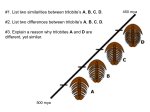
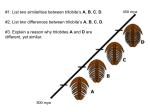
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 15
Sociocultural evolution wikipedia , lookup
Objections to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Jewish views on evolution wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Creation–evolution controversy wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Hindu views on evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Transitional fossil wikipedia , lookup
Chapters 14, 15, 16 Theories & The most dangerous book Mr. Lawrence can bring to class! 1 14 The Fossil Record Fossils and Ancient Life How Fossils Form Interpreting Fossil Evidence – Relative Dating – Radioactive Dating Geologic Time Scale – Eras – Periods 2 Radiometric Dating 3 Is this a good graph? Radioactive Decay 4 Geological Time Periods Era Period (millions of Time years ago) Quaternary 1.8–present Tertiary 65–1.8 Cretaceous 145–65 Jurassic 208–145 Triassic 245–208 Era (millions of Period Time years ago) Permian 290 – 245 Carboniferous 360–290 Devonian 410–360 Silurian 440–410 Ordovician 505–440 Cambrian 544–505 Era (millions of Period Time years ago) Vendian 650–544 5 15 - Background Charles Darwin – Voyage of the H.M.S. “Beagle” 6 15 - Continued Published his results – On The Origin of Species Evolution by Natural Selection – “Survival of the Fittest” Where did his ideas come from? 7 15 Idea’s That Influenced Darwin An Ancient, Changing Earth – Hutton and Geological Change – Lyell’s Principles of Geology Lamarck’s Evolution Hypotheses – Tendency Toward Perfection – Use and Disuse – Inheritance of Acquired Traits – Evaluating Lamarck’s Hypotheses Malthus and Population Growth 8 Evidence? Evidence of Evolution includes The fossil record Geographic distribution of living species Homologous body structures Similarities in early development which is composed of which indicates which implies which implies Physical remains of organisms Common ancestral species Similar genes Similar genes 9 15 Section Assessment What two ideas from geology were important to Darwin’s thinking? According to Lamarck, how did organisms acquire traits? According to Malthus, what factors limited population growth? How did Lyell’s Principles of Geology influence Darwin? 10 16-1 Evolution as Genetic Change Genetic Drift – Normal breeding – “Founder Effect” Remember the Macaques from the movie? – Hardy-Weinberg Principle Probability 11 Section Assessment Describe how natural selection can affect traits controlled by single genes. Describe three patterns of natural selection on polygenic traits. Which one leads to two distinct phenotypes? How does genetic drift lead to a change in a population’s gene pool? What is the Hardy-Weinberg principle? 12 Chapter 15 Section 1 History of Evolutionary Thought The Idea of Evolution Evolution is the process of change in the inherited characteristics within populations over generations such that new types of organisms develop from preexisting types. Evolutionary Relationships Between Whales and Hoofed Mammals Chapter 15 Section 1 History of Evolutionary Thought The Idea of Evolution, continued Ideas of Darwin’s Time – Scientific understanding of evolution began to develop in the 17th and 18th centuries as geologists and naturalists compared geologic processes and living and fossil organisms around the world. Chapter 15 Section 1 History of Evolutionary Thought The Idea of Evolution, continued Ideas about Geology – Among geologists, Cuvier promoted the idea of catastrophism, and Lyell promoted uniformitarianism. Chapter 15 Section 1 History of Evolutionary Thought The Idea of Evolution, continued Lamarck’s Ideas on Evolution – Among naturalists, Lamarck proposed the inheritance of acquired characteristics as a mechanism for evolution. Chapter 15 Section 1 History of Evolutionary Thought Lamarck’s Theory of Evolution Chapter 15 Section 1 History of Evolutionary Thought Darwin’s Ideas Descent with Modification – Darwin wrote On the Origin of Species, in which he argued that descent with modification occurs, that all species descended from common ancestors, and that natural selection is the mechanism for evolution. Chapter 15 Section 1 History of Evolutionary Thought Darwin’s Voyage Chapter 15 Section 1 History of Evolutionary Thought Darwin’s Ideas, continued Natural Selection – Organisms in a population adapt to their environment as the proportion of individuals with genes for favorable traits increases. – Those individuals that pass on more genes are considered to have greater fitness. Chapter 15 Section 1 History of Evolutionary Thought Natural Selection Chapter 15 Adaptation Section 1 History of Evolutionary Thought Chapter 15 Section 2 Evidence of Evolution The Fossil Record Evidence of evolution can be found by comparing several kinds of data, including the fossil record, biogeography, anatomy and development, and biological molecules. Evolutionary theories are supported when several kinds of evidence support similar conclusions. Chapter 15 Section 2 Evidence of Evolution The Fossil Record, The Age ofcontinued Fossils – Geologic evidence supports theories about the age and development of Earth. Chapter 15 Section 2 Evidence of Evolution The Fossil Record, continued The Distribution of Fossils – The fossil record shows that the types and distribution of organisms on Earth have changed over time. Chapter 15 Section 2 Evidence of Evolution The Fossil Record, continued Transitional Species – Fossils of transitional species show evidence of descent with modification. Chapter 15 Section 2 Evidence of Evolution Evidence of Whale Evolution Chapter 15 Section 2 Evidence of Evolution Biogeography Biogeography, the study of the locations of organisms around the world, provides evidence of descent with modification. Chapter 15 Section 2 Evidence of Evolution Anatomy and Physiology In organisms, analogous structures are similar in function but have different evolutionary origins. Homologous structures have a common evolutionary origin. Chapter 15 Forelimbs of Vertebrates Section 2 Evidence of Evolution Chapter 15 A Section 2 Evidence of Evolution Anatomy and Physiology, continued species with a vestigial structure probably shares ancestry with a species that has a functional form of the structure. Chapter 15 Section 2 Evidence of Evolution Vestigial Features Chapter 15 Section 2 Evidence of Evolution Anatomy and Physiology, continued Related species show similarities in embryological development. Chapter 15 Section 2 Evidence of Evolution Similarities in Embryology Chapter 15 Section 2 Evidence of Evolution Biological Molecules Similarity in the subunit sequences of biological molecules such as RNA, DNA, and proteins indicates a common evolutionary history. Chapter 15 Hemoglobin Comparison Section 2 Evidence of Evolution Chapter 15 Section 2 Evidence of Evolution Developing Theory Modern scientists integrate Darwin’s theory with other advances in biological knowledge. Theories and hypotheses about evolution continue to be proposed and investigated. Test: What To Study? These notes Vocabulary (Quiz on Monday) Section Assessments: – 14-2 q#2 – 15-1 q#1,2,3,4 – 16-1 q#5, 16-2 q#1,2,3,4,5 39