* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Evolution PowerPoint
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex wikipedia , lookup
Evolving digital ecological networks wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary mismatch wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
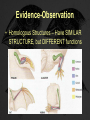
Evolution Ms. Bosinski/ Mrs. Newlove Evolution • Evolution-The process by which species change over time, or become extinct. • Species-All the organisms that can interbreed and produce fertile offspring, and look roughly alike. • Extinction-When all members of a species have died and that species no longer exists. Jean Lamarck • BEFORE Charles Darwin, Jean Lamark came up with ideas of how evolution worked. • His theories have been proven FALSE. He believed that organisms could CHANGE to fit the environment (Use/Disuse), and that those traits could be passed on to offspring Charles Darwin • Lived in England • When he was young, he took a voyage on the H.M.S. Beagle • They sailed into the Pacific Ocean, to the Galapagos, and Darwin discovered several new species, including species of finches that were found no where else. • This led him to think about why the finches on the Galapagos would be different than those in England. Darwin • Basically, Darwin said that living populations change over time because of changes in their environment. • Certain individuals are ‘selected’ to breed because they are better adapted to the change in the environment. • He called this process, ‘natural selection’ Evolution- Some terms • Adaptation-A trait that an organism has which helps it to survive its environment. • Natural Selection-The natural change in environment which will determine which traits are useful and which are not; those traits will be passed on to succeeding generations. Darwin’s Theory Includes: • • • • Overproduction (Too many offspring) Competition (Struggle for resources) Variations (Not all members are the same) Adaptations (Some have favorable characteristics) • Natural Selection (The best suited will survive/ Survival of the Fittest) • Speciation (Eventually a new species could form) THE IMPORTANCE OF VARIETY….. • If the environment changes, it is likely that SOME organisms of a species will survive if there is more VARIETY!! • The more DIVERSITY there is in a population the more stable that population is. MUTATIONS • The source of variations can be traced back to MUTATIONS, which change the genetic information (DNA, Genes, or Chromosomes) • MOST mutations are HARMFUL, but some can be helpful, as in the dark peppered moth! Peppered Moth • The peppered moth comes in two colors: white and black • The white color is favored by natural selection, because the bark of the trees that the moth rests on is white. This makes it hard to be spotted by birds. Peppered Moth • However, when the factories in England started up, the bark of the trees often was covered in soot. This made the bark of the trees black. Scientists started seeing the moth population change from almost all white to almost all black. Peppered Moth • If this had happened long enough, the moth may become a new species. Evidence-Observations • Evidence of Evolution • Fossils-Fossils can be imprints, casts, molds, or petrified parts of animals and plants that lived thousands to millions of year ago. • Fossils form in sedimentary rocks which form in water History of Life on Earth • The pattern seems to be from simpler forms to more complex forms • Several mass extinctions of large numbers of species have caused rapid evolution to occur, eg. 65 million years ago, and the Permian Mass Extinction Evidence-Observation • Homologous Structures – Have SIMILAR STRUCTURE, but DIFFERENT functions Evidence of Evolution • Comparative Embryology- Some organisms look VERY similar in the early stages of development. Evidence • DNA! • Scientists have compared the DNA of many organisms, and organisms that have similar structures often have very similar DNA. • Humans and Chimpanzees have 98% the same DNA How does Evolution Work? • Genetics! • Each species has a natural variation, because of different alleles. When something in the environment changes, some traits may provide an advantage, those traits, and therefore genes, are passed on to the next generation. So… • The genes which code for traits which help the organism survive are going to be passed on. • Those that are not helpful are not going to be passed on, but eliminated from the gene pool. • Over many generations, a new species can form. The Rate of Evolution For some species, the rate of evolution has been SLOW, as in the HORSESHOE CRAB which has changed very little over 300 million years. However, HORSES have evolved a lot over 60 million years. Evolution Videos • Structural Adaptations of Australian Wildlife • http://youtu.be/wEDxThDINgQ • How Evolution Works • http://youtu.be/xkwRTIKXaxg • Finches on the Galapagos • http://youtu.be/l25MBq8T77w • Natural Selection & Adaptations • http://youtu.be/kjgNT0rBy_8