* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Terminology - Midlandstech
Drosophila embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Body snatching wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Body Worlds wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Murder for body parts wikipedia , lookup
Human digestive system wikipedia , lookup
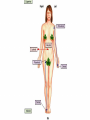
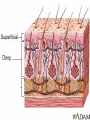
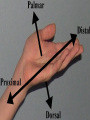
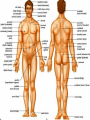
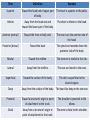
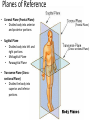
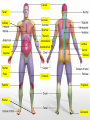
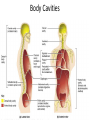
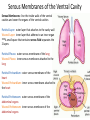
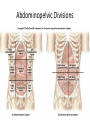
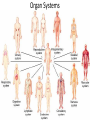
Anatomy- Quiz 1 Dr. Brasington Anatomical Position Term Definition Example Superior Toward the head end of upper part of body. The heart is superior to the pelvis. Inferior Away from the head end and toward the lower part of the body. The chest is inferior to the head. Anterior (ventral) Toward the front or belly side. The nose is on the anterior side of the head. Posterior (dorsal) Toward the back. The spinal cord extends down the posterior side of the body. Medial Toward the midline. The sternum is medial to the ribs. Lateral Away from the midline. The ears are lateral to the nose. Superficial Toward the surface of the body. The skin is superficial to the visceral organs. Deep Away from the surface of the body. The heart lies deep to the sternum. Proximal Toward a structure’s origin or point of attachment to the trunk. The shoulder is proximal to the elbow. Distal Away from a structure’s origin or point of attachment to the trunk. The wrist is distal to the shoulder. Planes of Reference • Coronal Plane (Frontal Plane) • Divides body into anterior and posterior portions • Sagittal Plane • Divides body into left and right portions • Midsagittal Plane • Parasagittal Plane • Transverse Plane (Crosssectional Plane) • Divides the body into superior and inferior portions (Frontal Plane) (Cross-sectional Plane) Cranial Facial Axillary Cervical Brachial Umbilical Thoracic Antecubital Antebrachial Inguinal Lumbar Sacral Gluteal Palmer Pubic Patellar Femoral Popliteal Plantar Calcaneal REGION: PERTAINING TO THE: REGION: PERTAINING TO THE: Facial Face Pubic Gential Region Cranial Cranium Inguinal Groin Cervical Neck Lumbar Lower Back Thoracic Chest (Thorax) Gluteal Buttock Axillary Armpit (Axilla) Popliteal Posterior Knee (Popliteal Fossa) Brachial Arm (Brachium) Patellar Anterior Knee Antecubital Anterior Elbow (Cubital Fossa) Plantar Sole of the Foot Antebrachial Forearm (Antebrachium) Sacral Tailbone Palmer Palm of the Hand Femoral Thigh Umbilical Naval (Umbilicus) Calcaneal Heel Body Cavities • Dorsal Cavity Body Cavities – Cranial Cavity: Brain – Vertebral Cavity: Spinal Cord • Ventral Cavity – Thoracic Cavity • Mediastinum: Esophagus, thymus, heart, trachea • Pleural Cavity: Lungs • Pericardial Cavity: Heart Diaphragm: skeletal muscle between the Thoracic and Abdominopelvic Cavities – Abdominopelvic Cavity • Abdominal Cavity: Liver, spleen, stomach, small intestines, large intestines • Pelvic Cavity: Bladder, internal genitalia (ovary and testes) • Retroperitoneal: Kidney, pancreas Nervous System Brain Spinal Cord Cardiovascular System Heart Respiratory System Trachea Lungs Digestive System Esophagus Stomach S. Intestine L. Intestine Liver Pancreas Urinary System Kidney Bladder Reproductive System Ovary Testes Serous Membranes of the Ventral Cavity Serous Membranes: line the inside walls of the ventral cavities and cover the organs of the ventral cavities Parietal Layer: outer layer that attaches to the cavity wall Visceral Layer: inner layer that adheres to an inner organ ***A small space that contains serous fluid separates the 2 layers Parietal Pleura: outer serous membrane of the lung Visceral Pleura: inner serous membrane attached to the lung Parietal Pericardium: outer serous membrane of the heart Visceral Pericardium: inner serous membrane attached to the heart Parietal Peritoneum: outer serous membrane of the abdominal organs Visceral Peritoneum: inner serous membrane of the abdominal organs Abdominopelvic Divisions Organ Systems The End