* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Theory of Evolution
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
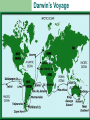
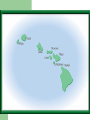
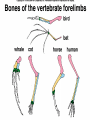
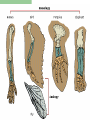
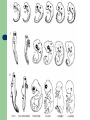
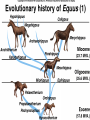
Bell Ringer – 1/11/2007 What can happen to a population when the environment changes? The Theory of Evolution History and evidence for… Evolution Gradual change in species through adaptations over time What are adaptations? Charles Darwin (1809-1882) English Naturalist Was NOT the first to propose that species evolve Was the first to propose how they evolve Natural Selection Darwin’s Voyage Facts that Darwin observed… 1. Without limiting factors, populations grow exponentially 2. Populations tend to fluctuate above and below carrying capacity 3. Resources are limited. Individuals struggle to survive Facts that Darwin observed… 4. Individuals are unique; variation exists within a population 5. Those individuals that are able to survive and reproduce keep their variations in the population Darwin Also Observed Artificial Selection Dogs being bred for certain traits Horses being bred for speed Cotton and wheat being bred for size Darwin theorized that there was a force in nature that worked just like artificial selection (natural selection) Muy Importante! Natural Selection acts on variations that exist in a population Quick Review Quick Review Quick Review Speciation – formation of new species Geographic Isolation Speciation Geographic isolation leads to reproductive isolation Populations become so different that they can no longer interbreed The presence of multiple niches speeds speciation Evidence for Evolution Structural Adaptations – favorable adaptations are selected for Camouflage Mimicry Etc. Evidence for Evolution Physiological Adaptations – changes to an organisms metabolic process Evidence for Evolution Anatomy – homologous structures Evidence for Evolution Anatomy – analogous structures Evidence for Evolution Anatomy – vestigial structures Evidence for Evolution Embryology – comparing embryos Evidence for Evolution Biochemistry – DNA, ATP, Enzymes Evidence for Evolution Fossils – show change over time Fossils Horse Evolution