* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Temporal dynamics of a neural solution to the aperature
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Response priming wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Psychophysics wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Biological motion perception wikipedia , lookup
Hard problem of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Multi-armed bandit wikipedia , lookup
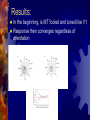
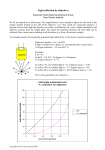
Temporal dynamics of a neural solution to the aperture problem in visual area MT of macaque brain Pack & Born Nature (2001) Harvard Medical School Q: Who solves the aperture problem? OR… What is the function of MT? Alternatives: MT solves aperture problem MT does not solve aperture problem L: V1 creates aperture problem because it has a small RF (is looking for edge) and MT solves because it’s neurons/RF are bigger MT response should be tuned for actual direction of motion and not for orientation of the contour (not in actual direction of the motion) Methods: Train macaques to fixate on small red square for liquid reward Using microelectrodes record monkey’s tuning curve in MT once fixated Field of moving bars (8 directions, 3 relative orientations) as stimulus presented 10 times Spikes recorded from 60-80 ms after onset of stimulus motion and recorded during the last 1,500 ms Results: In the beginning, is MT fooled and tuned like V1 Response then converges regardless of orientation Interpretation: MT solves the aperture problem Problems: Assumes that early MT responses reflects output from V1 What if there is no problem in V1? Need to measure time course in V1 V1 should never converge