* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture Exam #3 Review Slides
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
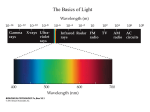
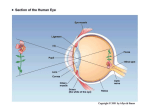
The Nose Malleus Tympanic Membrane Incus Stapes • The middle ear amplifies signal by increasing the pressure on the oval window • Inner ear muscles provide adjustable intensity control (dampen sounds) Basal Thick Stiff High frequency stapes Apical Thin Floppy Low frequency Basilar membrane We Love Fourier! One Version of the Auditory Pathway A1 A1 MGN MGN IC IC superior olive superior olive cochlear nucleus cochlear nucleus Different cells in the retina Back of eye 6. Pigment cells 1. Receptor Cells (Graded potential) (input) 2. Bipolar Cells (Graded potential) 3. Ganglion Cells (action potential) (Output) 4. Horozontal Cells (Graded potential) 5. Amacrine Cells (Graded/action potential) Front of eye Distribution of Rods and Cones Rods Cones High light sensitivity Night vision Low light sensitivity Day vision Achromatic Chromatic Low acuity—not in the fovea High acuity—in the fovea Slow response Fast response General organization of the visual pathway Receptive field • Definition: the area of the retina (or visual field) in which light signals evoke responses • It’s a property of the cell, not a cell or a part of the cell • It depends largely on the synaptic inputs to the cell and to some degree the biophysical property of the cell itself receptive field LGN cells cortical simple cell LGN layers • Parvocellular layers: 3-6 • Magnocellular layers: 1,2 • Contralateral eye: 1,4,6 • Ipsilateral eye: 2,3,5 • But all LGN layers represent contralateral visual field! Yang Dan is Way too Cool Circuitry -- inputs, outputs and layering 1 Input 2/3 LGN layer 4, layer 6 4A Layer 4 layer 2/3 layer 5 layer 6 4B 4 4C Output 4C Layer 2/3, Layer 4B other visual cortical areas 5 Layer 5 superior colliculus 6 Layer 6 LGN M P (LGN) fixation point left visual field nasal half right visual field left right nasal half temporal half temporal half nasal retina contra LGN temporal retina ipsi LGN optic chiasm LGN V1 V1 L visual field R LGN R V1 R visual field L LGN L V1 Transneuronal transport technique to look at OD columns eye LGN V1 layer 4 L radioactive R amino acid 6 5 4 3 2 1 C I C I I C L R 2 L R L V1 cells have orientation selectivity receptive field orientation response LGN cells 1 2/3 4 5 6 cortical simple cell Hypercolumn cortical surface layers 180o, ~1mm • One L/R cycle + one 180o rotation = one hypercolumn.