* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Natural Selection and the Origin of new species
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
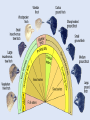
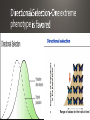
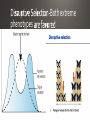
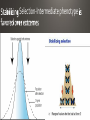
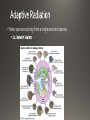
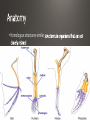
• Parents pass on traits that they get during their lives . Giraffes stretching to reach food Carrying capacity rare several million years 4.5 billion years • Humans make gradual changes to species to get organisms we want through encouraging breeding of those with desired traits selective breeding have traits designed to attract a mate https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CYcs73oeFkc Darwin • HMS Beagle Galapagos • Different finches. explanation for natural phenomena If an organism is better able to survive where it lives, it survives. lity to survive and reproduce in a given environment differences within a species are variations that allow an organism to better survive in their environment • Adaptations are central to Natural Selection • Variations that are beneficial are selected for • Camouflage-blending in with surroundings to keep from being spotted • Mimicry-looking like something dangerous, which makes predators afraid • Gives them an advantage over other members of their species • They are more likely to survive and pass the trait on Which of the organisms to the left can sting you? None of them! All are flies, and are 100% harmless. None even have stingers! extreme phenotype Both extreme phenotypes Selection-Intermediate phenotype • Extremely misunderstood topic • Change in the frequency of alleles in a population over time. • Over time, certain traits become more common in a population • The variations are often the result of a beneficial mutation giving the organism something it did not previously have • Ex. Antibiotic resistance in bacteria 2 species when part of the population becomes isolated https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YCoEiLOV8jc • Darwin’s way of describing evolution. • The similar species (ex. The different species of Finch on the Galapagos Islands) all had a common ancestor • A mother population of finches that changed over time into all of the different species that we see now. • Often caused by changing environmental conditions • For the finches, it was availability of food • Finches from the initial population that had slightly larger beaks did better than those with smaller beaks when large nuts and seeds were the primary food source available • This led Darwin to conclude that, over millions of years, all organisms descended from a single common ancestor • The “Tree of Life” • Convergent • Divergent • Coevolution • Many species evolving from a single ancestral species extinction • Extinction is the death of the last member of a species Fossils Biogeography Embryology-study of development At one point, you had gills and a tail! • Homologous structures-similar Vestigial Structures https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OAfw3akpRe8 • All organisms, past and present, share DNA • • • • All humans are 99.9% similar Humans and chimpanzees share 98% of DNA Humans and grass have 15% similar DNA Humans and bacteria have 7% similar DNA • Follows “tree of life” pattern • Organisms more closely related have more DNA in common