of some section of the universe reside on its BOUNDARY How do we reconcile this with LOCALITY? paradox Unitarity, Causality, ... Thie paradoxical behaviour is indeed reproduced in string / membrane theories ! -- at the expense of locality? -How does Nature process information ? Quantum Mechanics is usually seen as a blessing Quantum Mechanics solves the problem of the UV divergence in thermal radiation (Planck, 1900) But Quantum Mechanics generates new infinity problems of its own at the Planck scale ... Could Quantum Mechanics not be replaced by something better there ? The Cosmological Constant Problem L= stretchability very small g( 1 8 G R) stiffness very large Super Nova Luminosity against Red Shift The cellular automaton How does God produce random numbers ? Could these random numbers be actually created by “ordinary” physical processes at the Planck scale? 33 Determinism at the Planck length (10 cm) Why not ? Simple-minded, “direct” approaches are doomed to fail. Problem that keeps coming up: why is energy always positive ? Energy is related to time. If two systems are compared, both energies must be positive (but both being negative could also be allowed) Modest discovery : such a constraint might come about if the two clocks are allowed to be nonsynchronous (due to grav. fields), while we have the following restriction: if time goes forward in one system, it must also go forward in the other (and vice versa): dt1 0 dt2 What is the true nature of space and time ?