* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Particles & Strings - University of Southampton
Quantum state wikipedia , lookup
Symmetry in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Identical particles wikipedia , lookup
Quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Minimal Supersymmetric Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
Quantum tunnelling wikipedia , lookup
Quantum logic wikipedia , lookup
Casimir effect wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization group wikipedia , lookup
Double-slit experiment wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear structure wikipedia , lookup
Supersymmetry wikipedia , lookup
Higgs mechanism wikipedia , lookup
Eigenstate thermalization hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Relational approach to quantum physics wikipedia , lookup
ATLAS experiment wikipedia , lookup
Compact Muon Solenoid wikipedia , lookup
Atomic nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Canonical quantum gravity wikipedia , lookup
Quantum chromodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Grand Unified Theory wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
AdS/CFT correspondence wikipedia , lookup
Old quantum theory wikipedia , lookup
Future Circular Collider wikipedia , lookup
Quantum gravity wikipedia , lookup
Canonical quantization wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical formulation of the Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization wikipedia , lookup
Scalar field theory wikipedia , lookup
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Theory of everything wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
Quantum vacuum thruster wikipedia , lookup
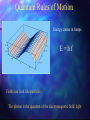
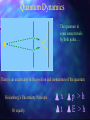
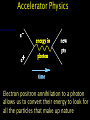
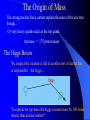
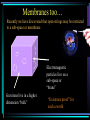
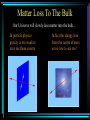
Particles and Strings “The search for a fundamental theory of the building blocks of nature and their interactions” Nick Evans University of Southampton Reality Check! Particles Hard Science & Strings Speculative Mathematically well defined A theory of quantum gravity Experimentally verified Maths rules still up for grabs New experiments - LHC No experimental verification No clear experiment to do! Search for a missing piece – the higgs particle Throws up fascinating possibilities! The Particle World Forces • Electromagnetism • Strong nuclear • Weak nuclear • Gravity Particles Three families (copies) of 2 quarks 1 electron plus their antiparticles 1 neutrinos Relativity The speed of light is the same for any observer This means nothing can travel with light – nothing can reach v=c! E= 1 mc 2 1-v2/c2 Rest mass = energy Space - Time A flash of light causes a spherical wave front even if you move relative to source This only makes sense if space and time mix! * t‘ = x‘= 2 2 2 (1 – v /c ) ( t – v x / c ) 2 2 (1 – v /c ) ( x – v t) Quantum Rules of Motion Energy comes in lumps E=hf Fields can look like particles The photon is the quantum of the electromagnetic field/ light Quantum Dynamics The quantum in some sense travels by both paths…. There is an uncertainty in the position and momentum of the quantum Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principle Or equally x t p >h E >h Dirac’s Legacy Electrons can absorb photons But in relativity observers do not agree on time ordering of events… so can we have What does it mean for an electron to travel backwards in time? We only measure charge… It looks like a +ve charge electron moving forward in time We have discovered anti-particles! Accelerator Physics Electron positron annihilation to a photon allows us to convert their energy to look for all the particles that make up nature The Quantum Vacuum E t >h The vacuum can borrow energy for short periods E = mc 2 The borrowed energy can be used to create particles (You can’t just create an electron because of charge conservation - but can create electron positron pair) The quantum vacuum is a seething mass of particles appearing and disappearing constantly…. How Can You Tell? The “virtual” particle pairs interfere in electron scattering processes. The effective charge seen in two electron scattering depends on the separation of the electrons. The Strong Nuclear Force The strong nuclear force is described by a theory that is similar to electromagnetism… except that the fields carry (colour) charge….. This difference changes the way in which the vacuum is polarized so that… Confinement You can never pull hard enough to liberate a quark from a proton… The Quantum Vacuum Every so often quantum effects create a quark anti-quark pair. The attractive