* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Evolution: descent with modification
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Dual inheritance theory wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Group selection wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
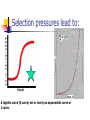
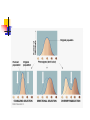
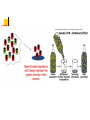
Evolution: Genetic Descent with Modification Before we being…. Evolutionary domains Individuals change, populations evolve Darwin’s journey and those before…. Prior to Darwin, Lamarck “Use/Disuse” 1859 published “On the Origin of the Species” Galapagos Islands-why so critical? Bio-geographic isolationism Gives us a way to determine which species are ancestral and which are derived in order to determine phylogeny leading to cladistics. Phylogeny, the connections between all groups of organisms as understood by ancestor/descendant relationships Cladistics, determining shared, derived traits to determine ancestry and evolutionary relationships 5 Key Observations Darwin made: 1) Organisms have unique traits (diversity) 2) Traits are inheritable 3) Organisms adapt 4) Nature is cruel-natural selection 5) Differential reproduction (not everyone produces the same # of offspring and not all offspring born survive) How do we get genetic change from one generation to the next? Micro-evolutionary process (codical domain) deals with the biological processes that change allele frequency. If there is no change in genes, it is NOT evolution. 5 Ways to get allele frequencies to change: Mutations- missense mutations are point level changes in the DNA. A single mutation can have a large effect, but in many cases, evolutionary change is based on the accumulation of many mutations. Gene flow is any movement of genes from one population of like organisms to another. (emigration and immigration) Sex- which egg and which sperm? Crossing Over- causes changes in gene sequencing which can change phenotype. Genetic Drift – in each generation, some individuals may, just by chance, leave behind a few more. The genes of the next generation will be the genes of the “lucky” individuals, not necessarily the healthier or “better” individuals. So which changes stick around and which ones don’t?? Whichever traits provide a benefit are selected for by nature (economic domain). Natural Selection Is the “chooser” Natural selection helps determine which changes stick around. (Remember 5 ways to get a change). Natural selection is the nonrandom process by which traits are selected for by nature because they provide some survival benefit. If a mutation provides a desirable phenotype, that phenotype produces a higher number of surviving offspring. (More than other phenotypes) For natural selection to be able to choose: There is variation in traits among species. There is heredity of those traits. What is “fitness”? Fitness is how well adapted, strong, sexy and capable an organism is based on its genetics. Those that are at least adequate, in terms of survival, will leave offspring. If not, no round two for you! This is why we maintain variation in any given species. Good enough clears the biological bar! Nature provides a “Normal trait” distribution in a population, reflecting adequate individuals: But why can’t we be less than adequate?? Nature’s cruel!! Limited resources means that organisms compete with themselves and others for survival. Because of this, nature weeds out inadequate individuals from the group so that only the most able produce diverse offspring. The diversity in each generation (descent with modification) allows each generation to try and produce “better” offspring in terms of survival. But even those offspring won’t all live and reproduce The selection process starts early for many species…. Selection pressures lead to: A logistic curve (S curve) not or rarely an exponential curve or J curve. 3 outcomes of natural selection that can be seen in different populations (Modes of selection): Directional selection: phenotype of the group shifts to favor one extreme over another. Disruptive selection: both extreme phenotypes are favored over the middle Stabilizing selection: the middle phenotype is favored over the extreme phenotypes Three Forms of Natural Selection Founder Effect and Bottleneck Effect Founder Effect describes the loss of genetic fitness of a population when a few individuals re-colonize a new area or when only a few survivors are left to repopulate an area. Bottleneck Effect (“Bottlenecking”) is a term to describe a significant loss in genetic diversity in a population. (Like from Founder Effect or Genetic Drift) Remember, even asexual creatures seek diversity! Asexual bacteria obtain genetic diversity through 1 of 3 process; conjugation, transduction or transformation https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sje SEngKGrg