* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Homo erectus
Sociocultural evolution wikipedia , lookup
Objections to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Origin of language wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Behavioral modernity wikipedia , lookup
Transitional fossil wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education wikipedia , lookup
Hindu views on evolution wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
Before the Dawn (book) wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Saltation (biology) wikipedia , lookup
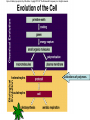
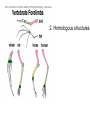
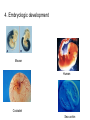
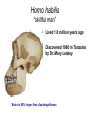
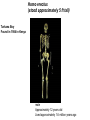
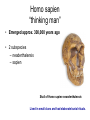
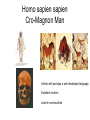
EVOLUTION Evolution (material for extra credit questions) Outline • Approximate date of earth formation • Theory of Chemical Evolution & evidence for chemical evolution – Miller’s Experiment • Timeline for emergence of first Cells • Evidence supporting evolution • Early Primate evolution – Evolution of the Genus Australopithecines – Evolution of the Genus Homo & modern humans 4.5 billion years ago the earth formed Qu ickTime™ an d a TIFF (U ncom pre sse d) de com pre ssor are nee ded to s ee th is p icture. Earth formed Chemical Evolution began 4.5 billion years ago 4 billion years ago First Prokaryotes emerged 3.5 billion years ago First Eukaryotes emerged 1.2 billion years ago Miller’s Experiment showed: • Organic molecules can be formed from components of Earth’s early atmosphere. heterotrophs autotrophs Collections of polymers. Ocean First species to come to land from our oceans were plants. PLANT LIFE • Plants provided O2 • Provided ozone layer • Protection against UV Evolutionary changes • Anatomical • Functional • Behavioral How do these changes occur? Charles Darwin: 1809-1882 1831-1836 1859 DARWIN’s TRAVELS 2 conflicting theories Key components of evolutionary process • Genetic variation • Natural selection • Survival of the Fittest Evidence supporting natural selection 1. Fossil records 2. Homologous structures 3. Biochemical similarities (DNA of fossils is also being studied) – DNA – Amino acids Humans 98% similar Chimpanzees 4. Embryologic development Mouse Human Cockatiel Sea urchin • 5. Biogeography Super continent 240 million years ago • 6. Experimental Evidence Primate Evolution Earliest primates included the Tarsiers Ruff lemur tarsier Consist of Prosimians Old world monkeys Primates (order) Anthropoids New world monkeys hominoids Consist of: Great Apes Lesser Apes Hominids Genus:Australopithecus Mandrill Spider Monkey Genus: Homo Australopithecus afarensis “Lucy” Approx. 25-30 years old Approx. 60 pounds Approx. 3 ft tall Discovered by Dr. Donald Johanson mid 70’s Approx. 3.2 mya Australopithecus afarensis • Bipedal • Approximately 3 to 5.6 ft in height • Over 1 million years ago Australopithecus disappeared. Homo habilis “skillful man” • Lived 1.8 million years ago • Discovered 1960 in Tanzania by Dr. Mary Leakey Brain is 50% larger than Australopithecus Homo erectus “upright man” • Lived 1.6 million years ago • H. erectus moved from Africa to Europe and Asia Used fire Homo erectus (stood approximately 5 ft tall) Turkana Boy Found in 1984 in Kenya male Approximately 12 years old Lived approximately 1.6 million years ago Homo sapien “thinking man” • Emerged approx. 300,000 years ago • 2 subspecies – neaderthalensis – sapien Skull of Homo sapien neanderthalensis Lived in small clans and had elaborate burial rituals. Homo sapien sapien • Neaderthanls disappeared about 40,000 years ago • About 300,000 years ago enter Homo sapien sapien Skull of early Homo sapien sapien Cro-Magnon Man Homo sapien sapien Cro-Magnon Man Artistic with perhaps a well developed language Excellent hunters Lived in communities Homo sapien sapien “modern man” • Appeared approximately 10,000 years ago • Very little change over the past 40,000 years The End!