* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Wed. 3/11 Evolution
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Inclusive fitness wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Saltation (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Evolving digital ecological networks wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
The eclipse of Darwinism wikipedia , lookup
Precambrian body plans wikipedia , lookup
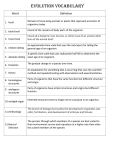
Warm Up • What do you think evolution means? Evolution The History of Life The Record of Life History in Rocks • FOSSILS • Any evidence of life from the past – A trace of a long-dead organism (most are hard parts such as bones, teeth, shells, and woody stems. Where are fossils found? 1. Sedimentary rock layers (strata) (Grand Canyon, AZ) 2. Frozen in Ice (wooly mammoth) 3. Stuck in tree sap or Amber (insects) 4. Stuck in Tar (Saber Toothed Tigers) Fossils are not always body parts but: • Imprints- a film of carbon remains after an organism decays • Mold- an imprint or impression in a rock of the shape or track of an organism • Cast- when sediments or hard minerals fill in a cavity left by a fossil mold • Replacement- when sediments or hard minerals replace the whole organism. ex. petrified wood Scientists Who Study Fossils… The Age of Fossils • Relative Age (relative dating) the fossil’s age compared or related to another fossil. (sequence of age) • Absolute Age- numerical age • Journal: Give an example of relative age and absolute age Radiometric Dating • The age of fossils can be determined by measuring the amount of a particular isotope it contains. This quantity is then compared with the amount of some other substance in the fossil that remains constant over time. • Carbon 14 -------------> Carbon 12 What is the half life of Carbon-14? Half life = amount of time for half of the substance to decay. The Geologic Time Scale A time scale for the history of the Earth *** I do not test you on eras, periods, or events*** Journal: What is the difference between a hypothesis, a theory, and a law? The Theory of Evolution • All the changes that have formed life on earth from its earliest beginnings to the diversity that characterizes today. Evidence used to support Evolution • Fossils • Structure of Organisms – Anatomy & Physiology • Embryology • Biochemistry The Fossil Record • Fossil-bearing strata show that species of organisms appear, existed for a while, and then disappear or became extinct • The fossil record indicates that there were several mass extinctions, – brief periods during which large numbers of species disappeared – e.g trilobites disappeared during the Permian extinction 245 million years ago. Geology in the 1800’s George Cuvier (1769-1875) French Anatomist Catastrophismsudden geologic catastrophes caused the extinction of large groups of animal at certain points in the past. Geology in the 1800’s • Charles Lyell (1797-1875) • English Geologist • Uniformitarianism Geologic processes have changed the shape of the earth’s surface in the past and continue to work in the same ways today Jean Lamarck • French Scientist (1744-1829) • Proposed that similar species descended from a common ancestor • To explain how species changed he hypothesized that acquired traits could be passed onto offspring Acquired Traits • Something that you gain in your lifetime…. – Journal: List some examples that you can think of… Jean Lamarck • His hypothesis was fiercely attacked and easily disproved • But, he was the first to clearly state that types of organisms changed over time and that similar types of organisms are modified descendents of older types. Charles Darwin An English Naturalist (1809-1882) • He proposed the hypothesis that species were modified by natural selection Charles Darwin • He Collected 1000s of samples of biological specimens and fossils Darwin’s Theories 1. Descent with Modification States that the newer forms appearing in the fossil record are actually the modified descendents of older species. (Describes the process of evolution) Darwin’s Theories 2. Theory of Natural Selection -Describes the mechanism or how evolution occurs. Natural Selection 5 parts: a) All organisms produce more offspring than can survive. b) All organisms within a species vary. c) Every organism faces a constant struggle to survive. d) Organisms best suited for their environment survive. e) Organisms that survive pass their traits onto their offspring. Example: The bacteria that causes Ulcers Antibiotic Resistance Figure 3: Mutation rate versus genome size for bacteria and other biological entities. From A mutation burst during the acute phase of Helicobacter pylori infection in humans and rhesus macaques Bodo Linz, et. al., Nature Communications 5, Article number: 4165 Darwin’s Theories • The resulting change in the genetic makeup of a population is Evolution. • In an evolving population, a single organism’s genetic contribution to the next generation is termed Fitness. Favorable Traits • The environment “selects” the traits that will increase a population. The kinds of traits that are favorable depend on the demands of the environment. Journal: Write down an example where the environment favors one trait over another. • A favorable trait is known as an adaptation or it gives an organism an adaptive advantage. Example: In an environment that is dark, the dark ducks survive better Create Your Own Natural Selection Diagram • Begin In Class – Due Next Class!!! a) All organisms produce more offspring than can survive. b) All organisms within a species vary. c) Every organism faces a constant struggle to survive. d) Organisms best suited for their environment survive. e) Organisms that survive pass their traits onto their offspring.