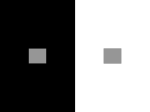* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Convolutional neural network wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
C1 and P1 (neuroscience) wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Efficient coding hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
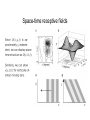
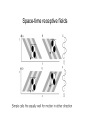
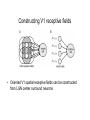
Chapter 2 Outline • Linear filters • Visual system (retina, LGN, V1) • Spatial receptive fields – V1 – LGN, retina • Temporal receptive fields in V1 – Direction selectivity Linear filter model White noise stimulus Fourier transform H1 neuron in visual system of blowfly • A: Stimulus is velocity profile; • B: response of H1 neuron of the fly visual system; • C: rest(t) using the linear kernel D(t) (solid line) and actual neural rate r(t) agree when rates vary slowly. • D(t) is constructed using white noise Deviation from linearity Early visual system: Retina • 5 types of cells: – Rods and cones: phototransduction into electrical signal – Lateral interaction of Bipolar cells through Horizontal cells. No action potentials for local computation – Action potentials in retinal ganglion cells coupled by Amacrine cells. Note • G_1 off response • G_2 on response Pathway from retina via LGN to V1 • • • Lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) cells receive input from Retinal ganglion cells from both eyes. Both LGNs represent both eyes Neurons in retina, LGN and visual cortex have receptive fields: – Neurons fire only in response to higher/lower illumination within receptive field – Neural response depends (indirectly) on illumination outside receptive field Simple and complex cells • Cells in retina, LGN, V1 are simple or complex • Simple cells: – Model as linear filter • Complex cells – Show invariance to spatial position within the receptive field – Poorly described by linear model Retinotopic map • Neighboring image points are mapped onto neighboring neurons in V1 • Visual world is centered on fixation point. • The left/right visual world maps to the right/left V1 • Distance on the display (eccentricity) is measured in degrees by dividing by distance to the eye Retinotopic map Retinotopic map Visual stimuli Nyquist Frequency Spatial receptive fields V1 spatial receptive fields Gabor functions Response to grating Temporal receptive fields • Space-time evolution of V1 cat receptive field • ON/OFF boundary changes to OFF/ON boundary over time. • Extrema locations do not change with time: separable kernel. Space-time receptive fields Space-time receptive fields Space-time receptive fields Direction selective cells Complex cells Retina and LGN receptive fields Retina and LGN receptive fields Comparison model and data Constructing V1 receptive fields • Oriented V1 spatial receptive fields can be constructed from LGN center surround neurons Summary • Linear filters – White noise stimulus for optimal estimation • Visual system (retina, LGN, V1) • Visual stimuli • V1 – – – – Spatial receptive fields Temporal receptive fields Space-time receptive fields Non-separable receptive fields, Direction selectivity • LGN and Retina – Non-separable ON center OFF surround cells – V1 direction selective simple cells as sum of LGN simple cells