* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download document 8546379
Survey
Document related concepts
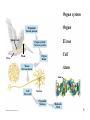
Transcript
Chp 1 Biology: Exploring Life 1.10 Biology, Technology, & Society are Connected What current Biology-related news topics have you read/heard about? 1 1.1 All Life Forms Share Common Properties What common property of life does each picture display? ✶ Sunflower, Macaques, tadpole, hummingbird feeding, dragonfly on Venus flytrap, Jackrabbit’s ears, Ptarmigan coloration 2 1.2 In Life’s Hierarchy of Organization, New Properties Emerge at Each Level ✶ Biology is the ______________ study of _________ (at any of its many levels of organization) 18th Century illustration of the bizarre world of microorganisms 3 Biosphere Biosphere Ecosystem Florida coast ___________ Community _____________ Community Organism All organisms on the Florida coast Population Biology’s Levels of Organization Group of brown pelicans Organism Brown pelican 4 Organ system Organ Organism Brown pelican Spinal cord Tissue Organ system Nervous system Nerve Brain Cell Organ Brain Tissue Atom Nervous tissue Atom Cell Nerve cell Nucleus Organelle Nucleus Molecule DNA 5 ✶ The – – – – upper tier is a global perspective of life _________________- all the environments on Earth that support life _________________- all the organisms and the physical factors of a particular area _________________- all of the organisms living in a particular ecosystem _________________ - all the individuals of a particular species within a specific area 6 middle tier is characterized by the organism, an individual living thing, which is composed of ✶ The – – – _________ ___________- have specific functions; are composed of multiple organs _____________- provide specific functions for the organism; composed of multiple ___________ ______________- composed of groups of similar cells 7 ✶ Life emerges at the level of the cell, the lower tier, which is composed of – – – ___________- living entities distinguished from their environment by a membrane; fundamental unit of life _____________ - membrane-bound structures within a cell that has specific functions ___________________ - clusters of atoms bonded together 8 1.3 Cells ✶ Two – are the Smallest Units of Life distinct types of cells exist on our planet Prokaryotic cells – Simple and small – Bacteria – are examples of _____________ cells Eukaryotic cells – Possess organelles surrounded by a ______________ – Plants, animals, and fungi are composed of ______________ cells 9 Prokaryotic cell Eukaryotic cell DNA (no nucleus) Membrane Nucleus (contains DNA) Organelles 10 EVOLUTION IS THE CORE THEME IN BIOLOGY 1.6 Diversity of Life is Arranged into 3 Domains ∗ The 3 ____________ (categories) of life – Bacteria—prokaryotic, and most are unicellular and microscopic – Archaea—like bacteria, are ____________, and most are unicellular and microscopic – Eukarya—are ____________ and contain a nucleus and organelles 11 Domain Eukarya Domain Bacteria Bacteria (multiple kingdoms) Protists (multiple kingdoms) Kingdom Plantae Domain Archaea Archaea (multiple kingdoms) Kingdom Fungi Kingdom Animalia 12 Tree of life: Based on analyzing chemical components of organisms ✶ Earliest living cells were ____________, then multicellular ____________ organisms evolved 13 1.7 Evolution Explains Unity & Diversity of Life 1859, __________ __________ published On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection ✶ In ✶ The book accomplished two things – – Presented evidence to support the idea of evolution Proposed a mechanism for evolution called ______________ ____________ Charles Darwin (1809-1882) 14 ✶ Natural selection is an editing process – – – Individuals within a _____________ have inherited variations Population exposed to “outside” factors that favor reproductive success of some individuals over others Over time, this results in a change in the ________________ = biological evolution (1) Population with varied inherited traits (2) Elimination of individuals with certain traits (3) Reproduction of survivors Figure 1.6B Natural selection 15 Evolution = “descent with modification” ✶ History – – of life resembles a multi-branched tree ________ of tree are current living species, twigs and limbs are lines of descent, branches are ______________ ____________ Living species are descendants of ancestral species 16 THE PROCESS OF SCIENCE 1.8 Scientific Inquiry Asks and Answers Questions About Nature ∗ 2 approaches to understand natural causes for natural events – – Inductive reasoning- draw general conclusions from many observations ____________ reasoningcome up with ways to test a hypothesis and see if results support the hypothesis Science: A method of inquiry 17 In Science, Hypothesis & Theory are Different ✶ Hypothesis - a proposed explanation for a set of observations ✶ Theory − - an explanatory idea that is 1) ________ in scope 2) Supported by a large body of ____________ and 3) Widely ___________ What is an example of a hypothesis, and a theory ✶ Science seeks natural causes for natural events – Limits scope to those structures/processes that – Can be _________________ and ___________________ 18 1.9 Scientists Form and Test Hypotheses ✶ Case – ✶ A study Flashlight failure ____________ that has been tested and not falsified is tentatively accepted Observations Question Hypothesis # 1: Dead batteries Hypothesis # 2: Burnt-out bulb Prediction: Replacing batteries will fix problem Prediction: Replacing bulb will fix problem Test prediction Test falsifies hypothesis Test prediction Test does not falsify hypothesis Figure 1.8A The hypothesis-based scientific method 19 Scientists Conduct Controlled Experiments ✶ Each factor that might influence a process is a variable – To evaluate hypotheses about one variable, all other variables must be kept constant experimental group has one variable altered. In the ____________ group, that variable is not altered ✶ The – All other aspects the two groups are identical ✶ Controls are used to make the results of an ____________ meaningful 20 ✶ Case study: Spider mimicry Zebra spider and snowberry fly. Pounce rate (% of trials in which spider jumped on fly) What is the hypothesis? What do these results tell you about the hypothesis? Control group (untreated flies) Experimental group (wing markings masked) 21 Objective Checklist ! Name the common properties of all life ! Describe life’s hierarchy of organization ! Describe the two types of cells and name some of their structural features ! Explain the theory of evolution by natural selection and how current species are descendants of ancestral species ! Describe the process of hypothesis-based science ! Describe the difference between a hypothesis and a theory 22