* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 4Modern Evolution Regents
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Dual inheritance theory wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive evolution in the human genome wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Peppered moth evolution wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
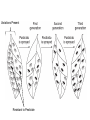
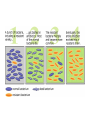
Modern Evolution Miss Hoffman Charles Darwin • Darwin could not account for the genetic reasons for variations that he observed among organisms – Therefore theories to how variations occur were created. • Mutation Theory • Modern Theory of Natural Selection Mutation Theory • What is a mutation? – Changes in the genetic information – Occurs during DNA replication • Occurs randomly – Causes variations • How does this cause variations in species? – If a mutation is favorable, and it helps the organisms survive and reproduce, it is inherited Modern Theory of Natural Selection • What happens if the Environment changes? – Genes that previously were neutral or had low adaptive value may become favorable and increase in number Species that are… • More likely to evolve: - Reproduce quickly and often - reproduce sexually - genetically varied - have more mutations Ex. insects • Less likely to evolve: - reproduce asexually - no genetic variation - have fewer mutations Ex. amoeba Evolution in Our Time • Spraying of insecticides – DDT sprayed to kill black flies – After a few spraying most died – Some flies had genes that made them resistance to DDT – Before DDT these genes were neutral – After the spraying, only the flies that were resistant survived – Since most were killed, little competition – Resistant genes rapidly increase in number – DDT was no longer effective Variations Present Resistant to Pesticide Evolution in Our Time • Antibiotics and Bacteria – Some bacteria are naturally resistant to antibiotics – Therefore they live and pass on the resistant gene – Antibiotics no longer work on that bacteria Evolution in Our Time • English Peppered Moth – In Manchester- there existed two colors of peppered moth (light and dark) – Before the industrial revolution trees were lighter. – Light colored moths were more common, because they blended with the environment (white birch trees) – Soot and pollution from the industry made the environment darker – Light colored moths became visible and were eaten by birds – Dark moths could not be seen, so they were able to reproduce and pass on the dark colored gene – Population shifted from light to dark Population of Peppered Moths changed from white (normal) to dark grey (mutant) over many generations Prior to Industrial Revolution After Clean Air Act After IR Before Clean Air Act Environmental changes causes the allelic frequency to change Human Affect Our Own Evolution • How can humans affect our evolution? – Medical knowledge: • Permits survival of individuals with genetic traits that would not have otherwise survived – Modern Transportation: • Humans are less affected by geographic isolation – Advanced Technology: • Better nutrition and greater control over their reproductive success – Genetic Engineering: • May lead to the appearance of new traits and the elimination of others