* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Marketing
Affiliate marketing wikipedia , lookup
Perfect competition wikipedia , lookup
Darknet market wikipedia , lookup
Grey market wikipedia , lookup
Service parts pricing wikipedia , lookup
Bayesian inference in marketing wikipedia , lookup
Market analysis wikipedia , lookup
Dumping (pricing policy) wikipedia , lookup
Food marketing wikipedia , lookup
Market segmentation wikipedia , lookup
First-mover advantage wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
Marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Ambush marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing research wikipedia , lookup
Digital marketing wikipedia , lookup
Sports marketing wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Multi-level marketing wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Segmenting-targeting-positioning wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
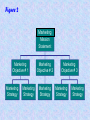
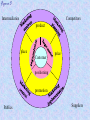
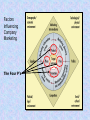
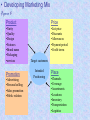
Marketing: An Introduction Armstrong, Kotler Chapter Two Strategic Planning and the Marketing Process Looking Ahead • Explain companywide strategic planning and its four steps. • Discuss business portfolio design and strategies. • Explain marketing’s role in strategic planning and the importance of value chains and networks. • Describe the elements of a customer-driven marketing strategy and mix. • List the marketing management functions and elements of a marketing plan. What Is Strategic Planning? Strategic Planning is the process of developing and maintaining a strategic fit between the organization’s goals and capabilities and its changing marketing opportunities. Steps in Strategic Planning We look first at the organization’s overall strategic planning, then we discuss how marketers guided by the strategic plan, work closely inside and outside the company to serve customers, finally we examine marketing strategy and planning. Corporate level 1. Define the company mission. 2. Set company objectives and goals. 3. Design the business portfolio. Figure 1 Business unit, product and market levels. – Plan marketing and other functional strategies. Steps in Strategic Planning Figure 1 Defining the Company mission Setting company Objectives & goals Designing the Business portfolio Planning marketing And other functional strategies Corporate level 1- Defining a clear company mission: “Purpose” • Mission Statement of marketing unit ; should be realistic, specific, motivated, and should fit the market environment. • Examples; Company Disney Mercedes Product-oriented definition Market-oriented definition We run theme Parks We create fantasies- a place where is America still works the way it’s supposed to. We build cars With a leadership position in the industry comes a responsibility to give back Corporate level 2- Setting company objectives and goals • The company’s mission needs to be turned into detailed supporting objectives for each level of management. Mission leads to business objectives and marketing objectives. • Example; if the business over all objective is to “increase the company market share”. marketing strategic plan might increase products availability and promotion, and that may require more sales people and more budget. Figure 2 Figure 2 Marketing Mission Statement Marketing Objective # 1 Marketing Strategy Marketing Strategy Marketing Objective # 2 Marketing Strategy Marketing Objective # 3 Marketing Strategy Marketing Strategy Market level 3- Designing the Business portfolio • The business portfolio is the collection of businesses and products that make up the company. • The company must: – Analyze its current business portfolio or Strategic Business Units (SBUs). – Decide which SBUs should receive more, less or no investment.. Figure 3 4- Developing strategies for growth and downsizing; Example; product/ market expansion grid. Figure 4 Analyzing the current business portfolio Using; growth share matrix developed by Boston consulting Group ( BCG) The objective is which question marks can be turned to Starts, and Which starts can be turned into cash flows, and clear decisions about dogs Stars Question Marks ? • High growth market & high share • High growth, low market share • Profit potential “Require a lot of cash to “May require heavy hold market share” investment to grow” Cash Cows • Low growth market, high share • we have to establish, successful SBU’s “ Less investment, but a lot Of cash” Dogs • Low growth market & share • Low profit potential “ low cash flow may be generated” Potential Matrix Problems • Can be time consuming and costly. • Difficult to define SBUs and measure market share and growth. • Focus on the current business, not future planning. • Can place too much emphasis on growth. • Can lead to poorly planned diversification. Market level 4- Developing strategies for growth and downsizing; Example; product/ market expansion grid. Figure 4 Strategies for growth business Market penetration; making more sales to current customers without changing its products. By improving services, re prices, menu selection. Market development; opening new market for the existing products. New market target, international market. Product development; new product for current market. Add a breakfast special, buy one get one free…. Diversification; Buy businesses of outside of its current products and markets. Starbuck coffee sells music CDs. Analyze Opportunities by Tim Horton’s • Product-Market Expansion Grid identifies four potential growth areas. Figure 4 Existing Products New Products Existing Markets Market Penetration Product Development New Markets Market Development Diversification Marketing strategy and the marketing mix Marketing strategy; marketing logic to by which the company hopes to achieve a profitable lifelong relationship with customers. It involves deciding which customers to serve (segmentation and targeting) and with what value proposition ( differentiation and positioning),Figure 5 Figure 5 Intermediaries Competitors product place Customer price positioning promotion Publics Suppliers Factors Influencing Company Marketing The Four P’s Market segmentation; dividing the market into different groups of buyers who have different needs, and who might require separate products or marketing mix. Target marketing; the process of evaluation each market segment’s attractiveness and selecting one ore more segments to enter. Market positioning; placing a product to occupy a clear and desirable place relative to competitors in consumer’s minds. Blazer “ Like a rock”. Lexus ” The passionate pursuit of excellence’. Marketing Mix; set of controllable tactical marketing tools (Product, price, place, promotion) to influence the demand for its product in the market. Create Marketing Mix • Product – offers the right product, service or experience. • Price – controls perceived value and satisfaction. • Place – allows customers easy access to product and support. • Promotion – communicates the offer and the value proposition. Figure 6 • • Developing Marketing Mix Figure 6 Product Price •Varity •Quality •Design •Features •Brand name •Packaging •services •List price •Discounts •Allowances •Payment period •Credit terms Target customers Promotion Intended Positioning •Advertising •Personal selling •Sales promotion •Public relation Place •Channels •Coverage •Assortments •Locations •Inventory •Transportation •Logistics The Four Ps and the Four Cs • PRODUCT provides CUSTOMER SOLUTION • PRICE represents CUSTOMER COST • PLACE provides CONVENIENCE • PROMOTION is 2-way COMMUNICATION Manage Marketing Effort • Build strong operational marketing plan. • Carry out the plan. – Organize marketing department. – Leverage value chain and value network. • Exercise control. – Set goals. – Measure and evaluation performance. • Take corrective action. Figure 7 • Marketing analysis; It’s the process of planning, implementing, and control Analysis Planning Implementation Control Develop strategic plans Carry out the plan Measure results Evaluate results Develop marketing plans Take corrective Action