* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - Hope Christian College Parent and Student Portal
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Molecular paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Evolving digital ecological networks wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Inclusive fitness wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Saltation (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
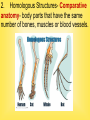
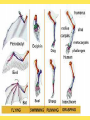
Natural selection and evolution Chapter 3. What is Evolution? It’s a gradual change in a species over time. Fossils and evolution: • • We have already learnt that fossil evidence has convinced scientists that creatures have evolved form one to the other; not that we have to accept this as truth….but learn their evidence and consider their theory. Review your previous notes if you need to! We look at some more evidence soon!??? Background History: Charles Darwin: Explorer on a observation trip aboard the HMS Beagle in the Galapagos Islands. He found a variety of species similar to those found in South and Central America and some completely new. Darwin came up with the theory of Natural Selection Natural Selection: means that organisms with traits best suited to their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce.- this is affected by the environment-or selective pressures This could be temperature, water availability, predation or disease amongst others “Survival of the Fittest” 1. Organisms produce more offspring than can survive. 2. Variations are found among individuals of a species. 3. Variations are passed on to offspring.-via the genes 4. Some variations allow members of a population to survive and reproduce better than others- peppered mothsRead from pg 80 to students. Over time, offspring of individuals with helpful variations make up more and more of a population. Variations: an inherited trait (change in the DNA) that makes an individual different from other members of the same species. Could be colour, shape, behaviour or chemical makeup • Bacteria- as you know these are • • • • single celled organisms and many can cause disease. It was found by Alexander Fleming that fungus can produce natural chemicals that kill bacteria. These were called antibiotics 1st was penicillin The practice of using antibiotics has become widespread and bacteria in some instances have become immune to them via natural selection. • As bacteria can reproduce every 20 mins it is easy for the “adapted or selected ones” to produce lots of themselves quickly creating a whole new species that can be resistant to the antibiotics. • Some bacteria like golden Staff are resistant to many antibiotics and this causes lots of concern for doctors. 1st….some definitions to know • Species- when the organisms are alike physically and can breed and produce fertile offspring • DNA is also used to identify species – DNA codes for genes which code for proteins-identical proteins should mean identical genes and therefore same species. • This is useful in fossil DNA to determine ancestry. Speciation• • • This is when one species splits into two or more species- not a whole new creature…just a different type i.e different type of bird like a different coloured parrot that can’t any longer breed with the other colour one to produce a fertile offspring/baby. Speciation means greater biological diversity or more variation in the ecosystem or variety of organisms. It occurs in 3 steps –variation, isolation and selection Variation: • Must be variation in a population • The genes or attributes most suited will be selected and those organisms will survive a given environment Isolation: • Next the “ different variety of organisms must be isolated or separated from their relatives “ • This occurs physically first-i.e a flood separates two groups, and they continue to develop differently according to selective pressures in each of their new environments. • These physical separtors are called geographical barriers and could also include temperature, currents mountain ranges rivers etc. Selection-speciation: • • • Once isolated the barriers prevent cross breeding And as stated the organisms continue to adapt and change often through mutations of the DNA to the new environments via natural selection Changes in courtship behaviour, breeding seasons, etc. all lead to a new species being formed. Evolution can happen in two ways: 1. Gradualism - a slow steady process where you can see different forms of the new species. Minor changes happen Example: horse 2. Punctuated Equilibrium happens quickly . Sometimes intermediate species are not there. • Species branch off and evolve simultaneously. Example: elephants Practical pg 84 natural selection Branching Diagram Essential Questions: 1. Give a brief description of the evolutionary changes that occurred in the organism. 2. During which time period did the fossils differentiate into two branches? How did you know to branch off? 3. Explain how the chart illustrates both punctuated equilibrium and gradualism. 1. Fossil Record Oldest fossils are at the bottom Newest at the top 2. Homologous Structures- Comparative anatomy- body parts that have the same number of bones, muscles or blood vessels. 3. Vestigial Structures - a body part that doesn’t seem to have a function at this time. Example Pelvic bone in whales 4. Embryology- studying organisms at the very early stages of development to see how they are the same. Show overhead 5. DNA - Organisms that have close relatives have similar DNA. Example: dogs are the closest relative to bears. Human Evolution- students to read copy of text book page Practical pg 98/99