force is so strong that binding energy >> mass energy The vacuum has lower energy if it fills itself with quark antiquark pairs! The vacuum is really full of quark anti-quark pairs with a density 15 3 like that of an atomic nucleus (10 grams/cm ) !! The Proton Mass The quark pairs are responsible for the proton’s mass Interaction energy provides proton mass The Origin of Mass The strong nuclear force cannot explain the mass of the electron though… Or very heavy quarks such as the top quark top mass = 175 proton mass The Higgs Boson We suspect the vacuum is full of another sort of matter that is responsible – the higgs…. To explain the top mass the higgs vacuum must be 100 times denser than nuclear matter!! The Search for the Higgs To find the higgs we must “excite” the vacuum – produce a higgs particle… we collide electrons, protons etc so there is 100 times nuclear energy density in some region…. We haven’t found it so far but… The Large Hadron Collider in Switzerland will switch on in 2008… There are many versions of the “higgs theory” – when we find it we can study its properties in detail…. Quantum Gravity If the vacuum is full of all this stuff shouldn’t we be pulled gravitationally by it? Since it is uniformily distributed there is no net pull (equal space to all sides) But General Relativity says the energy should uniformily curve space-time… the Universe should be the size of a grapefruit!! There’s something big we don’t understand about quantum gravity Gravity is so weak that we’ve never measured it’s effects between individual particles or on distance scales smaller than 1mm! Gravity is different to the other forces – it’s only attractive… In General Relativity this shows up in that gravitational waves have different polarizations to electromagnetic waves What fundamental theory can encompass both types of fields? String Theory String theory unifies gravity and other forces String theory is A quantum theory of gravity.. Is it THE quantum theory of gravity? - entering realm of speculation! What are these strings? We describe them only in terms of a fundamental tension – as for a rubber band T How big are they? A particle of energy E has a wavelength E=hc/l So can probe down to scales of order l…. So far we’re down to 1/1000th size of atomic nucleus… strings could be 10 19 times smaller! Extra Dimensions Surprisingly the mathematics of string theory only makes sense in 9 spatial dimensions and 1 time dimension! A prediction…. But wrong!! Compactification We can imagine a space where directions are curled up We study A string in this space not ALL the strings that make the space…. Why are 6 dimensions compact… by what mechanism? UNKNOWN! The radius must be at least 1000 times smaller than an atomic nucleus! Membranes too… Recently we have discovered that open strings may be restricted to a sub-space or membrane Electromagnetic particles live on a sub-space or “brane” Gravitons live in a higher dimension “bulk” “Existence proof” for such a world Could Our Universe Be A Brane? S U 2 pR The strength of gravity is determined by the number of spatial dimensions (gravitons spread out around mass) F=GMm r2 D=3+1 But…. we don’t know anything about gravity on length scales below 1mm… R could = 1mm… and we wouldn’t know it! If so we’ve miscalculated the strength of gravity (G) – it could become strong in our particle accelerators at any new energy!! Matter Loss To The Bulk Our Universe will slowly lose matter into the bulk… In particle physics gravity is too weak to ever see these events In fact the energy loss from the centre of stars is too low to see too! Other Branes Why should there be only one brane in the higher dimension spacetime? There could be entire Universes only mm away! W S E U N The matter on the other brane will only interact with our world gravitationally – it’s dark matter…. Until we can produce high energy gravitons that are strongly interacting there’s little way to directly probe this idea though Brane Collisions There’s no reason branes should be static in the extra dimensions…. So they could collide! This would be catastrophic! Huge amounts of energy would be dumped into our Universe…. Could that have triggered the currently observed expansion of the Universe??!! Overview • Particle physics has a concise description of matter and forces • The missing element is the higgs that generates mass (plus explanation of why the building blocks are what they are) • Our theories of particles don’t fit with theories of gravity • String Theory is an attempt to construct a sensible theory of both • We are realizing it predicts wild possibilities • Extra dimensions and other Universes • Many exciting possibilities but very hard to experimentally test because gravity is very very weak….