* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Top-Down Processing in Neurocognitive Networks
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Music psychology wikipedia , lookup
Attitude change wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Neo-Piagetian theories of cognitive development wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
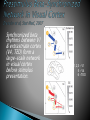
Steven L. Bressler Cognitive Neurodynamics Laboratory Center for Complex Systems & Brain Sciences Department of Psychology Florida Atlantic University http://www.ccs.fau.edu/~bressler/ • Top-down processing is a tractable problem in cognition • Neurocognitive networks provide a workable theoretical framework for understanding topdown processing in the brain • Novel approaches are being developed to investigate top-down processing by neurocognitive networks • Cognitive Science: Effect of knowledge on sensory processing • Brain Science: Effect of “higher-level” neurons on “lower-level” neurons • Attention: selecting items in perception • Expectation: priming items for perception • Inference: identifying items in perception • The Dorsal Attention Network (DAN) is a system of frontal and parietal regions consistently activated by cues indicating where a visual object will appear. • The DAN is postulated to exert attentional topdown control of visual cortical. Prestimulus Processing in Visual Expectation Poststimulus Processing in Visual Inference Synchronized beta rhythms between V1 & extrastriate cortex (V4, TEO) form a large-scale network in visual cortex before stimulus presentation. 1,2,3 – V1 5 – V4 6 –TEO A. Prestimulus extrastriate & V1 beta rhythms are synchronized. B. Synchronized beta rhythms support top-down extrastriateto-V1, but not bottom-up V1-to-extrastriate, influences. “The concept of localization of functions … has come to mean a network of complex dynamic structures or combination centers, consisting of mosaics of distant points of the nervous system, united in a common task.” Higher Cortical Functions in Man, 1962 NeuroCognitive Networks are large-scale systems of distributed and interconnected neuronal populations in the brain organized to perform cognitive functions. Bressler, Scholarpedia, 2008 Bressler & Menon, TICS, 2010 Fuster & Bressler, TICS, 2012 Meehan & Bressler, NBR, 2012 • Top-down processing in the brain involves the effect that neurons in a “higher” area have on neurons in a “lower” area. • It can be observed in the brain wherever a hierarchical order exists • It may involve effects within or between NeuroCognitive Networks (NCNs): Between NCNs: FEF V4 Within NCN: V4 V1 • A variety of analytic techniques are used to investigate top-down processing in the brain ▶ Stimulation: TMS, TACS, CMS ▶ Ablation: clinical analysis of stroke ▶ Electrophysiological Time Series Recording ▶ BOLD Time Series Recording ▶ Causal Time Series Modeling: AR models, DCM ▶ Biophysical Modeling: Neural mass models, integrate-and-fire models • Multi-Site Recording Modalities • Improved Causal Modeling Techniques • Improved Large-Scale Biophysical Modeling • Graph Theoretic Methods Tailored to Brain Networks • • Top-down processing is essential in cognition Top-down processing underlies attention, expectation, and inference – all used in perception • Top-down processing in cognitive science has a parallel interpretation in neuroscience • Top-down processing in the brain is readily accommodated by the concept of neurocognitive networks • Numerous analytic techniques are available, or are being developed, to study top-down processing by neurocognitive networks.