* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Evolution - s3.amazonaws.com
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Objections to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Sociocultural evolution wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Transitional fossil wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Hindu views on evolution wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
Vestigiality wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
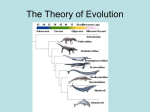
Warm-up Jan. 19th & 20th Write this on the TOP HALF of your full sheet of white paper that you picked up as you walked in. Define in your own words: EVOLUTION & Draw a picture Natural Selection and the Evidence for Evolution Chapter 15 (p 393-417) I. Charles Darwin and Natural Selection A. Who is Charles Darwin? – The “father of evolution” – English scientist (1809-1882) – Compiled major aspects of the process of evolution as possible explanations of how species have evolved. – First to publish his ideas that were shaped by fossil evidence. B. Why is fossil evidence important? • Shows evidence that an organism lived long ago. • Geologists provided evidence indicating that earth was much older than people had originally thought (4.6 billion years old) • Biologists suspected that species change over time, or evolve. C. What is natural selection? Development of the theory of Evolution. • Early theory of evolution by Lamark contained 3 main ideas: –1. Organisms constantly strive to improve. –2. Structures not used disappear (use and disuse). –3. Acquired traits can be passed on. Darwin’s Theory of Evolution was influenced by several major factors. • Geology • Artificial Selection • Population Control 1. Geology – • Charles Lyell reasoned that the earth must be much older than previously thought. 2.Artificial Selection – observation that selective breeding of crops and animals by farmers could produce more desirable offspring. Darwin did his own pigeonbreeding experiments that demonstrated artificial selection. 3. Population Control – Thomas Malthus stated that the human population was increasing so fast that the supply of resources could not keep up with the demand. War, starvation, and disease occurred to limit the population. Darwin’s Theory of Evolution (known as Natural Selection) contains 4 main ideas. • There is variation within a population. • Some variations allow an organism a better chance of survival. • More organisms are born than are expected to survive. • Individuals that survive and reproduce pass their traits to the next generation. Evolution of New Species Adaptations & Competition D. Vocabulary • Species – interbreeding populations of organisms that can produce offspring capable of reproduction. • Variation – differences between individuals within a population. • Evolution – process of change in a population over time. • Theory – a hypothesis that is supported by evidence. End of Day 1- Jan. 23/24 WARM-UP Write down assignment, complete warm-up in your notebook • Compare and Contrast the following: –Natural Selection –Artificial Selection Use your notes from last class to help you. II. Adaptations: Evidence for Evolution Adaptation • A. Adaptation – evolution of a structure, behavior, or internal process that enables an organism to respond to environmental factors and to live to produce offspring. –Examples: rose’s thorns, giraffe neck, tendrels on vines, etc. Other types of structural adaptations: –Mimicry – enables one species to resemble another. –- Physiological adaptations • B. Physiological adaptations – change in metabolic process (internal change) **direct evidence of evolution – Many disease causing bacteria are today no longer affected by penicillin because bacteria have evolved to prevent being killed by penicillin – Many insects and weeds that are pests are now resistant to pesticides that are used to kill them. C. Anatomical adaptations structure of an organism • Homologous Structure • Analogous Structure • Vestigial Structures • Homologous Structure – traits that are similar in different species because species share a common ancestor. –**Similar structure, different function. –Ex. an arm, fin and wing Same structure, different function • Analogous Structure – do not have a common evolutionary origin. ** Different structure, similar function. •Ex. insect wing and a bird wing. Used for flight but totally different structure Same function, different structure • Vestigial Structures – structures that are inherited but often not used. – **suggests that they were structures of their ancestors. – Ex. pythons have a hipbone, humans have an appendix, eyes of blind-mole rats and cave fish. Vestigial Structure Review End of Day 2- Jan. 25th Embryology (pg 402) • D. Embryology – the study of embryos –Embryo – an early stage of growth and development of both plants and animals. –It is the shared features that suggest evolution from a distant common ancestor. Fish Reptile Bird Mammal Embryology Biochemistry (pg. 403) • E. Biochemistry – the study of a living organism’s chemistry ( DNA, ATP, enzymes) –Organisms that are biochemically similar have fewer differences in their amino acid sequences. Groups that share more similarities are interpreted as being more closely related. Biochemistry Biochemical Similarities of Organisms Comparison of Organisms Birds vs. mammals Two orders of mammals Amphibians vs. birds Fish vs. land vertebrates Insects vs. vertebrates Algae vs. animals Percent Substitutions of Amino Acids in Cytochrome c Residues 5 and 10 8-12 14-18 18-22 27-34 37 Factors that effect EVOLUTION Fossil Record Anatomy Biochemistry Embryology Works Cited • "Natural Selection," a caricature of Darwin.. IRC. 2005. • • • • unitedstreaming. 10 January 2006 <http://www.unitedstreaming.com/> Greatest Discoveries with Bill Nye: The Origin and Evolution of Life. Discovery Channel School. 2005. unitedstreaming. 10 January 2006 <http://www.unitedstreaming.com/> Evolution. AIMS Multimedia. 1993. unitedstreaming. 10 January 2006 http://www.unitedstreaming.com/ Camouflage, definition Source: Paul Fuqua Copyright: 2003 Adaptations, animal and plant Source: Paul Fuqua Copyright: 2004