* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download wk01review
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
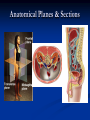
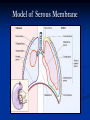
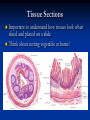
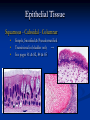
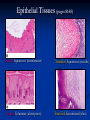
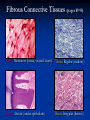
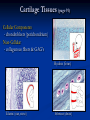
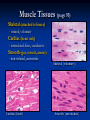
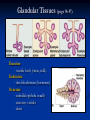
Anatomy 301 Review Week 1 Noel Hastings [email protected] Course Objectives & Grades No matter what I say here, know your course objectives that were given to you! These handouts are the key!!! Try to do well on quizzes and take home assignments. These are easy points!! Terminology & Vocabulary • • • • • • Study of Anatomy Inspection Palpation Auscultation Percussion Dissection Radiography (1895) • • X ray – bones MRI – soft tissue • • • • • • • Anatomical Position Medial – Lateral Proximal – Distal Superficial – Deep Superior – Inferior Cranial/Rostral – Caudal Ventral – Dorsal Anterior – Posterior Anatomical Planes & Sections Body Cavities & Membranes Dorsal Cavity • Cranial cavity (brain) • Ventral canal (cord) • Superior Ventral Cavity Thoracic cavity • Lungs Meninges (DAP) Inferior Ventral Cavity Abdominal cavity (guts!) • Parietal peritoneum • Visceral peritoneum • • • Parietal pleura Visceral pleura Heart • • Parietal pericardium Visceral pericardium (epicardium) Model of Serous Membrane Tissue Sections Important to understand how tissues look when sliced and placed on a slide. Think about cutting vegetable at home! Microscopic Anatomy (Histology) Cells + Matrix = Tissue Know Some Locations for Each Tissue Type 1) 2) 3) 4) Epithelial (Squamous, Cuboidal & Columnar) Connective (Fibrous, Supportive & Fluid) Muscle (Smooth, Skeletal & Cardiac) Nervous (Neurons & Glial Cells) Epithelial Tissue Squamous - Cuboidal - Columnar • • • Simple, Stratified & Pseudostratified Transitional in bladder only → See pages 81 & 82, 84 & 85 Epithelial Tissues (pages 81-85) Simple Squamous (membranes) Stratified Squamous (mouth) Simple Columnar (absorption) Stratified Keratinized (skin) Connective Tissue Fibrous – Supportive – Fluid • • • Fibrous: tendons, ligaments, membranes, matrix Supportive: cartilage & bone Fluid: blood Cellular Components: Fibroblasts, Mac’s, Leuk’s, etc… Non-Cellular Components: Collagen, Elastin, GAG’s Fibrous Connective Tissues (pages 89-90) Loose Mesentery (fascia, visceral layers) Dense Regular (tendons) Loose Areolar (under epithelium) Dense Irregular (dermis) Cartilage Tissues (page 91) Cellular Components - chondroblasts (perichondrium) Non-Cellular - collagenous fibers & GAG’s Hyaline (fetus) Elastic (ear, nose) Fibrous (discs) Bone Tissues (page 92) Cellular Components - osteoblasts (build bone) - osteoclasts (remove bone) Non-Cellular Components - collagen - calcified matrix Structures - lacunae - Haversian canals - lamellae - canaliculi - periosteum Nervous Tissues (page 94) Cellular Components - neurons - glial cells (support) Structures - dendrites - axons - nerve body (soma) - brain & cord Muscle Tissues (page 95) Skeletal (attached to bones) - striated, voluntary Cardiac (heart only) - intercalated discs, conductive Smooth (gut, vessels, uterus) - non-striated, autonomic Cardiac (heart) Skeletal (voluntary) Smooth (autonomic) Glandular Tissues (page 96-97) Exocrine - outside body (sweat, milk) Endocrine - into bloodstream (hormones) Structure - cuboidal epithelia usually - secretory vesicles - ducts Membranes (page 97 & 98) Types • cutaneous (skin) • serous (pleura, peritoneum, etc…) • mucous (mouth, vagina) Structure • epithelial tissue only! • serous = 2 layers + fluid • respiratory has cilia Tissue Changes (page 99-100) • Hyperplasia: growth through cell number increase • Hypertrophy: growth through cell size increase • Atrophy: cell size decrease (from lack of use usually) • Necrosis: abnormal cell death, messy • Apoptosis: controlled cell death (development) • Fibrosis: scar formation • Metaplasia: change from one type into another • Neoplasia: tumor development, uncontrolled growth and can be benign or malignant !